About Data Modulation Format (802.11b/g DSSS/CCK/PBCC)
Data Modulation parameters specifies how the VSA determines the input signal's PSDU 1) PHY Service Data Unit, or 2) PLCP SDU data modulation format. The available modes are and :
-
The VSA automatically determines the data modulation format. For IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. A US-based membership organisation that includes engineers, scientists, and students in electronics and related fields. The IEEE developed the 802 series wired and wireless LAN standards. Visit the IEEE at http://www.ieee.org 802.11b and 802.11g DSSS Direct sequence spread spectrum. The data transmission scheme (sometimes referred to as a "'modulation" scheme) used in 802.11b WLANs. DSSS uses a radio transmitter operating at a fixed centre frequency, but using a relatively broad range of frequencies, to spread data transmissions over a fixed range of the frequency band. 802.11a and 802.11g (when not operating in 802.11b mode) use Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). modulated signals, the VSA uses the SIGNAL and SERVICE field data within the PLCP Physical layer convergence protocol Header to determine the data modulation format.
-
The PSDU data modulation format is manually specified. The VSA ignores the format transmitted in the 802.11b/g DSSS/CCK complementary code keying/PBCC packet binary convolutional code burst and sets the VSA's demodulator to the modulation format specified in the text box.
The following table lists the available 802.11b/g DSSS/CCK/PBCC data modulation formats and the corresponding payload characteristics:
| Data Modulation Formats and Payload Characteristics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Modulation Formats | Spread Sequence Code scheme | Data Rate(Mbps) | Symbol Rate(Msps) | Chip Rate (Mcps Mega Chip Per Second: A measure of the number of bits (chips) per second in the spreading sequence of direct sequence spreading code.) | Bits per Symbol | Modulation |
|
Barker1 |
11 Chip Barker |
1 |
1 |
11 |
1 |
|
|
Barker2 |
11 Chip Barker |
2 |
1 |
11 |
2 |
|
|
CCK 5.5 |
8 chip CCK |
5.5 |
1.375 |
11 |
4 |
DQPSK |
|
CCK 11 |
8 chip CCK |
11 |
1.375 |
11 |
8 |
DQPSK |
|
PBCC5.5 |
PBCC |
5.5 |
11 |
na |
0.5 |
|
|
PBCC11 |
PBCC |
11 |
11 |
na |
1 |
QPSK |
|
PBCC22 |
PBCC |
22 |
11 |
na |
2 |
8PSK |
|
PBCC33 |
PBCC |
33 |
16.5 |
na |
2 |
8PSK |
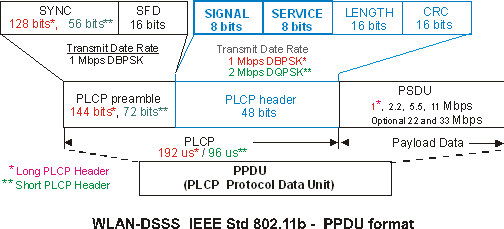
The next figure shows the SIGNAL and SERVICE field data structures within the IEEE STD 1) abbrevation for "standard" or 2) Selective Transmit Diversity: A transmit diversity technique using multiple base stations to originate the signal and provide spatial diversity on the downlink. In STD, the transmitter selection is based on a QoS measurement made at the mobile station. See also transmit diversity, TDTD and TSTD. 802.11b/g PPDU PLCP Protocol data unit frame:
See Also
