802.11 OFDM Overview
Introduction to 802.11a OFDM
The 802.11a Wireless LAN Local Area Network: A communications network that serves users within a local geographical area, typically over distances of around 100m. Wireless LANs use wireless communicaitons to network devices so there is no need for data cabling. amendment to the original 802.11 standard was ratified in 1999. The 802.11a standard uses the same core protocol as the original standard, operates in 5 GHz Gigahertz: A frequency measurement which equals one billion hertz. band, and uses a 52-subcarrier orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing: OFDM employs multiple overlapping radio frequency carriers, each operating at a carefully chosen frequency that is Orthogonal to the others, to produce a transmission scheme that supports higher bit rates due to parallel channel operation. OFDM is an alternative tranmission scheme to DSSS and FHSS.) with a maximum raw data rate of 54 Mbit/s, which yields realistic net achievable throughput in the mid-20 Mbit/s. The raw data rate is reduced to 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9 then 6 Mbit/s if required. 802.11a originally had 12 to 13 non-overlapping channels, 12 channels can be used indoor and 4 to 5 of the 12 channels that can be used in outdoor point to point configurations. 802.11a is not interoperable with 802.11b as they operate on separate bands, except if using equipment that has a dual band capability.
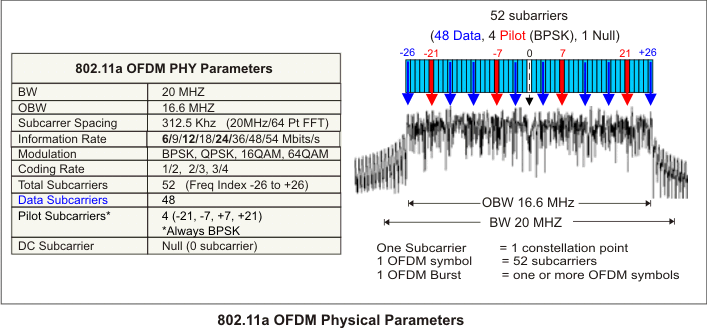
802.11a OFDM Signal and Physical Layer Overview
IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. A US-based membership organisation that includes engineers, scientists, and students in electronics and related fields. The IEEE developed the 802 series wired and wireless LAN standards. Visit the IEEE at http://www.ieee.org 802.11a/g and HIPERLAN/2 signals are pulsed (or burst) type signals. The total channel bandwidth is 20 MHz Megahertz: A unit of frequency equal to one million hertz or cycles per second. with an occupied bandwidth of 16.6 MHz. A single OFDM symbol contains 52 subcarriers; 48 are data subcarriers and 4 are pilot subcarriers. The center, "DC" or "Null", zero subcarrier is not used. All data subcarriers use the same modulation format within a given burst. However, the modulation format can vary from burst to burst. The possible data subcarrier modulation formats are BPSK Binary phase shift keying - A type of phase modulation using 2 distinct carrier phases to signal ones and zeros., QPSK Quadrature phase shift keying, 16QAM, and 64QAM. Pilot subcarriers are always modulated using BPSK and a known magnitude and phase. Each OFDM subcarrier carries a single modulated data symbol, or "constellation point", along with its magnitude and phase information . This means that the magnitude and phase will vary for each subcarrier and OFDM symbol in the transmitted burst.
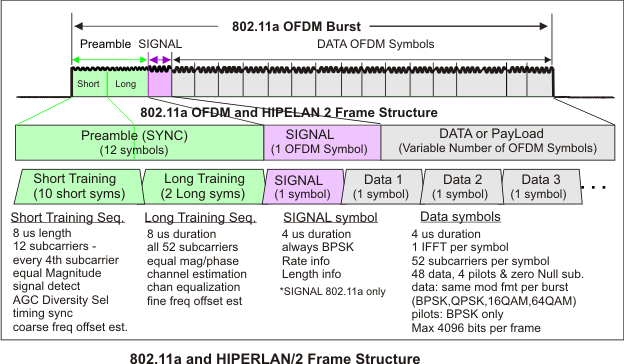
802.11a OFDM Frame Structure
The basic frame structure of an 802.11a burst contains a preamble field followed by a SIGNAL field and multiple data fields. At the start of the burst, a preamble is transmitted at a well-known magnitude and phase. The preamble is used for synchronization and channel equalization. The SIGNAL field (not used in HIPERLAN 2 signals) is transmitted using BPSK, and contains the length, modulation type, and data rate information. Then multiple OFDM symbols containing the input data bits are appended to complete the burst.
802.11a OFDM Signal Timing Parameters
The following table lists the timing parameters associated with the 802.11a signal:
802.11a Timing Related Parameters
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Total subcarriers NST | 52 |
| Data subcarriers NSD | 48 |
| Pilot subcarriers NSP | 4 (subcarriers -21, 7, 7, 21) |
| Subcarrier Frequency Spacing FSP | 312.5 KHz (20MHz/64) |
| Symbol Interval Time TSYM | 4 us (TGI Guard interval +TFFT Fast Fourier Transform: A mathematical operation performed on a time-domain signal to yield the individual spectral components that constitute the signal. See Spectrum.) |
| Data Interval Time TDATA | 3.2 us (1/FSP) |
| Guard Interval (GI) Time TGI | 0.8 us (TFFT/4) |
| IFFT Inverse Fast Fourier Transform/FFT Period TFFT | 3.2 us (1/FSP) |
| SIGNAL Symbol TIme TSIGNAL | 4 us (TGI +TFFT |
| Preamble TPREAMBLE | 16 us (TSHORT +TLONG) |
| Short Training Sequence TSHORT | 8 us (10xTFFT/4) |
| Long Training Sequence TLONG | 8 us (TGI2 + 2xTFFT) |
| Training symbol GI TGI2 | 1.6 us (TFFT/2) |
| FFT sample size | 64 point |
See Also
