FM broadcasting is a broadcast technology which utilizes frequency modulation (FM) to provide high-fidelity sound over broadcast radio.
|
Country/Regions |
Broadcast Band(MHz) |
|---|---|
|
Worldwide generally |
87.5 to 108.0 |
|
U.S |
87.8 to 108.0 |
|
Japan |
76 to 90 (0.1 MHz channel spacing) |
|
Soviet republics and Eastern Bloc nations |
65.9 to 74 |
The MPX stereo signal consists three parts.
-
The first is a normal audio signal made up of the Sum of the left and right channels. This is the signal you hear on a Mono radio and is the same as switching the Stereo/Mono Switch on an amplifier to "Mono'.
-
In addition a difference signal (Left - Right) is generated and then used to modulate a 38 Khzsubcarrier using Double sideband suppressed carrier (DSBSC) modulation. This is an AM modulation of the subcarrier.
-
To keep the receiver decoder locked into the 38Khz subcarrier a 19 Khz pilot tone (EXACTLY 1/2 of 38 Khz) is transmitted at well. The relative percentage of modulation put into the pilot is 10%.
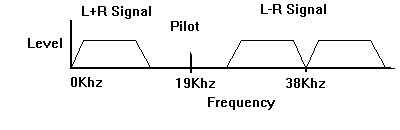
At the receiver the L+R and L-R signals are added for the Left channel ((L+R)+(L-R)=2L) and subtracted for the right channel ((L+R)-(L-R)=2R).
This is the 'Classic' method. An easier to build method simply switches between the left and right channels at a 38 KHz rate. The mathematics of this produce a signal the same as the classic method but there is less likelihood of differences between channels sneaking in.
-
Pre-emphasis: the enhancement on high frequency components of input signal from the receiver
-
De-emphasis: the suppression on high frequency components of output demodulated signal
Pre-emphasis is applied to both channels before the Multiplexing process. A corresponding de-emphasis is applied at the receiver.
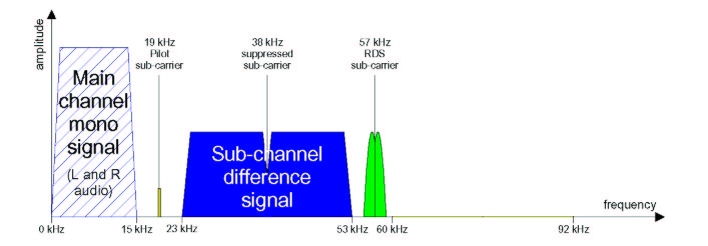
Figure 3 The baseband layout of FM broadcasting
-
50 Hz to 15 kHz Main Channel (Sum of all 4 channels) (LF+LB+RF+RB) signal, for Mono FM listening compatibility.
-
19 kHz Pilot synchronizing signal
-
23 to 53 kHz (sine Quadrant Subcarrier) (LF+LB) - (RF+RB) Left minus Right difference signal. This signal's modulation in algebraic sum and difference with the Main channel was used for 2 channel stereo listener compatibility.
-
23 to 53 kHz (cosine Quadrant subcarrier) (LF+RF) - (LB+RB) Front minus Back difference signal. This signal's modulation in algebraic sum and difference with the Main channel and all the other subcarriers is used for the Quadraphonic listener.
-
61 to 91 kHz (sine Quadrant subcarrier) (LF+RB) - (LB+RF) difference signal. This is the Diagonal difference signal. This signal's modulation in algebraic sum and difference with the main channel and all the other subcarriers is also used for the Quadraphonic listener.
-
95 kHz SCAsubcarrier, phase locked to 19 kHz pilot, for reading services for the blind, background music, etc.
RDS stands for Radio Data System, which is intended for application to VHF/FM sound broadcasts in the range 87.5 MHz to 108.0 MHz which may carry either stereophonic (pilot-tone system) or monophonic programmes. The use of more and more frequencies for radio programmes in the VHF/FM range make it increasingly difficult to tune a conventional radio to a desired programme.
The main objective of RDS
-
Enhance functionality for FM receivers, making them more user-friendly.
-
Using features such as PI (Programme Identification), PS (Programme Service) name display
-
Automatic tuning for portable and car radios, in particular. (The relevant basic tuning and switching information therefore has to be implemented by the type 0 group, and it is not optional, unlike many of the other possible features in RDS).
-
Also used in Hi-Fi fidelity sound box, radio and DVD players
Radio Broadcast Data System is the official name used for the U.S. version of RDS, along with RBDS, The two standards are nearly identical, with only slight differences, mainly in which numbers are assigned to each of 31 musical and other programme formats the RBDS system could identify. Both of the two standards use a 57kHz subcarrier to carry data at 1187.5 bits per second. The 57kHz was chosen for being the third harmonic (3×) of the pilot tone for FM stereo, so it would not cause interference or intermodulation with it, or with the stereo difference signal at 38kHz (2×). The data format utilizes error correction. RDS defines many features (see below), including how private (in-house) or other undefined features (such as differential GPS) could be "packaged" in unused programme groups.
