Digital Video Broadcasting Terrestrial (DVB-T, ETSI EN 300 744) is the most popular digital terrestrial transmission system in the world. It has been successfully deployed in the UK, Germany, Sweden, Finland, Spain, Italy, Netherlands, Switzerland, Singapore and Australia. An image would be good to show the different standards used around the world. DVB-T trials are on-going in Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam, Ukraine, Azerbaijan, Croatia, South Africa and other countries.
Based on coded orthogonal frequency divisional multiplexing (COFDM) and QPSK, 16 QAM and 64 QAM modulations, it is the most sophisticated and flexible digital terrestrial transmission system available today. DVB-T allows service providers to match, and even improves on, analog coverage - at a fraction of the power. It extends the scope of digital terrestrial television in the mobile field, which was simply not possible before, or with other digital systems.
Digital Video Broadcasting Handheld (DVB-H) , extension to DVB-T, is suitable for small screens, handheld portable and mobility reception. Despite the success of mobile DVB-T reception, the major concern with any handheld device is battery life. The power consumption of DVB-T front-end is too high to support handheld receivers that are expected to last from one to several days on a single charge. The new DVB-H standard addresses this requirement of broadcasting to handhelds. A time-slicing mechanism allows receivers to switch off for inactive periods, leading to power savings of approximately 90%. The other major requirements of DVB-H were an ability to receive 15Mbits per second in an 8 MHz channel and in a wide-area single frequency network (SFN) at high speed.

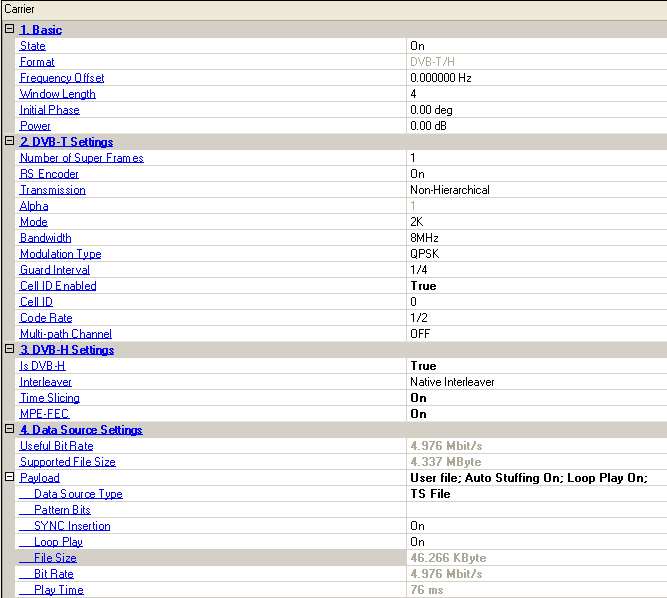
Choice: On |Off
Default: On
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to control the operating state of the carrier.
The format of the carrier.
Range: -40.0 to 40.0 MHz
Default: 0.000000 Hz
Set the frequency offset for the carrier relative to the signal generator’s frequency setting. The valid range will be different for every format due to the different over-sampling ratios.
For example, for 2 carriers configuration, set the center frequency of signal generator to 1 GHz, and make the two carriers distributed on the both sides of the center frequency with 5 MHz offset each. Therefore, the actual frequency of each carrier would be 1GHz+5MHz and 1GHz-5MHz respectively.
Range: 0 to 32
Default: 4
Set the window length of OFDM symbol.
Range: 0 to 359 degrees
Set the initial phase of the carrier.
Range: -50 to 0 dB
Set the carrier’s power relative to the signal generator’s amplitude setting.
Range: different settings are corresponding to different range values.
Set the number of super frames, which is composed of four frames, and the transmitted signal is organized in frames.
8K mode - Each frame consists of 68 OFDM symbols and each symbol is constituted by a set of K = 6817 carriers
2K mode - Each frame consists of 17 OFDM symbols and each symbol is constituted by a set of K = 1705 carriers
For DVB-T 8k mode, the frame structure can be shown as follows:
Choice: On |Off
Default: On
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the RS encoder. For DVB-T/H, when the RS encoder is off, the payload is treated as the output of a RS encoder and fed into the convolutional interleaver directly.
Choice: Hierarchical | Non Hierarchical
Default: Non Hierarchical
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select Hierarchical or Non Hierarchical Transmission. When Hierarchical is selected, the following cell configuration( HP Code Rate and LP Code Rate) will be enabled.
Choice: 1 | 2 | 4
Default: 1
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the Alpha from 1/2/4, which will be effective only when Transmissionis Hierarchical.
Alpha is the minimum distance separating two constellation points carrying different HP-bit values. Non-hierarchical transmission uses the same uniform constellation as the case with α = 1.
