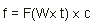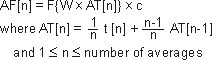Spectrum (Trace Data)
The trace data displays the spectrum of the selected channel. The spectrum trace has frequency on the x axis and, by default, amplitude is shown on the y axis.
The following formulas show how the VSA calculates spectrum information:
| Averaging Type | Spectrum trace data |
|---|---|
|
No averaging |
|
|
RMS Average |
|
|
RMS Exponential AF[n] Average |
|
|
Peak Hold or Continuous Peak Hold Average |
|
|
Time Average |
|
|
Time Exponential Average |
|

As shown in the previous formulas, the spectrum may be a linear spectrum or power spectrum as follows:
|
If the average is... |
then the spectrum trace data is... |
|---|---|
|
Averaging OFF |
Linear |
|
rms Average |
Power |
|
Continuous peak |
Power |
A linear spectrum contains magnitude and phase (real and imaginary) information.
A power spectrum contains only magnitude (real) information. This occurs with rms averages, for instance, because the results of the FFT Fast Fourier Transform: A mathematical operation performed on a time-domain signal to yield the individual spectral components that constitute the signal. See Spectrum. are squared. Remember that the FFT yields both real and imaginary information. When the VSA squares the results of the FFT, the imaginary part becomes zero.