
| 3GPP2 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Channel Coding | ||
|
|
||
|
Channel Coding Parameters |
||
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
Graphs |
||
|
|
||
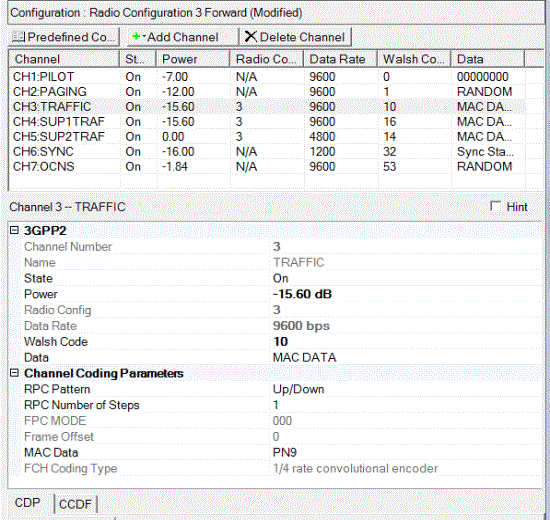
This table enables you to view the key parameters for each channel in the carrier. You can also add or delete channels using the buttons above the table (see descriptions below). Clicking a channel row activates the setup tables for that channel. You can use a maximum of 256 channels.
Opens a  drop-down menu
of predefined channel configuration selections. Double-clicking a configuration
replaces the current configuration in the Channel Configuration Summary
Table.
drop-down menu
of predefined channel configuration selections. Double-clicking a configuration
replaces the current configuration in the Channel Configuration Summary
Table.
Opens a  drop-down menu
which allows you to add a channel to the current configuration. The following
types of channels can be added to the channel configuration: Pilot, Paging,
Traffic, Sync, or two supplemental traffic channels
drop-down menu
which allows you to add a channel to the current configuration. The following
types of channels can be added to the channel configuration: Pilot, Paging,
Traffic, Sync, or two supplemental traffic channels
The new channel is added immediately above the currently highlighted channel in the Channel Configuration Summary Table.
When selecting from the Traffic or the supplemental traffic channels,
 additional drop-down menus
are displayed which allow you to select the available Radio Config (RC)
and data rate choices for each channel type.
additional drop-down menus
are displayed which allow you to select the available Radio Config (RC)
and data rate choices for each channel type.
 All available RC and Data Rate
choices…
All available RC and Data Rate
choices…
Deletes the currently highlighted channels in the Channel Configuration Summary Table and the current configuration. You can highlight multiple channels by holding down the CTRL key while selecting the channels. You can also use the SHIFT key to select a succession (group) of channels.
Displays the channel type or name that is selected in the Channel Configuration Summary Table.
Selections: On, Off
Default: On
Sets the state of the selected channel to either on or off. The ![]() icon at the right of the entry box displays the
valid selections.
icon at the right of the entry box displays the
valid selections.
Range: -60 to 0 dB
Default: 0.00 dB
Sets the power of the selected channel.
Displays the data rate setting of the selected channel. This value was set when the predefined configuration was selected or the channel was added as a new channel.
Range: 0 to 63
Default: 0
Sets the Walsh Code for the selected channel.
Allows you to select or specify the data for the selected channel. The
icon at the right of the entry box opens the
 Data Source Selection dialog box.
Data Source Selection dialog box.
Selections: On, Off
Default: Off
This setting is only for the paging channel and sets whether the paging channel uses coded or uncoded data.
On | The channel uses uncoded data. |
Off | The channel uses coded data. |
This parameter appears in the software's GUI only when Minor Enhancement Update (MEU) Option U02 or greater is valid. Refer to Licenses for more information.
Range: 0 to 511
Default: 6
Sets the protocol revision level for Sync channel.
Range: 0 to 511
Default: 6
Sets the minimum protocol revision level for Sync channel.
Range: 0 to 511
Default: 0
Sets the system identification in Sync channel.
Range: 0 to 511
Default: 0
Sets the network identification in Sync channel.
Range: 0 to 2016
Default: 387
Sets the frequency assignment field in Sync channel.
Choice:Up/Down; Down/Up; All Up; All Down; User Defined Bits
Select a data type using the RPC Selection dialog box.
Opens the  user data entry area,
which lets you customize the transmitted data.
user data entry area,
which lets you customize the transmitted data.
