Mag Err (Digital Demod)
is the RMS-average of the IQ magnitude error over all symbol times and expressed as a percentage of the EVM Normalization Reference. For all signals except FSK Frequency Shift Keying: A form of modulation using multiple carrier frequencies to carry the digital information. The most common is the two frequency FSK system using the two frequencies to carry the binary ones and zeros. and CPM Continuous Phase Modulation (FM Frequency Modulation), IQ magnitude errror is the difference in amplitude between the I/Q measured signal and the I/Q reference signal (for FSK or CPM (FM), see Mag Err: FSK).
The following graphic shows the calculation of IQ magnitude error for a single symbol (the normalization factor in this case is the ).
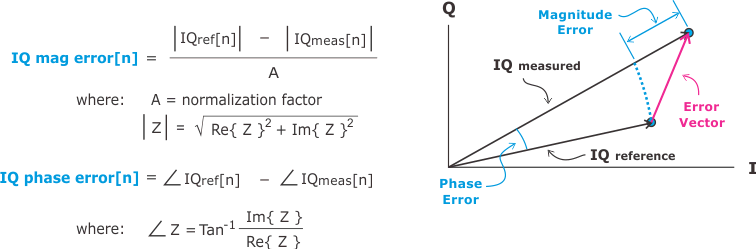
Magnitude error is an indicator of the quality of the amplitude component of the modulated signal. For example, a very high magnitude error might indicate high incidental AM Amplitude Modulation - CW modulation using amplitude variation in proportion to the amplitude of the modulating signal. Usually taken as DSB-LC for commercial broadcast transmissions and DSB-SC for multiplexed systems. modulation on the signal.
The magnitude error shown in the symbol table is computed only from data at the symbol times (the instant in time when symbols are detected). The computation does not include points between symbols. Therefore, the value of has no effect on this error data.
The symbol table also shows the symbol that has the largest magnitude error (peak magnitude error).
OQPSK Offset Quadrature Phase Shift Keying: A type of QPSK modulation that offsets the bit streams on the I and Q channels by a half bit. This reduces amplitude fluctuations and helps improve spectral efficiency./SOQPSK uses two points-per-symbol (symbols and midpoints between symbols) to compute magnitude error and the peak magnitude error due to the offset between I and Q.
For the EDGE Enhanced Data for Global Evolution: A technology that gives GSMA and TDMA similar capacity to handle services for the third generation of mobile telephony. EDGE was developed to enable the transmission of large amounts of data at a high speed, 384 kilobits per second. (It increases available time slots and data rates over existing wireless networks.) demodulation format, the EVM Error vector magnitude (EVM): A quality metric in digital communication systems. See the EVM metric in the Error Summary Table topic in each demodulator for more information on how EVM is calculated for that modulation format., Phase, and Magnitude Error data results may vary for different points/symbol settings. When points/symbol is set to 1 (default), the trace data results are compensated for ISI Inter-Symbol Interference: An interference effect where energy from prior symbols in a bit stream is present in later symbols. ISI is normally caused by filtering of the data streams. (inter-symbol interference). For points/symbol greater than one, the trace data results are not compensated for the effects of ISI.
See Also
