IQ Mag Error (802.11b/g DSSS/CCK/PBCC)
When 802.11b/g DSSS Direct sequence spread spectrum. The data transmission scheme (sometimes referred to as a "'modulation" scheme) used in 802.11b WLANs. DSSS uses a radio transmitter operating at a fixed centre frequency, but using a relatively broad range of frequencies, to spread data transmissions over a fixed range of the frequency band. 802.11a and 802.11g (when not operating in 802.11b mode) use Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)./CCK complementary code keying/PBCC packet binary convolutional code Demodulation is enabled, the trace shows the magnitude error between the I/Q measured and the I/Q reference signals at each demodulated chip time.
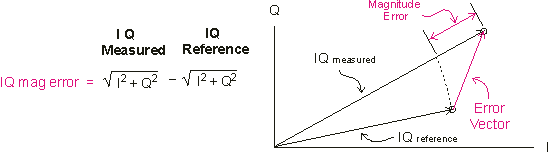
:
The VSA compares the magnitude, for each chip time, of the I/Q measured signal with the magnitude of the I/Q reference signal. The VSA then displays the difference, in magnitude, between the two signals.
If normalization is OFF, the VSA displays the instantaneous magnitude error. If normalization is ON, the VSA displays the magnitude error as a percentage ( Normalize IQ Traces explains how this percentage is derived).
Phase Drift Compensation
Circular arcs in the constellation of the trace display is an indicator of phase drift. The Track Phase demodulation parameter can be used to remove the phase drift, which will improve the IQ constellation trace and reduce the EVM Error vector magnitude (EVM): A quality metric in digital communication systems. See the EVM metric in the Error Summary Table topic in each demodulator for more information on how EVM is calculated for that modulation format. data results ( check box).
See Also
