The mode switch mechanism enables a device using the SUN FSK PHY to change its symbol rate and/or modulation scheme on a packet-by-packet basis. This is done as a PHY layer operation, requiring minimal involvement from the MAC layer. A specific mode switch PPDU is used to inform the receiver of the mode switch and specifies the new PHY mode of the following PPDU.
Using the mode switch mechanism, the current PHY mode (that is, symbol rate or modulation scheme) can be overridden for a single packet. For example, the mode switch mechanism can be invoked by a device that is configured to operate at the SUN FSK mode with a lower data rate (e.g., 50 kb/s) to enable higher data rate communications when needed. This might be used to facilitate a common communication PHY mode, while enabling higher data rate communications for those devices that are already established in the network. Also, this mechanism permits two devices using the FSK PHY to establish the communication in a different PHY mode.
To take advantage of this mechanism, the system implementer would typically configure devices with identical mode switch parameters. However, a source device wishing to use the mode switch mechanism would typically request SUN PHY capability information (including the mode switch parameter entries) from the destination device(s) to ensure that the mode switch mechanism, with the identical parameters, is supported by the destination device(s).

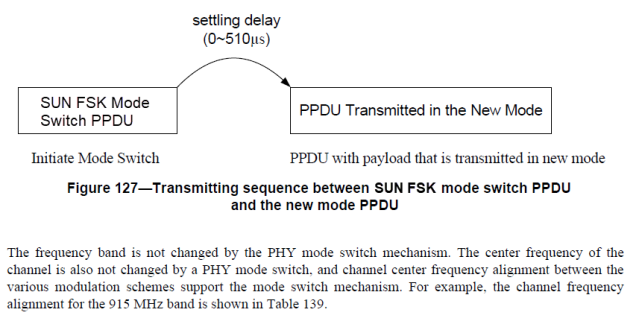
The mode switch mechanism is enabled by setting the Mode Switch field to one. The SUN FSK mode switch PPDU is transmitted on phyCurrentChannel, as defined in 9.3, and the PPDU containing the PSDU is transmitted on the channel that corresponds to the same center frequency used for the SUN FSK mode switch PPDU. When an SUN FSK mode switch PPDU, as described in Figure 113, is received, a device that supports mode switching shall change its mode of operation to the new mode defined in the SUN FSK mode switch PPDU, in order to receive the following packet.
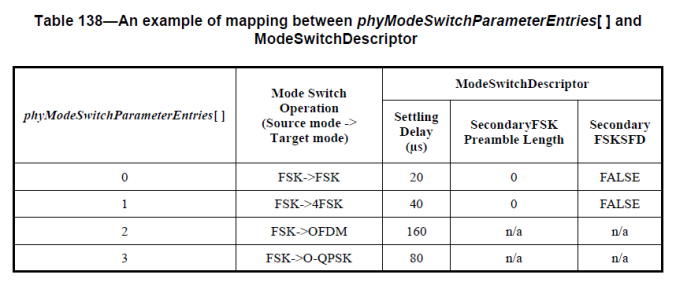
When changing from the current operating mode to the new mode, a settling delay may exist. If the modulation scheme of the new mode is FSK, the settling delay shall be in the range of zero to 100 μs. If the modulation scheme of the new mode is not FSK, the settling delay shall be in the range of 200 μs to 500 μs. The settling delay value is part of a ModeSwitchDescriptor, as described in Table 71b. The value specified in the Mode Switch Parameter Entry field of the PHR, as described in Figure 115, is the index of the PIB attribute array PhyModeSwitchParameterEntries, as defined in 9.3, which contains the elements of the ModeSwitchDescriptor. How the Mode Switch Parameter Entry field maps to ModeSwitchDescriptor is exemplified in Table 138. For the mode switch operation of FSK->FSK, the symbol rate is changed. For the mode switch operation of FSK->4FSK, the modulation order and/or the symbol rate is changed. The Mode Switch Parameter Entry table may be defined by the next higher layer.