The user data entry area contains buttons to import, export, or clear user data along with the ability to insert PN9 or PN15 data. Optionally you can manually insert or delete data. To manually insert data, simply place the cursor within the data entry area or highlight existing bits, and insert data. There are three ways to insert data:
using the 1 and 0 keys on the keyboard
using the Insert PN9 button
using the Insert PN15 button
pasting data from a file or from within the current view
(The key board shortcuts Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V work for user data entry.)
To delete data, simply place the cursor at the desired location within the data or highlight bits, and delete the data. The key board shortcut Ctrl+Z also deletes highlighted data.
The maximum number of bits for the user data entry area is 65,536, which is also the maximum file size.
The expanded area has four buttons that can be used to manipulate data for the channel.
Range: 1-80
Enter the RPC Number of Steps value when RPC Pattern 'UP/Down' or 'Down/Up' is used.
Displays Forward Power Control mode.
Select a data type using the Data Source Selection dialog box. Mac Data is used when Forward channel data is 'Mac Data' (default).
Set the FCH Coding Type:
1/2 rate convolutional encoder
1/4 rate convolutional encoder
No Coding
Set the SCH Coding Type:
1/2 rate convolutional encoder
1/4 rate convolutional encoder
1/2 rate turbo encoder
1/3 rate turbo encoder
1/4 rate turbo encoder
1/5 rate turbo encoder
No Coding
Shows the Code Domain Power (CDP) graph. This graph shows the position
and power level of each channel, relative to the Walsh Code applied. Select
the channel setup in the  tree view
to view the CDP distribution for that carrier.
tree view
to view the CDP distribution for that carrier.
Click on a  channel in the graph
to view the parameter selections for that channel.
channel in the graph
to view the parameter selections for that channel.
Hold the cursor over any individual channel to view a  tool tip showing the channel number, type, Walsh Code, rate, and
power.
tool tip showing the channel number, type, Walsh Code, rate, and
power.
Toggles between two code order display formats, Hadamard and Bit Reverse.
uses an algorithm that displays each Walsh code in sequence and the composite representation of the traffic channel.
uses an algorithm
that rearranges the location of the bits of data such  the bit in most significant bit (MSB) position is rearranged and
placed into the least significant bit (LSB) position
and so on until all of the bits are rearranged.
the bit in most significant bit (MSB) position is rearranged and
placed into the least significant bit (LSB) position
and so on until all of the bits are rearranged.
Each channel is also displayed as a bar where the height of the bar is proportionately representative of the channel's power and the width of the bar is proportional to the data rate.
Shows the Complimentary Cumulative Distribution Function (CCDF) graph. This graph shows the plot and peak-to-average values for the current carrier. This topic describes the CCDF functionality using the graph in the Channel Setup view.
The CCDF graph displays the probability (in percentage) of the generated carrier's calculated peak-to-average power ratio (measured in dB) meeting or exceeding a certain level. The table to the left of the CCDF plot displays the calculated peak-to-average values for the carrier. For additional information, see Understanding CCDF Curves.
Click  or
or  from the main tool
bar to generate an I/Q waveform and plot the CCDF graph using the
current channel configuration. Any changes to the channel configuration
setup do not appear on the graph until you generate the waveform. The
status bar at the bottom
of the screen shows waveform generation progress.
from the main tool
bar to generate an I/Q waveform and plot the CCDF graph using the
current channel configuration. Any changes to the channel configuration
setup do not appear on the graph until you generate the waveform. The
status bar at the bottom
of the screen shows waveform generation progress.
Each time you adjust parameters and generate a waveform, a plot is added
to the  graph.
The graph retains your three most recent plots (in shades of gray), allowing
you to make comparisons of waveform characteristics.
graph.
The graph retains your three most recent plots (in shades of gray), allowing
you to make comparisons of waveform characteristics.
Use the buttons shown below to plot the Gaussian data, reference data and generated waveform data to the CCDF graph. The graph's initial state shows only the Gaussian curve (blue) until you generate a waveform.
Toggles the view of the band-limited Gaussian noise curve (blue).
Toggles the view of the reference curve (red). The reference appears as a flat line until you generate a waveform and click the button
Sets the current waveform curve to yellow and the reference curve to red. Click the Reference button to view the reference curve.