Other topics about Advanced Calibration
This section demonstrates the procedure to define a different open standard for each frequency band, based on the following information:
|
Standard |
Label name |
Frequencies to be defined |
|
Open |
Open 3G |
1 GHz - 3 GHz |
|
Open |
Open 6G |
3 GHz - 6 GHz |
Press Cal key.
Click Cal Kit.
Select a calibration kit you want to define.
Click Modify Kit > Define STDs.
Select #1, click Label, and enter Open 3G using the character input pad that appears on the screen.
Click Open as the standard type (STD Type).
Set a necessary standard coefficient.
Enter 1G as the minimum frequency for Min Frequency.
Enter 3G as the maximum frequency for Max Frequency.
Click Return.
In the same way, select #2, press Label, and enter Open 6G using the character input pad that appears on the screen.
Select Open as the standard type (STD Type).
Set a necessary standard coefficient.
Enter 3G as the minimum frequency for Min Frequency.
Enter 6G as the maximum frequency for Max Frequency.
Click Return.
This section demonstrates the procedure to specify a different OPEN standard for each frequency band, using subclasses #1 and #2. In this example, the standards created in Defining different standard for each frequency band are used.
Press Cal Key.
Click Cal Kit.
Select a calibration kit you want to use.
Click Modify Kit > Specify CLSs.
Click Sub Class > Sub Class 1.
Select the standard type Open, press Set All, make settings for all ports.
Select #1 (Open 3G).
Click Return.
Then, press Sub Class, and select Sub Class 2.
Select the standard type Open, press Set All, make settings for all ports.
Select #2 (Open 6G).
Click Return.
The following procedure shows how to disable a standard defined for a subclass. You cannot disable subclass 1 because at least one standard must exist. The following procedure shows how to disable an OPEN standard of subclass 2.
Press Cal key.
Click Cal Kit.
Select a calibration kit you want to use.
Click Modify Kit > Specify CLSs.
Click Sub Class > Sub Class 2.
Select the standard type Open, click Set All, make settings for all ports.
Select None.
Click Return.
By using several subclasses, you can set a different standard for each frequency, but note the following on frequency ranges. The following table shows possible cases and whether calibration is possible.
|
Possible cases of frequency ranges |
Execution of calibration |
|
Example 1, When frequency ranges specified with subclasses overlap |
Possible |
|
Impossible |
|
|
Possible |
|
|
Possible |
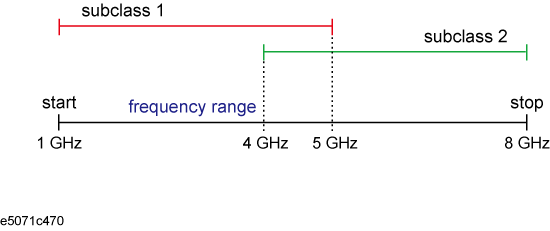
For the measurement frequency range (1 GHz - 8 GHz), if you execute calibration with a standard of subclass 1 (1 GHz-5 GHz) and then with a standard of subclass 2 (4 GHz-8 GHz), the standard last executed is applied for the overlapping portion (4 GHz-5 GHz).

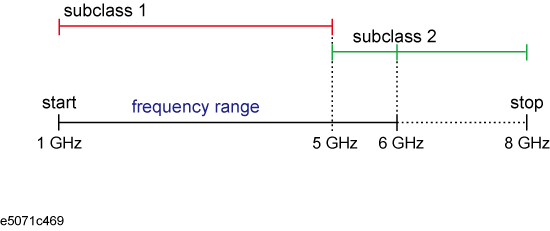
For a measurement frequency range (1 GHz to 8 GHz), if you execute calibration with a standard of subclass 1 (1 GHz to 5 GHz) and then with a standard of subclass 2 (6 GHz to 8 GHz), Done is NOT available for the undefined portion (5 GHz-6 GHz).
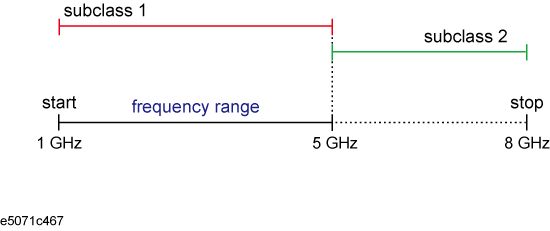
For a measurement frequency range (1 GHz to 5 GHz), if you define a standard of subclass 1 (1 GHz to 5 GHz) and a standard of subclass 2 (5 GHz to 8 GHz), calibration possible for subclass 2 although it is out of the measurement frequency range. The calibration coefficients, however, are disregarded. (There is no check mark on the softkey.) Note that, because the standard of subclass 1 covers the measurement frequency range, Done is available.
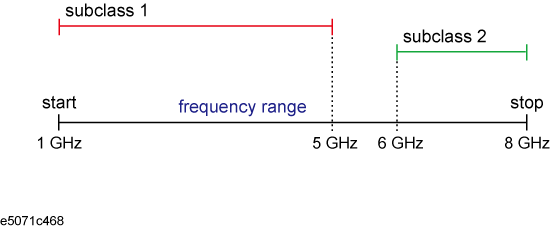
For a measurement frequency range (1 GHz to 6 GHz), if you define a standard of subclass 1 (1 GHz - 5 GHz) and a standard of subclass 2 (5 GHz to 8 GHz), a part of subclass 2 (6 GHz to 8 GHz) lies outside the measurement frequency range, but the other part (5 GHz to 6 GHz) lies within it, so calibration is possible.