802.11-2007 1000 chip Peak EVM (802.11b/g DSSS/CCK/PBCC)
802.11-2007 1000 chip Peak EVM Error vector magnitude (EVM): A quality metric in digital communication systems. See the EVM metric in the Error Summary Table topic in each demodulator for more information on how EVM is calculated for that modulation format. is the normalized Error Vector Magnitude as defined in section 18.4.7.8 "Transmit modulation accuracy", of the IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. A US-based membership organisation that includes engineers, scientists, and students in electronics and related fields. The IEEE developed the 802 series wired and wireless LAN standards. Visit the IEEE at http://www.ieee.org Std 802.11-2007 Wireless LAN Local Area Network: A communications network that serves users within a local geographical area, typically over distances of around 100m. Wireless LANs use wireless communicaitons to network devices so there is no need for data cabling. specification.
The "802.11-2007 1000-chip Peak EVM" is computed per section 18.4.7.8 with the following comments or exceptions:
-
For 802.11g PBCC packet binary convolutional code formats using 8PSK modulation, the specified formulas are adjusted so the 802.11-2007 1000 chip Peak EVM results are meaningful.
-
The 1000 chip sample requirement are taken from the first 1000 chips in the measurement interval, if the measurement interval (or the burst length) is less than 1000 chips the "802.11-2007 1000-chip Peak EVM" is not computed and a value of zero is returned.
-
The IEEE Std 802.11b - 1999 specification requires that the worst-case normalized Error Vector Magnitude is less than or equal to 35%
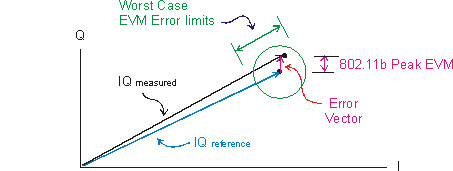
The VSA also provides the percent RMS EVM for the specified measurement interval (see EVM (802.11b/g DSSS/CCK/PBCC)).
See Also
