Other topics about Advanced Calibration
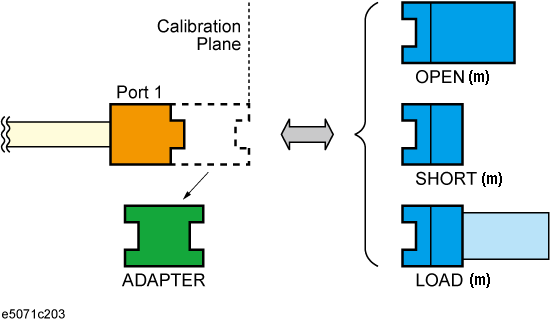
Adapter Removal is a technique used to remove any adapter characteristics from the calibration plane. The E5061B uses the following adapter removal process to remove the adapter characteristics:
Perform calibration with the adapter in use.
Remove the adapter from the port and measure Open, Short, and Load values to determine the adapter's characteristics.
Remove the obtained adapter characteristics from the error coefficients in a de-embedding fashion.
Open, Short, and Load values measured with the adapter removed

The adapter removal and partial overwrite function is only available when the calibration status is [Cor] and not for [C?] or [C!].
The above described method also makes it possible to add adapter characteristics to a port with n-port full calibration. This allows you to make a measurement with the adapter. E5061B uses the following adapter insertion process to insert the adapter characteristics:
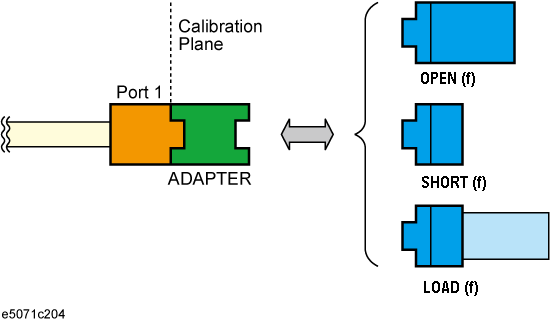
Perform calibration without adapter in use.
Insert the adapter to the port and measure Open, Short, and Load values to determine the adapter's characteristics.
Insert the obtained adapter characteristics to the error coefficients in an embedding fashion.
Open, Short, and Load values measured with adapter attached
In order to determine the adapter characteristics (with four unknown parameters) by making three measurements (Open, Short, and Load), the adapter must satisfy the following requirements:
Adapter must be Reciprocal (with S21 and S12 equal) in nature. It should have a consistent behavior, and independent of the direction from which it is used.
The electrical length of Adapter should be known with the accuracy of ±1/4 of wavelength.
Adapter removal and insertion is not available in Gain-Phase measurement.
The S parameter of a reciprocal adapter can be determined when the following data is available:
Open, Short, and Load measurements.
Actual values derived from the CalKit definitions.
An approximate length of the adapter.
Nature of the intended operation: removal or insertion.
To use Adapter Removal/Insertion, follow the below procedure:
Perform a full n-Port calibration using your calibration kit so that the port used to conduct adapter insertion/removal is calibrated.
When you need to remove an adapter from the calibration plane (adapter removal) to connect your DUT, perform the calibration with an adapter so that you can make a calibration with your calibration kit. When you need to add an adapter into the calibration plane (adapter insertion) to connect your DUT, perform the calibration without an adapter.
Press Cal > Calibrate > Adapter Removal.
Select a proper standard Calkit you need to use from CalKit (e.g. 85033E) to characterize the adapter. The calibration kit is used at the plane from which the adapter is removed (adapter removal), or the plane in which adapter is inserted (adapter insertion).
Select Port 1 or Port 2 which you want to insert/remove Adapter characteristics from/to. A * sign appears in front of the port is the valid port to conduct adapter removal/insertion as the full n-port calibration has been performed on the port.
Connect Open, Short, and Load of the selected Calkit (e.g. 85033E) with the selected port respectively and click/press Open, Short, and Load respectively. ENA measures the cal kit standard, calculates the adapter characteristics, and then conducts adapter removal/insertion.
A checkmark ![]() appears in (Open, Short, and Load) menu after each type of calibration is completed.
appears in (Open, Short, and Load) menu after each type of calibration is completed.
Click Done to complete the process.
In cases where the auto phase fails, select Rotate Adapter to move the adapter's phase (which is removed or inserted) to 180 degrees.
When you want to set the adapter length manually, press Length then input the value. Input 0s set at the Auto mode.
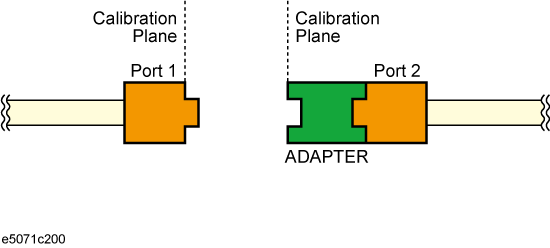
Usually, two-port network analyzers remove the adapter characteristics by performing two sets of Full 2 Port Calibration as shown below:
Calibration performed with the adapter connected to Port2
Calibration performed with the adapter connected to Port1
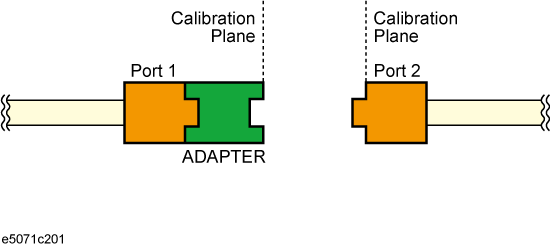
Removing adapter characteristics using two (above) sets of calibration
However, this method is not suitable for a multi-port network analyzer because it requires Full 2 Port Calibration as many as twice the number of port combinations. Therefore, the E5061B uses an advanced method to remove the Adapter characteristics described in About Adapter Insertion.