EVM (Custom IQ)
(Error Vector Magnitude) is the Root Mean Square (RMS) of the error vectors computed and expressed as a percentage of the EVM Normalization Reference.
The error vector magnitude is the length of the vector—at the detected symbol location—which connects the I/Q reference-signal vector to the I/Q measured-signal vector. The following graphic shows the calculation of the metric as well as a diagram showing how a single error vector is calculated.
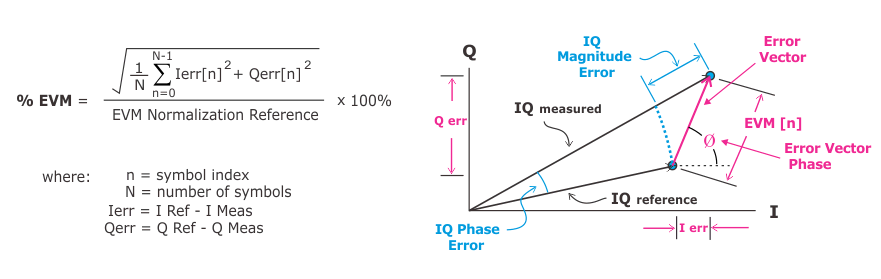
is calculated from the symbol points (the instant in time when symbols are detected). The computation does not include points between symbols. Therefore does not affect the value. The table also shows the location of the symbol that has the largest EVM Error vector magnitude (EVM): A quality metric in digital communication systems. See the EVM metric in the Error Summary Table topic in each demodulator for more information on how EVM is calculated for that modulation format..
For constellations with constant magnitude (QPSK Quadrature phase shift keying, BPSK Binary phase shift keying - A type of phase modulation using 2 distinct carrier phases to signal ones and zeros., 8PSK, etc.), the EVMs are always normalized to the constellation maximum. For constellations with multiple possible magnitudes (APSK, StarQAM, 16QAM, 32QAM, etc.), the EVMs are normalized to the EVM Normalization Reference.
Shaped OQPSK Offset Quadrature Phase Shift Keying: A type of QPSK modulation that offsets the bit streams on the I and Q channels by a half bit. This reduces amplitude fluctuations and helps improve spectral efficiency. and Offset QPSK use two points-per-symbol (symbols and midpoints between symbols) to compute EVM and peak EVM due to the offset between I and Q.
For Offset QPSK, when the Half Sine Filter is selected, the OQPSK reference constellation points fall on a circle with a magnitude of sqrt(2)/2, but the EVM is still expressed as a percentage of the magnitude of a QPSK symbol point (magnitude = 1).
If the EVM is larger than expected, see the troubleshooting tips in Troubleshooting.
See Also
