Nominal Bandwidth (802.16 OFDM)
: See 802.16 OFDM Standard Setups/Presets Table.
is the nominal channel bandwidth specified in the 802.16 standard. The actual signal bandwidth will be slightly less than this and the OFDM Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing: OFDM employs multiple overlapping radio frequency carriers, each operating at a carefully chosen frequency that is Orthogonal to the others, to produce a transmission scheme that supports higher bit rates due to parallel channel operation. OFDM is an alternative tranmission scheme to DSSS and FHSS. FFT Fast Fourier Transform: A mathematical operation performed on a time-domain signal to yield the individual spectral components that constitute the signal. See Spectrum. sample rate is slightly larger. This parameter, combined with the parameter (and knowledge of the FFT length) determines the OFDM subcarrier spacing. See Manual Fs/BW Ratio
How to specify the Nominal Bandwidth.
- Select the test
signals Standard format: .
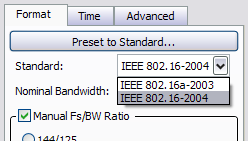
- Determine the test signals nominal bandwidth, see "Determining the Nominal Bandwidth" below).
- Specify the . Use the property, which will also configure the demodulator to a preset configuration or specify the value manually in the property. For this example 7 MHz Megahertz: A unit of frequency equal to one million hertz or cycles per second. was selected from the drop-down list of .
Determining the Nominal Bandwidth
If the of the signal is not known, use the trace data to determine an approximate value.
To show the trace data and determine the approximate bandwidth: Click
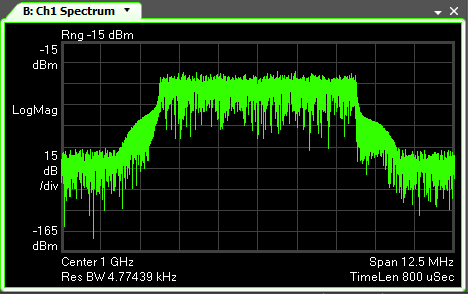
In this example the spectrum is approximately 5.5 gradicules wide and each gradicule is 1.25 MHz wide. This makes the approximate bandwidth 5.5 x 1.25 = 6.875 MHz. Recall from above that the actual signal bandwidth is slightly less than the . A of 7 MHz would make a good choice.
See Also
