The SUN frequency shift keying (SUN-FSK) provides good transmit power efficiency due to the constant envelope of the transmit signal.
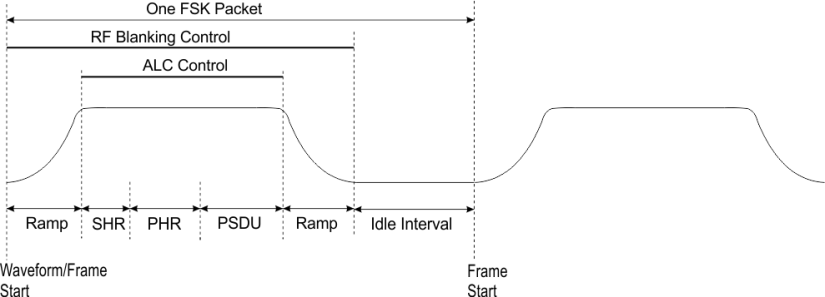
The 802.15.4 SUN FSK signal is generated on a packet/frame basis. A packet shall include SHR, PHR, PSDU parts as defined in the spec and possibly the ramp up & down and idle interval as configured by user. Below is a figure illustrating the structure of a FSK packet. A waveform can include one or more packets, depending on user's setting. When idle interval is set to zero, a continuous (non-bursted) will be generated without any ramp up & down and idle interval.

The PPDU format for SUN MSK is illustrated as follows.
Format of the SUN FSK PPDU
| Octets | |||||||
| 2 | Variable | ||||||
| SHR | PHR | PHY Payload | |||||
| Preamble | SFD |
|
PSDU | ||||
Format of the SUN FSK PPDU (optional, if mode switch is enabled)
| SHR | PHR | |||||||
| Preamble | SFD |
|
||||||
The modulation for SUN FSK is either a 2- or a 4- level filtered FSK.
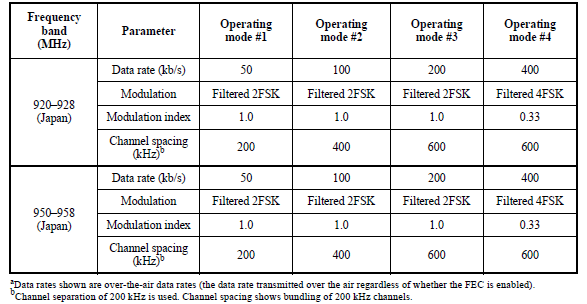
802.15.4-2015 defines various operating modes for SUN FSK using various frequency bands, data rates, modulation and channel spacing. All fields in the SUN FSK PPDU shall use the same symbol rate and modulation order.
A device shall support operating mode #1 and may additionally support operating modes #2 and #3.
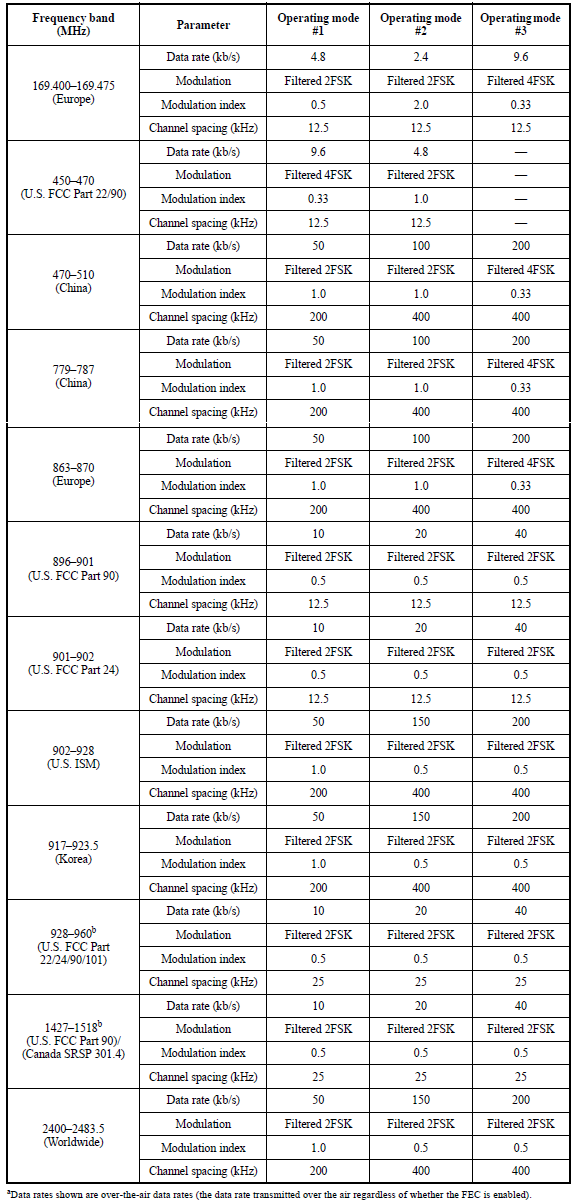
For Japanese bands, a device shall support both modes #1 and #2 and may additionally support operating modes #3 and #4.
The nominal frequency deviation is defined as:
Δf = (symbol rate x modulation index)/2
For filtered 2FSK, fdev = Δf
For filtered 4FSK, fdev = 3 x Δf
The figure below give the symbol encode for 802.15.4 SUN FSK.
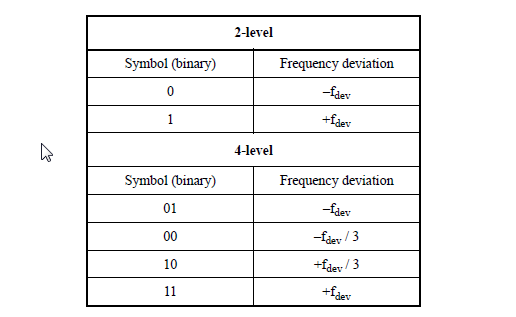
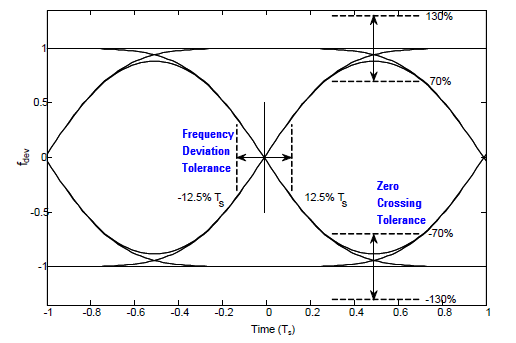
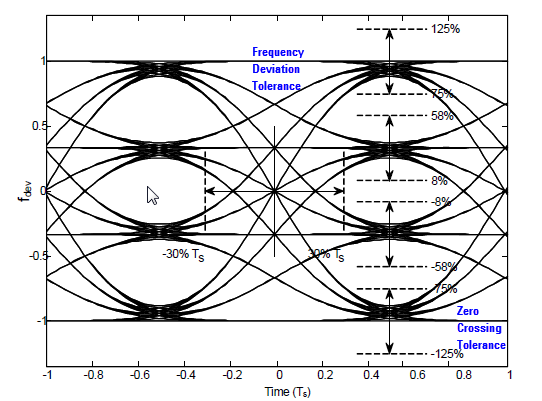
Frequency Deviation Tolerance and Zero Crossing Tolerance are measured to evaluate the modulation quality for 802.15.4 SUN FSK.
The following figure show the eye diagrams for filtered 2FSK and filtered 4FSK. For more requirements on regulatory compliance, refer to IEEE 802.15.4-2015.