
This topic is specific to Dual-Band DPD. Refer to Digital Pre-Distortion (DPD) Concept for more basic information.
A 2-D digital pre-distortion (2-D-DPD) solution is provided to support the linearization of concurrent dual-band power amplifiers. This solution characterizes and pre-distorts each band separately hence requires lower sampling rate for DAC and ADC compared to conventional single band DPD techniques. The RF output signals in each band from the power amplifier are captured. Then the DPD model is extracted based on the baseband input signals and RF output signals (digitized) of each band. It compensates for the effect of cross modulation to ensure better linearity.
Step 1: Two RF signals operating on two separated bands go through the DUT (PA).
Step 2: Analyzer capture the PA output signal on each band respectively. For each band, the PA input and PA output are time aligned for further signal processing.
Step 3: With knowing the PA input on both bands, and the PA output on a single band, a PA model are extracted for that single band.

DPD models are the inverse of corresponding PA models. Below is a detailed example using memory polynomial algorithm.
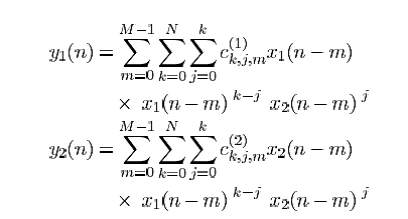
Where, y1 and y2 are the PA output signal, and x1 and x2 are the PA input signals. M is the memory order and N is the nonlinear order. By solving the matrix, dual band DPD model, C{1,2}, is got.
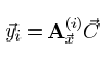
Step 4: The signals are pre-distorted by applying the DPD models.
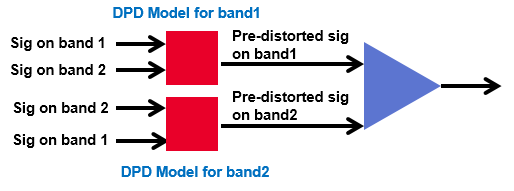
For above memory polynomial algorithm example, pre-distort the two signals by applying the matrix C.
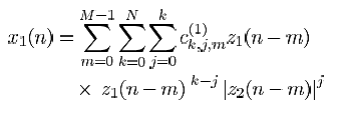
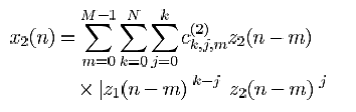
Where the z1 and z2 are the signals to be pre-distorted, and x1 and x2 are the resultant signals.