Data Subcarrier Modulation Format (802.11a/g/j/p OFDM)
Data Subcarrier Modulation Format specifies the data subcarrier modulation format. The modulation format is shown in the symbol table ModFmt error summary trace data.
-
The VSA uses information detected within the OFDM Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing: OFDM employs multiple overlapping radio frequency carriers, each operating at a carefully chosen frequency that is Orthogonal to the others, to produce a transmission scheme that supports higher bit rates due to parallel channel operation. OFDM is an alternative tranmission scheme to DSSS and FHSS. burst to automatically determine the data subcarrier modulation format
-
For IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. A US-based membership organisation that includes engineers, scientists, and students in electronics and related fields. The IEEE developed the 802 series wired and wireless LAN standards. Visit the IEEE at http://www.ieee.org 802.11a/g OFDM and IEEE 802.11g DSSS Direct sequence spread spectrum. The data transmission scheme (sometimes referred to as a "'modulation" scheme) used in 802.11b WLANs. DSSS uses a radio transmitter operating at a fixed centre frequency, but using a relatively broad range of frequencies, to spread data transmissions over a fixed range of the frequency band. 802.11a and 802.11g (when not operating in 802.11b mode) use Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM).-OFDM signals, the VSA uses the SIGNAL Symbol - RATE field data to determine the subcarrier modulation format.
-
For HIPERLAN/2 OFDM signals, the VSA examines data from the second Data Symbol to determine the subcarrier modulation format. HIPERLAN/2 Demodulation does not detect the Rate information.
-
-
Specifies the data subcarrier modulation format. The VSA ignores the format determined from the OFDM burst and sets the demodulator to the modulation format specified in the text box.
The contents of this topic include the following information about the Data Subcarrier Modulation parameters:
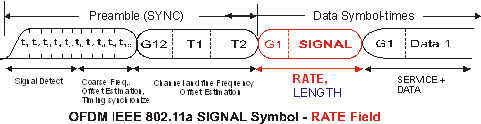
OFDM IEEE 802.11a/g SIGNAL symbol - RATE Field
As shown in the following figure, the OFDM burst structure contains the Preamble symbols followed by the SIGNAL symbol and Data symbols. The SIGNAL symbol contains the RATE and LENGTH fields. The RATE field transmits the data rate, which conveys information about the type of subcarrier modulation, and the coding rate used in the rest of the packet. The encoding of the SIGNAL, single OFDM symbol, is performed with BPSK Binary phase shift keying - A type of phase modulation using 2 distinct carrier phases to signal ones and zeros. modulation of the subcarriers. These parameters do not affect the demodulation of the pilot subcarriers, which are always BPSK modulation.
Determining the Subcarrier modulation format
IEEE 802.11a/g/j/p OFDM and IEEE 802.11g DSSS-OFDM Standard OFDM Signals
For IEEE 802.11a/g/j/p OFDM and IEEE 802.11g DSSS-OFDM signals the subcarrier modulation format is a data rate dependent parameter. The RATE field, which is in the SIGNAL symbol, contains the data rate information, which is used to set the subcarrier modulation format according to the following table:
|
Data Rate (Mbits/s) |
Subcarrier Modulation |
|---|---|
|
6 |
BPSK |
|
9 |
BPSK |
|
12 |
|
|
18 |
QPSK |
|
24 |
|
|
36 |
16-QAM |
|
48 |
64-QAM |
|
54 |
64-QAM |
HIPERLAN/2 Standard OFDM Signals
For HIPERLAN/2 standard OFDM signals, the VSA auto detects the modulation format by examining the data received in the second data symbol. HIPERLAN/2 Demodulation does not detect Rate information.
Return to Top of Page
See Also