Choice: 2K | 4K | 8K
Default: 2K
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the mode.
DVB-T has two kinds of sub-carrier mode, in short 8k mode and 2k mode.
|
Parameter |
8k mode |
2k mode |
|---|---|---|
|
Symbol Period |
896μs |
224μs |
|
Number of Carriers |
6817 |
1705 |
|
OFDM Symbol |
6817 |
1705 |
|
One OFDM Frame (contains) |
68 OFDM symbols |
17 OFDM symbols |
|
Useful data carriers |
6048 |
1512 |
|
Carrier Interval |
1.116kHz |
4.464kHz |
|
Guard interval values (Δ/TU) |
1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 |
1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 |
|
Pilot |
continuous and discrete |
|
|
Pilot Mode |
BPSK |
|
|
Modulation Type |
QPSK 16QAM 64QAM |
|
Choice: 5MHz | 6MHz | 7MHz | 8MHz
Default: 8MHz
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the bandwidth.
Choice: QPSK | 16 QAM | 64QAM
Default: QPSK
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the modulation type .
The DVB-T system adopts Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex (OFDM) transmission. The modulation type for all the data carriers in one OFDM is either QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM, non-uniform 16-QAM or non-uniform 64-QAM constellations.
When Transmissionis Hierarchical, HP stream adopts QPSK while LP stream have 2 types of modulation to select: 16 QAM and 64QAM.
Choice: 1/4 | 1/8 | 1/16 | 1/32
Default: 1/4
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the guard interval.
The purpose of the guard interval is to introduce immunity to propagation delays, echoes and reflections, to which digital data is normally very sensitive.
Guard Interval (Tg) is a part of waveform which is copied from the rear and added at the front of a carrier. Therefore, a OFDM symbol period consists of Tu and Tg, which is called cyclic prefix. At the DVB-T receiver side, as long as the signal delay is less than Tg, the receiver will capture the original signal correctly.
Choice: True | False
Default: False
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to control the cell ID state.
Range: 0 to 65535
Default: 0
Set the cell ID.
The most significant byte of the Cell ID, i.e. b15 - b8, shall be transmitted in super-frames with the frame number 1 and 3. The least significant byte of the Cell ID, i.e. b7 - b0, shall be transmitted in super-frames with the frame number 2 and 4.
This cell is only enabled when Cell ID Enabled is True.
Choice: 1/2 | 2/3 | 3/4 | 5/6 | 7/8
Default: 1/2
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the code rate of convolutional coder. This cell is only enabled when Transmissionis Non-Hierarchical.
In order to achieve hierarchy, two different code rates may be applied to two different levels of the modulation.
Choice: 1/2 | 2/3 | 3/4 | 5/6 | 7/8
Default: 1/2
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the HP (High Priority) code rate of convolutional coder. This cell is only enabled when Transmissionis Hierarchical.
Choice: 1/2 | 2/3 | 3/4 | 5/6 | 7/8
Default: 1/2
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the LP (Low Priority) code rate of convolutional coder. This cell is only enabled when Transmissionis Hierarchical.
Default: OFF
Click
in the right side of the cell to open the
 Multi-path Channel
configuration window.
Multi-path Channel
configuration window.
The performance of DVB-T system through simulation with two channel models can be explored in this step, and up to 20 paths are supported.
P1 - portable reception, Simulating Rayleigh fading
F1 - fixed reception
Besides, User Defined provides a more flexible way configuring each path's attenuation ρ, relative delay τ and phase shift from scattering θ.
Edit the parameters values in the table directly.
Or,
click on the button, and select a fading file (*.fading) previously configured.
When
you finished editing the user defined parameter configuration, click on
 button to make a copy.
button to make a copy.
|
I |
ρi Attenuation of the i'th path |
τi [μs] Relative delay of the i'th path |
θi [rad] Phase shift from scattering of the i'th path |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
0,057 662 |
1,003 019 |
4,855 121 |
|
2 |
0,176 809 |
5,422 091 |
3,419 109 |
|
3 |
0,407 163 |
0,518 650 |
5,864 470 |
|
4 |
0,303 585 |
2,751 772 |
2,215 894 |
|
5 |
0,258 782 |
0,602 895 |
3,758 058 |
|
6 |
0,061 831 |
1,016 585 |
5,430 202 |
|
7 |
0,150 340 |
0,143 556 |
3,952 093 |
|
8 |
0,051 534 |
0,153 832 |
1,093 586 |
|
9 |
0,185 074 |
3,324 866 |
5,775 198 |
|
10 |
0,400 967 |
1,935 570 |
0,154 459 |
|
11 |
0,295 723 |
0,429 948 |
5,928 383 |
|
12 |
0,350 825 |
3,228 872 |
3,053 023 |
|
13 |
0,262 909 |
0,848 831 |
0,628 578 |
|
14 |
0,225 894 |
0,073 883 |
2,128 544 |
|
15 |
0,170 996 |
0,203 952 |
1,099 463 |
|
16 |
0,149 723 |
0,194 207 |
3,462 951 |
|
17 |
0,240 140 |
0,924 450 |
3,664 773 |
|
18 |
0,116 587 |
1,381 320 |
2,833 799 |
|
19 |
0,221 155 |
0,640 512 |
3,334 290 |
|
20 |
0,259 730 |
1,368 671 |
0,393 889 |
Choice: True | False
Default: False
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select if this configuration is DVB-H. If this value is true, DVB-H TS files are required for payload.
