Sequential Input Channel Acquisition Overview
What is Sequential Input Channel Acquisition
The 89600 VSA software allows you to virtually increase the channel count of your measurement hardware by taking multiple acquisitions and treating them as separate input channels to the measurement. Using a repetitive signal and trigger, you can create a sequence of acquisitions where data acquired in each step is treated as if taken at the same point in time. Each acquisition can contain one or more physical channels.
Unlike sequenced multi-measurement (one acquisition per measurement), sequential input channel acquisition allows for multiple data acquisitions in a single measurement. Sequential input channel acquisition is often a faster, more efficient method of data acquisition than sequenced multi-measurement.
With sequential input channel acquisition, a single measurement performs multiple acquisitions before analyzing the data. Each acquisition may have different hardware settings and input extension values. For example, you might need to step the DUT Device under Test: An acronym used to describe some type of electrical apparatus connected to test instrumentation. The apparatus can range from a single component to a complex subsystem such as a mobile phone, base station or MSC. power level and change the Input Range of the VSA measurement for each acquisition in the sequence. Or you may need to change the center frequency between each acquisition. Or perhaps even multiple parameters between each (like center and input range at the same time).
In the Input > Extensions panel, the Per Acquisition State parameter allows the state of each acquisition's input extension to be independently controlled for versatility, while the Parameter Coupling setting provides a menu of parameter coupling choices to help you find the best balance between versatility and convenience.
User Scenarios
Use sequential input channel acquisition if you have a single VSA measurement to make, but the measurement requires multiple acquisitions. Here are a few example scenarios:
- Sequential input channel acquisition - contiguous carrier aggregation: Using an external trigger, emulates multi-channel acquisition of contiguous carriers, but requires a fraction of the bandwidth because each carrier is acquired separately (assumes a repetitive timing boundary, no acquisition parameter changes).
- Sequential input channel acquisition - non-contiguous carrier aggregation: Using an external trigger, emulates a single wideband multi-channel acquisition for non-contiguous carriers, but uses a fraction of the bandwidth and time because each carrier is acquired separately without capturing unwanted parts of the signal or gaps between spectrum regions (assumes a repetitive timing boundary, but changes in center frequency and bandwidth, and likely range).
- Sequential acquisition - Selective data viewing: Using an external trigger, acquire different views of data for improving auto-detection mechanisms
- Spectral Emissions Mask - multiband measurement: Emulates a single wideband acquisition for SEM measurement when the total of all carriers and offsets extends beyond the hardware's maximum IF bandwidth. Another scenario is possible where a mixture of high and low power signals are present and either significantly different ResBW/VBW or range settings are required for different spectrum regions.
Examples
Example 1: 4-carrier 5G NR signal measured with a 1 channel X-Series signal analyzer
The following measurement example performs a separate acquisition for each of four carriers in a 5G NR signal, resulting in one acquired carrier per measurement channel.
- Configure the input channels for four acquisitions
Select Input > Channels > Custom...
Set the Acquisition Count to 4 and click OK, then click Apply.
Notice that the Channel Configuration dialog shows four separate acquisitions using the same X-Series Signal Analyzer RF Radio Frequency: A generic term for radio-based technologies, operating between the Low Frequency range (30k Hz) and the Extra High Frequency range (300 GHz). input, each connected to a separate measurement channel (Ch1-Ch4).

- Select the 5G NR Measurement Type and configure a 4-carrier 5G NR signal with a separate carrier definition for each carrier.
In the Configuration tab's Carriers panel, enable (click) Allow Multiple Carrier Definitions.
Click Configure... and select Carrier per-measurement channel
This will create a carrier for each measurement channel.

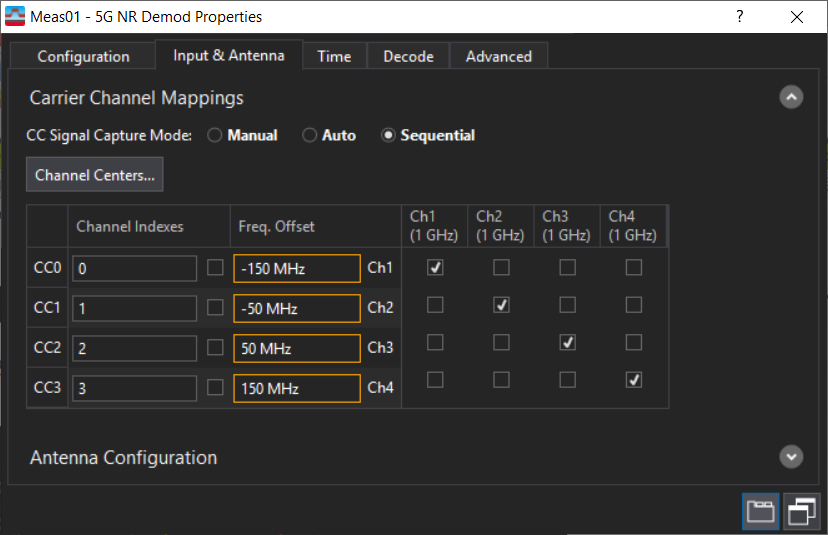
- In the 5G NR Demod Properties Input & Antenna tab
Set the CC Signal Capture Mode to Sequential.
Set the frequency offset for each carrier. You can also set a different center frequency for each measurement channel in the Channel Centers... dialog (or in MeasSetup > Frequency… for non-5G NR measurements).