Other topics about Fixture Simulator
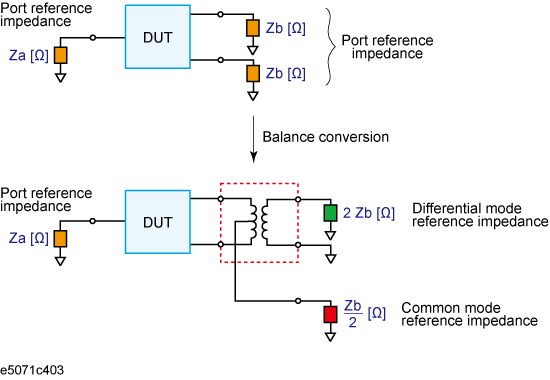
By using the port impedance conversion function, you can specify the impedance of each test port. As a result of this conversion, the impedance of the balanced port in differential mode is set to a value twice as large as the impedance of the two unbalanced ports before conversion, and in common mode to a value one-half as large.
Port impedance after a balance-unbalance conversion

As described above, the impedance of the balanced port is automatically specified as the result of specifying the impedance of the two unbalanced ports prior to balance-unbalance conversion. However, the port impedance can be changed to an arbitrary value by using the differential port impedance conversion function and the common port impedance conversion function.
If you turn on the differential port impedance conversion function, the port reference impedance in the differential mode is converted to an arbitrary value specified with this function instead of the value in the above figure.
Press Analysis key, then click Fixture Simulator > Diff Z Conversion.
Click Diff Z Conversion to set the differential impedance conversion function to ON.
You can only turn on or off Differential Port Impedance Conversion for all of the balanced ports together, not for each port individually. If you want to turn off only a specific port, set the reference impedance of the port to the value in the above figure.
Press Analysis key, then click Fixture Simulator > Diff Z Conversion.
Specify the port reference impedance in differential mode.
Select the balanced port from Port 1 (bal) Real, Port 2 (bal) Real, or Port 3 (bal) Real to set the differential port reference impedance in "Real" format.
Select Port 1 (bal) Real and Port 1 (bal) Imag, Port 2 (bal) Real and Port2 (bal) Imag, or Port 3 (bal) Real and Port 3 (bal) Imag to set the differential port reference impedance in "Complex" format.
Ports 1, 2, and 3 refer to the logical ports 1, 2, and 3.
If you turn on the common port impedance conversion function, the port reference impedance in the common mode is converted to an arbitrary value specified with this function instead of the value the above figure.
Press Analysis key, then click Fixture Simulator > Cmn Z Conversion.
Click Cmn Z Conversion to set the common port impedance conversion function to ON.
You can only turn on or off Common Port Impedance Conversion for all of the ports together, not for each port individually. If you want to turn off only a specific port, set the impedance of the port to the value in the above figurerocedure to set common port reference impedance
Press Analysis key, then click Fixture Simulator > Cmn Z Conversion.
Specify the port reference impedance in common mode.
Select the balanced port from Port 1 (bal) Real, Port 2 (bal) Real, or Port 3 (bal) Real to set the common port reference impedance in "Real" format.
Select Port 1 (bal) Real and Port 1 (bal) Imag, Port 2 (bal) Real and Port2 (bal) Imag, or Port 3 (bal) Real and Port 3 (bal) Imag to set the common port reference impedance in "Complex" format.
Ports 1, 2, and 3 refer to the logical ports 1, 2, and 3.