DVB-H system, carrying multimedia data over digital terrestrial broadcasting networks, is aiming at handheld terminals. Due to its mobility characteristics, constraints on power supply and varying transmission are the major concern in DVB-H system.
Choice: Native Interleaver | In-depth Interleaver
Default: Native Interleaver
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the interleaver.
native interleaver : 2k mode /4K mode/8k mode
In-depth symbol interleaver : 2K and 4K-modes, for further improving their robustness in mobile environment and impulse noise conditions.
Choice: ON | OFF
Default: OFF
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select whether the time slicing flag is set in TPS. This cell is only enabled when Is DVB-H is True.
Time-slicing is aiming at reducing the average power consumption of the terminal and enabling smooth and seamless service handover. For one thing, time-slicing enables a receiver to stay active only a fraction of the time, while receiving bursts of a requested service. For another, It also supports the possibility to use the receiver to monitor neighboring cells during the off-times (between bursts). In other words, time slicing is a method to deliver MPE (Multiprotocol Encapsulation) sections and MPE-FEC sections in bursts.
Choice: ON | OFF
Default: OFF
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select whether the MPE-FEC flag is set in TPS. This cell is only enabled when Is DVB-H is True.
MPE-FEC (Multiprotocol Encapsulation - Forward Error Correction) is aimed at improving the C/N and Doppler performance in mobile channels and improving the tolerance to impulse interference.
The useful bit rate. The bit rate is determined by current bandwidth, encoding, modulation and framing configurations.
The supported file size for current settings.
The TS payload settings.
Choice: Test Pattern | Demo File | TS File
Default: Test Pattern
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select which type to be used as the data source.
If "TS File" is selected, "File Name" is required.
Learn more about the different Data Source Types, refer to the page Data Source Type.
TS Wizard is not available for this format.
The data bits used as test pattern.
Click the right button
to open  "Data Pattern Selection"
dialog and select test pattern to use.
"Data Pattern Selection"
dialog and select test pattern to use.
Choice: True | False
Default: False
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to determine whether a SYNC byte (0x47) should be inserted into the test pattern.
Choice: NTSC | PAL
Default: PAL
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select whether the PAL or NTSC file is demo File. This cell is only enabled when Data Source Type is Demo File.
There are two predominant worldwide video-based source material formats, shown as follows:
NTSC: National Television System Committee, the system used in America & Canada
PAL: Phase Alternating Line, the system used in Western Europe and Australia
Table 2 NTSC parameters list
|
N T S C National Television System Committee |
|
|
Lines/Field |
525/60 |
|
Horizontal Frequency |
15.734 kHz |
|
Vertical Frequency |
60 Hz |
|
Color Sub-carrier Frequency |
3.579545 MHz |
|
Video Bandwidth |
4.2 MHz |
|
Sound Carrier |
4.5 MHz |
Table 3 PAL parameters list
|
P A L Phase Alternating Line |
|||
|
SYSTEM PAL |
PAL |
PAL N |
PAL M |
|
Line/Field |
625/50 |
625/50 |
525/60 |
|
Horizontal Freq. |
15.625 kHz |
15.625 kHz |
15.750 kHz |
|
Vertical Freq. |
50 Hz |
50 Hz |
60 Hz |
|
Color Sub Carrier |
4.433618 MHz |
3.582056 MHz |
3.575611 MHz |
|
Video Bandwidth |
5.0 MHz |
4.2 MHz |
4.2 MHz |
|
Sound Carrier |
5.5 MHz |
4.5 MHz |
4.5 MHz |
Click
on
in the right side of the cell, and select the file name you set as payload.
Choice: ON | OFF
Default: ON
This cell is only enabled when Data Source Type is TS File. Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select whether or not to use auto-stuffing to agree with transport bit rate.
Choice: ON | OFF
Default: ON
This cell is only enabled when Data Source Type is TS File. Double-click or use the drop-down menu to determine whether or not to modify the TS file to make it suitable for loop play.
The size of opened file.
The bit rate of the opened file.
The time that file can be played.