Carrier Mag Error (FSK) (Digital Demod)
(Available only when the digital-demodulation is .)
The VSA AM Amplitude Modulation - CW modulation using amplitude variation in proportion to the amplitude of the modulating signal. Usually taken as DSB-LC for commercial broadcast transmissions and DSB-SC for multiplexed systems. demodulates the FSK Frequency Shift Keying: A form of modulation using multiple carrier frequencies to carry the digital information. The most common is the two frequency FSK system using the two frequencies to carry the binary ones and zeros. signal to obtain its AM envelope. The VSA then compares the carrier magnitude at each point n to the average carrier magnitude and shows the difference as follows:
|
Carrier Magnitude Error = |
avg( Mag Err[n] ) |
|
Mag Err[n] = |
envelope[n] - (avg. envelope) |
|
|
|
|
where: |
|
|
envelope[n] = |
Magnitude of AM envelope at current point in the FSK signal. |
|
avg. envelope = |
rms magnitude of AM envelope over all points. |
If normalization is ON, the (Carrier Magnitude Error) is shown as a percentage of the average envelope:
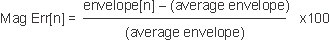
Additional Tips
Here's some additional information:
- The Result Length determines the number of symbols in the trace. The Points / Symbol determines the number of points between symbols.
- The trace uses all points in the FSK signal. To compare only those points at the symbol times, set to one (1).
- The band-power markers compute the over all points in the FSK signal. Again, to compute the error only at the symbol times, set to one (1).
- For a block diagram that shows how is derived, see FSK demodulation .
