APSK (Digital Demod)
Select the , , or demodulation format to demodulate 16 or 32 APSK signals. The and support to the Digital Video Broadcast (DVB) standard: ETSI European Telecommunications Standard Institute: The European standardization body for telecommunications. EN 302 307 V1.1.1.
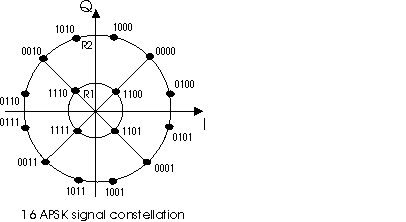
The modulation constellation is composed of two concentric rings of uniformly spaced 4 and 12 PSK Phase Shift Keying: A broad classification of modulation techniques where the information to be transmitted is contained in the phase of the carrier wave. points, respectively in the inner ring (R1) and the outer ring (R2).
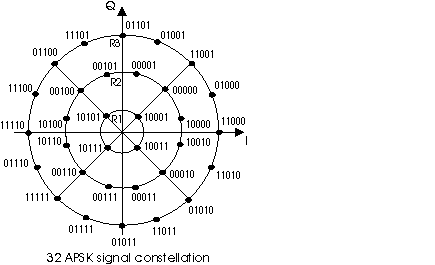
The modulation constellation is composed of three concentric rings of uniformly spaced 4, 12, and 16 PSK points, respectively in the inner ring (R1), the intermediate ring (R2), and the outer ring (R3).
DVB signals have periodic Pi/2 BPSK Binary phase shift keying - A type of phase modulation using 2 distinct carrier phases to signal ones and zeros. header slots and may have randomized QPSK Quadrature phase shift keying pilot slots. These non-APSK slots can affect the measurement. To solve this problem, the VSA has defined synthetic constellations composed of the real APSK states and other states for the headers and pilots. These additional formats are called and . The ideal state positions are shown with circles in the default setup and these alternate states (header and pilot states) are shown with a cross. The header and pilot states have the same power as the average of the ideal states ( or ).
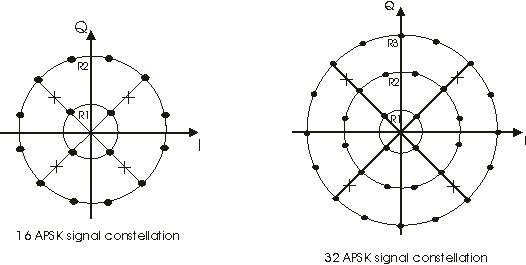
There are some side-effects of the synthetic constellation:
- The header and pilot demodulated symbols are treated as 4 or 5 bit symbols instead of 1 bit. These symbols are displayed in the Syms/Err trace. To simplify setting up the constellation sync search on the DVB header SOF (Start of Frame), search patterns for the SOF are provided in the drop-down list of Sync Search Patterns (). These sync search patterns are named (APSK 16)SOF and (APSK 32)SOF.
- The EVM Error vector magnitude (EVM): A quality metric in digital communication systems. See the EVM metric in the Error Summary Table topic in each demodulator for more information on how EVM is calculated for that modulation format. on these psuedo-states is computed relative to the magnitude of the outer APSK ring instead of the QPSK/BPSK magnitude. SNR Signal-to-Noise Ratio (MER) is computed normally.
- It is not possible to correctly demodulate just a part of these non-APSK slots with no APSK data present. The demod couldn't tell which of the rings, or the header, the symbols are on. This situation could happen only if the is 90 symbols or less.
See Also
