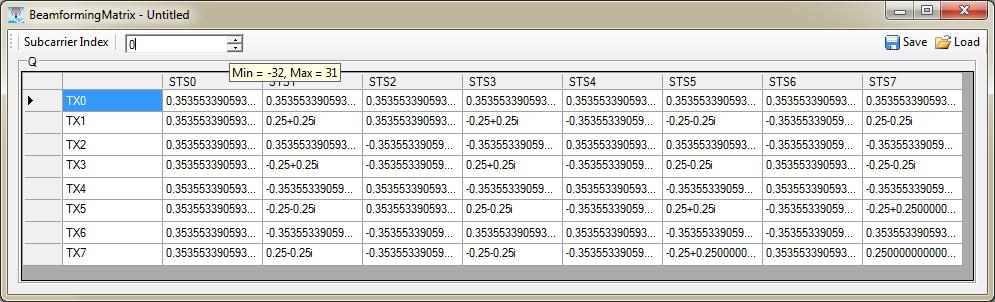
To allow the user to view and edit the beamforming matrix, it is displayed in a window. The beamforming matrix is a three-dimensional matrix of the transmit antenna, space time stream, and subcarrier. The window displays a 2-D table with the transmit antennas in rows and space time streams in columns. The third dimension of subcarrier index can be selected using the parameter above the table.The figure below is an example of an 8×8×64 beamforming matrix.

Select a subcarrier index by typing a number in the field or use the arrows to scroll through the available range. The available range depends on the Bandwidth. To view the currently available range, hover the cursor over the input field.
The Q matrix (Beamforming Matrix) displays a two dimensional matrix in terms of transmit chains and spatial time streams. For the currently selected Subcarrier Index, the rows of matrix are transmitting chains and the columns are spatial time streams.
The elements in the matrix are complex values. If R denotes the real part of a complex value and I denotes the image part of it, a valid complex value could take following formats:
R+Ii, e.g. 2+3i
R+Ij, e.g. 3+4j
[R I], e.g. [2 3]
(R I), e.g. (2 3)
The default value of the Beamforming Matrix is a degenerated two dimensional matrix, which means all the subcarriers are using the same two dimensional matrix. The values in the 2-D matrix are the same as the matrix used when the Spatial Mapping Scheme is Spatial Expansion. Consequently, a beamforming matrix with different dimensional size has different default values. Upon the change of dimensional size, like altering Ntx, Nsts or Nsc, the BF matrix will be reset to its default matrix with based on the current sizes.
Select to display the Open file dialog. Use the Open file dialog to navigate to the desired matrix file and open it. Matrix files can have either .bfm or .csv file extensions.
The BF matrix file is a file with a specific format. When trying to load a file, its format will first be validated. If the format is correct, the matrix stored in it can be successfully read into the N7617C software.
The following shows an example of a BF matrix file.
| Matrix file content | Description |
|---|---|
|
Ntx,4 Nsts,3 Nsc,64 |
File header to indicate the size of the three dimensions. The number of complex values in file must be equal to Ntx×Nsts×Nsc. Columns are delimited by commas and rows are separated by carriage returns. |
|
0.35,0.35,0.35 0.35,0.25+0.25i,0.35i 0.35,0.35i,-0.35 0.35,-0.25+0.25i,-0.35i |
Ntx-by-Nsts matrix for the first subcarrier. The first subcarrier is the subcarrier with the lowest subcarrier index. In this example, Nsc is 64, so the first subcarrier is the one with subcarrier index -32. Each value in the matrix can be a real or complex number. |
|
0.35,-0.35,0.353 0.35,-0.25-0.25i,0.35 0.35,-0.35i,-0.35 0.35,0.35,0.35 |
Ntx-by-Nsts matrix for the subcarrier -31. |
|
0.35,0.25+0.25i,0.35i 0.35,0.35i,-0.35 0.35,-0.25+0.25i,-0.35i 0.35,-0.35,0.35 |
Ntx-by-Nsts matrix for the subcarrier -30. |
| … | The matrixes for the remaining 61 subcarriers. |
If the matrix file fails to load, an error message is displayed and the previous matrix remains. The following conditions will prevent a matrix file from being loaded:
Incorrect file header -- the keywords in the header are not “Ntx”, “Nsts” or “Nsc” or they are not followed by integer numbers
Invalid file format -- the number of matrix elements in the file does not match Ntx X Nsts X Nsc, based on the values in the header
Invalid element values -- such as characters instead of complex values
Select to display the Save As file dialog box. Use the dialog box settings to navigate to the location where you want to save the file and to name the file. You can save the matrix file with a .bfm file extension or a .csv file extension. Regardless of which file extension you choose, the matrix files are saved in the same format.