Spectrum (802.11b/g DSSS/CCK/PBCC)
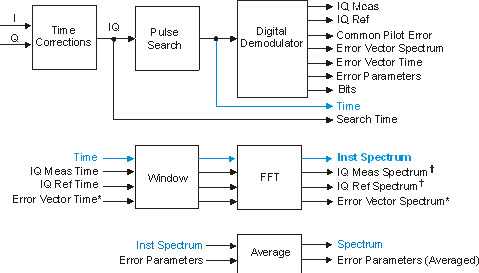
When 802.11b/g DSSS Direct sequence spread spectrum. The data transmission scheme (sometimes referred to as a "'modulation" scheme) used in 802.11b WLANs. DSSS uses a radio transmitter operating at a fixed centre frequency, but using a relatively broad range of frequencies, to spread data transmissions over a fixed range of the frequency band. 802.11a and 802.11g (when not operating in 802.11b mode) use Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)./CCK complementary code keying/PBCC packet binary convolutional code Demodulation is enabled, the trace is the averaged, Inst Spectrum trace data, as shown in the following block diagram (the block diagram is part of the Digital Demodulation Block Diagram). If averaging is OFF, the and displays are identical.
The trace has the following characteristics:
-
It is derived from pre-demodulated time data, which is 20% larger than the result length.
-
It is averaged if averaging is ON and the average type is RMS(Video), RMS(Video) Exponential or Continuous Peak Hold averaging.
If averaging is ON, a scan is not included in the average if any of these conditions exist: Pulse Not Found, Sync Not Found, Carrier Unlock, or certain DATA? conditions.
See Also
