FSK (Digital Demod)
format demodulates 2-state, 4-state, 8-state and 16-state FSK Frequency Shift Keying: A form of modulation using multiple carrier frequencies to carry the digital information. The most common is the two frequency FSK system using the two frequencies to carry the binary ones and zeros. (Frequency-Shift Keyed) signals. The following FSK demodulation formats are available from the box on the Format tab:
| Format Box Selection | FSK Format | |
|---|---|---|
|
2 FSK |
2-state FSK signals |
|
|
4 FSK |
4-state FSK signals |
|
|
8 FSK |
8-state FSK signals |
|
|
16 FSK |
16-state FSK signals |
FSK is the process of shifting (modulating) an analog carrier frequency at a digital rate. FSK closely resembles standard FM Frequency Modulation (Frequency Modulation). With FSK, the modulating signal is not a sinusoidal signal but a series of dc pulses that vary between two discrete voltage levels.
FSK is often used in modems. For example, a modem may use a 1700 Hz carrier that is shifted up 500 Hz for a logic 1 (mark), and down 500 Hz for a logic 0 (space). Thus, as the digital signal alternates between 1 and 0, the carrier is shifted back and forth between 1200 and 2200 Hz.
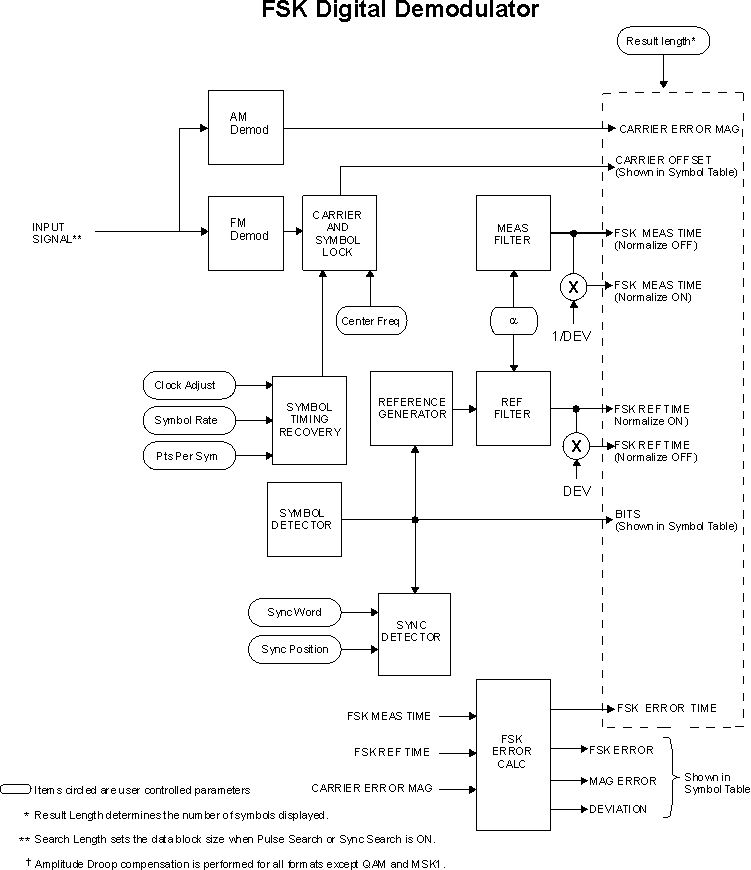
The following block diagram shows how the VSA demodulates FSK signals when FSK demodulation is selected.
See Also
