See other Frequency Converting Device Measurements
What is Conversion Compression?
Conversion compression is a measure of the maximum input signal level for which a mixer will produce linear operation. It is very similar to the gain compression experienced in amplifiers.
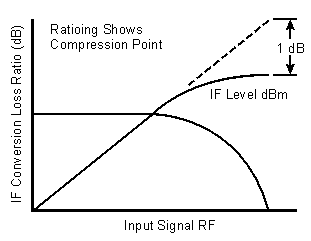
To understand conversion compression, you must first understand conversion loss. This is the ratio of the mixer output level to the mixer input level. This value remains constant over a specified input power range. When the input power level exceeds a certain maximum level, the constant ratio between input and output power levels begins to change. The point at which the ratio has decreased 1 dB is called the 1-dB compression point. This is illustrated in the graphic below.

Why Measure Conversion Compression?
Conversion compression is an indicator of the dynamic range of a device. Dynamic range is generally defined as the difference between the noise floor and the 1-dB compression point.
How to Measure Conversion Compression
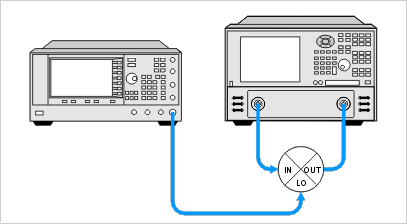
The equipment and setup used to measure conversion compression are essentially the same as for measuring conversion loss and is illustrated in the following graphic.
The PNA performs a power sweep using frequency-offset mode and the resulting display shows the mixer's output power as a function of its input power. The 1-dB compression point (or others such as 3-dB) can be determined using markers.
Measurement Accuracy Considerations
The couplers in the PNA have very good directivity. If the return loss of the DUT is bad, the reflected signal gets sampled by the PNA and can result in errors. This relates to error in DUT gain. To increase the accuracy, an attenuator can be added between the PNA's source port and the DUT's input port. Normally a 6- to 10-dB attenuator is sufficient. Addition of this attenuator, however, decreases the available drive to the DUT.
With high drive levels the PNA can be driven into compression resulting in measurement error. With excessive drive levels, the PNA can be damaged. Add an attenuator between the output of the DUT and the receiver input of the PNA to avoid these problems.
Source power calibration can be used to provide a high level of accuracy for this measurement.