IQGainImb (Custom OFDM)
( IQ Gain Imbalance) compares the gain of the I signal with the gain of the Q signal, as follows:
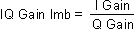
Because gain imbalance is expressed as a logarithmic value, it may have a positive or negative value.
Understanding Custom OFDM IQ Gain Imbalance
IQ Gain imbalance for Custom OFDM Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing: OFDM employs multiple overlapping radio frequency carriers, each operating at a carefully chosen frequency that is Orthogonal to the others, to produce a transmission scheme that supports higher bit rates due to parallel channel operation. OFDM is an alternative tranmission scheme to DSSS and FHSS. demodulation differs from gain imbalance for single subcarrier modulation in that gain imbalance does not show up in the constellation diagram as a width different than height. That's because gain imbalance is in the time domain signal, but OFDM constellations are in the frequency domain. In an OFDM signal, gain imbalance causes each subcarrier to interfere with the opposing subcarriers resulting in each constellation point to spread into a miniature copy of the entire constellation.
Interpreting a Zero IQ Gain Imbalance and IQ Quadrature Error Data Result
The VSA IQ Gain Imbalance and IQ Quadrature Error algorithm require that a subcarrier and it's mirror subcarrier (for example, subcarrier +10 and subcarrier -10) to have non-zero power for two consecutive symbols. When this criteria is not satisfied for the measurement signal, the IQ Gain Imbalance and IQ Quadrature Error data result is shown as zero.
See Also
Available Trace DataAvailable Error Summary Results
