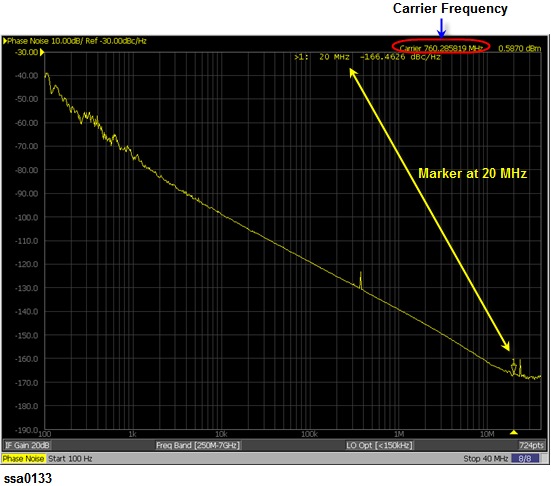
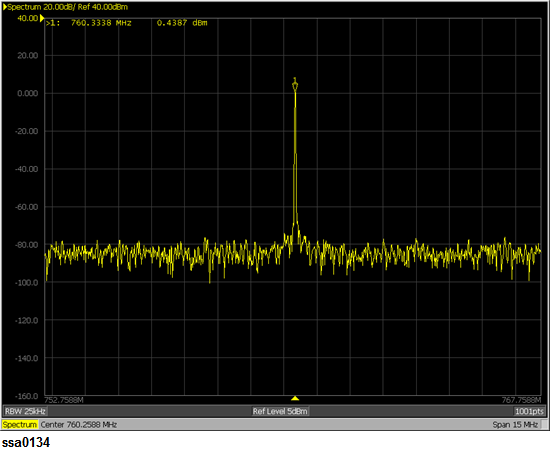
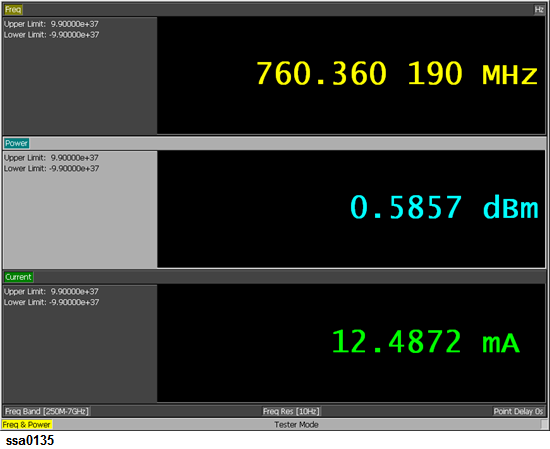
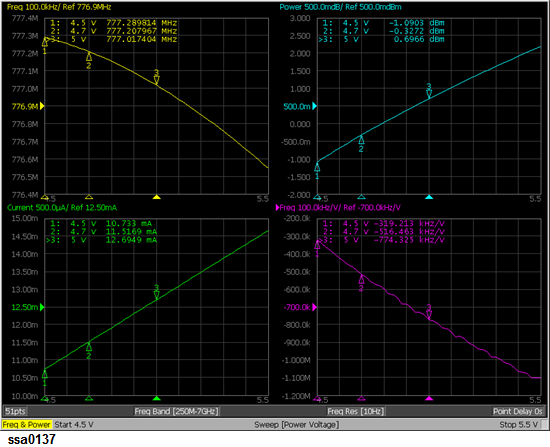
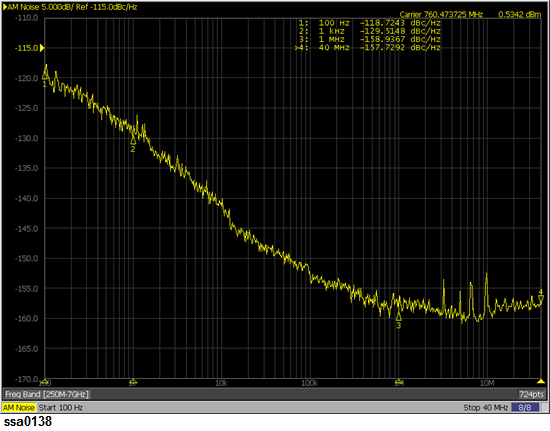
Setting measurement conditions
-
Preset the E5052B to factory settings by Preset > Factory.
-
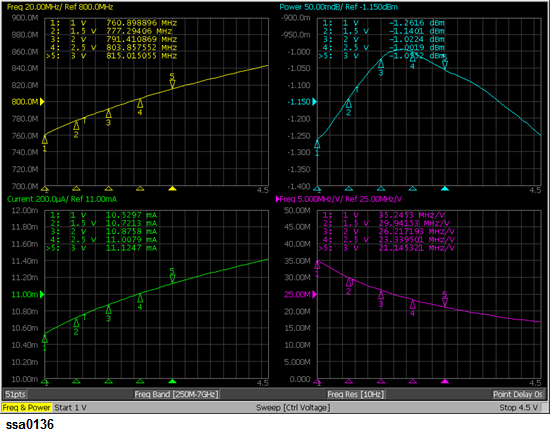
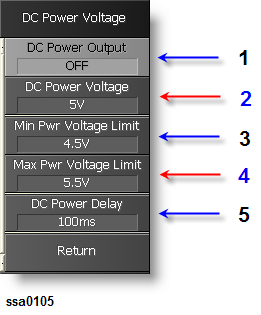
Set DUT (VCO) Bias Voltage (Vcc) Settings by DC Power:
-
-
Set Min Pwr Voltage Limit as 4.5 V (3 in the figure below).
-
Set Max Pwr Voltage Limit as 5.5 V (4 in the figure below).
-
Set DC Power Delay as 100ms (5 in the figure below).
-
Set DC Power Voltage as 5V (2 in the figure below).
-
-
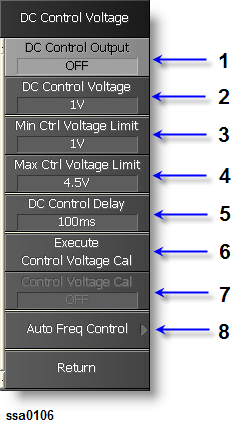
Set DUT (VCO) Tuning Voltage (Vt) Settings by DC Control:
-
Set Min Ctrl Voltage Limit as 1.0 V (3 in the figure below).
-
Set Max Ctrl Voltage Limit as 4.5 V (4 in the figure below).
-
Set DC Control Delay as 100ms (5 in the figure below).
-
Set DC Control Voltage as 1V (2 in the figure below).
-