The following information fields are normally contained in the :
-
AF
Alternative Frequencies. The list of alternative frequencies gives information on the various transmitters broadcasting the same programme in the same or adjacent reception areas. This facility is particularly useful in the case of car and portable radios.
When the PI code indicates local coverage-area, i.e. only one frequency is used, AF list may contain this frequency.
-
EON
Enhanced Other Networks. This feature could be used to update the information stored in a receiver about programme services other than the one received. Alternative frequencies, the PS name, Traffic Programme and Traffic Announcement identification as well as Programme Type and Programme Item Number information could be transmitted for each other service. The relation to the corresponding program is established by means of the relevant Programme Identification.
-
PI
Programme Identification.
This information consists of a code enabling the receiver to distinguish between countries, areas in which the same programme is transmitted, and the identification of the programme itself. The code is not intended for direct display and is assigned to each individual radio programme, to enable it to be distinguished from all other programs. One important application of this information would be to enable the receiver to search automatically for an alternative frequency in case of bad reception of the program to which the receiver is tuned; the criteria for the change-over to the new frequency would be the presence of a better signal having the same PI code.
The PI code consists of four characters. The first two characters have special meaning, second two are used to clearly identify different stations.
The first character identifies country. The second character identifies programme type in terms of area coverage:
0 - Local (Local program transmitted via a single transmitter only during the whole transmitting time.)
1 - International (The same program is also transmitted in other countries.)
2 - National (The same program is transmitted throughout the country.)
3 - Supra-regional (The same program is transmitted throughout a large part of the country.)
4 to F - Regional (The program is available only in one location or region over one or more frequencies, and there exists no definition of its frontiers.)
-
PS
Programme service name, which is the label of the program service consisting of not more than eight alphanumeric characters, which is displayed by RDS receivers in order to inform the listener what program service is being broadcast by the station to which the receiver is tuned.
-
Programme Type. This coding of up to 31 pre-defined programme types e.g. (in Europe): PTY1 News, PTY6 Drama, PTY11 Rock music, allows users to find similar programming by genre. PTY31 seems to be reserved for emergency announcements in the event of natural disasters or other major calamities.
-
RT
Radio Text.
This function allows a radio station to transmit a 64-character free-form textual information that can be either static e.g. station slogans or in sync with the programming such as the title and artist of the currently-playing song. This refers to text transmissions, primarily addressed to consumer home receivers, which would be equipped with suitable display facilities.
-
TA
This is an on/off switching signal to indicate when a traffic announcement is on air. The signal could be used in receivers to:
-
switch automatically from any audio mode to the traffic announcement;
-
switch on the traffic announcement automatically when the receiver is in a waiting reception mode and the audio signal is muted;
-
switch from a program to another one carrying a traffic announcement.
After the end of the traffic announcement the initial operating mode will be restored.
-
-
TP
This is a flag to indicate that the tuned program carries traffic announcements. The TP flag must only be set on programs which dynamically switch on the TA identification during traffic announcements. The signal shall be taken into account during automatic search tuning, therefore it's recommend to turn this flag on even though no traffic announcement is transmitted.
-
CT - Clock-Time and Date
Time and date codes should use Coordinated Universal Time and Modified Julian Day. The listener, however, will not use this information directly and the conversion to local time and date will be made in the receiver's circuitry. CT is used as time stamp by various RDS applications and thus it must be accurate.
-
M/S - Music/speech switch
This is a two-state signal to provide information on whether music or speech is being broadcast. The signal would permit receivers to be equipped with two separate volume controls, one for music and one for speech, so that the listener could adjust the balance between them to suit his individual listening habits.
The following table lists the RDS and RBDS Programme Type codes and their meanings:
|
PTY code |
RDS Programme type (EU) |
RBDS Program type (USA ) |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
No programme type or undefined |
No program type or undefined |
|
1 |
News |
News |
|
2 |
Current affairs |
Information |
|
3 |
Information |
Sports |
|
4 |
Sport |
Talk |
|
5 |
Education |
Rock |
|
6 |
Drama |
Classic Rock |
|
7 |
Culture |
Adult Hits |
|
8 |
Science |
Soft Rock |
|
9 |
Varied |
Top 40 |
|
10 |
Pop Music |
Country |
|
11 |
Rock Music |
Oldies |
|
12 |
M.O.R. Music |
Soft |
|
13 |
Light classical |
Nostalgia |
|
14 |
Serious classical |
Jazz |
|
15 |
Other Music |
Classical |
|
16 |
Weather |
Rhythm and Blues |
|
17 |
Finance |
Soft Rhythm and Blues |
|
18 |
Children’s programmes |
Language |
|
19 |
Social Affairs |
Religious Music |
|
20 |
Religion |
Religious Talk |
|
21 |
Phone In |
Personality |
|
22 |
Travel |
Public |
|
23 |
Leisure |
College |
|
24 |
Jazz Music |
Unassigned |
|
25 |
Country Music |
Unassigned |
|
26 |
National Music |
Unassigned |
|
27 |
Oldies Music |
Unassigned |
|
28 |
Folk Music |
Unassigned |
|
29 |
Documentary |
Unassigned |
|
30 |
Alarm Test |
Unassigned |
|
31 |
Alarm |
Unassigned |