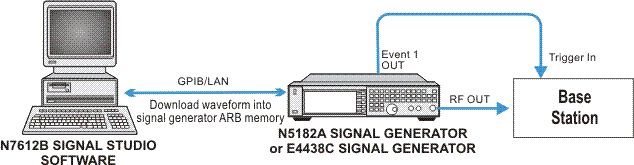
This example shows you how to set up the equipment and configure the N7612C Signal Studio for TD-SCDMA/HSPA 2018 software to create a single carrier uplink TD-SCDMA waveform in Advanced Capability for a typical base station BER receiver sensitivity measurement.
In this example, the N5182A MXG or E4438C ESG signal generator will be used and the Signal Studio for TD-SCDMA/HSPA software generates the waveform based on the waveform, carrier, timeslot/channel parameters configuration, then download the waveform into the signal generator.

Click in the tree view (left pane of the main window) to configure waveform parameters. The parameter view (right pane) now displays the Carrier Configuration Summary table and the Waveform Setup section. The Waveform Setup section contains the key waveform related parameters.
Add one Advanced Carrier: You have the option of adding either a Basic or Advanced carrier to the current carrier selection showing in the configuration summary table.
In
the configuration summary table, click the Add new carrier button  .
.
Select from the drop-down menu.
Make sure you have one Advanced Carrier listed in the table.
Set the waveform parameters:
: Set the waveform name as desired. The name you define here is displayed on the signal generator when you download the waveform.
: Set to 3 for this example so that the TS4, TS5 and TS6 are downlink timeslots.
: Set to a multiple of the number of subframes in one TTI and long enough to perform BER measurement. For example, for 40ms TTI, there are eight subframes in one TTI (one subframe is 5 ms), therefore, the number of subframes must be set to a multiple of 8. Set to 120 for this example to ensure that we have enough long waveform for BER testing.
: Select Root Raised Cosine, set Alpha = 0.22, Length = 64 symbol for this example. You can set other filter types as desired.
: Set to to use the truncated PN as transport channel input data. The purpose of the truncation is to ensure that the PN sequence repeats integer times in the waveform, providing a predictable bit pattern for the BER measurement. To get details on how the payload is truncated, see Transport Channels User Files.
: Set to to export the channel payload data into text files, which you can use as the expected data at the receiving end to calculate the BER.
: Select the directory to export the payload data files.
: Set to to ensure the Event 1 output present the first sample point of each subframe.
Leave all other parameters settings at their default values.
Now you can see the  advanced
carrier
displayed in the tree view. Click the carrier node in the tree view to
set the carrier parameters. The Carrier Setup in the parameter view displays
the baseband and 3GPP parameters for that carrier.
advanced
carrier
displayed in the tree view. Click the carrier node in the tree view to
set the carrier parameters. The Carrier Setup in the parameter view displays
the baseband and 3GPP parameters for that carrier.
: Set the SYNC-DL ID to 0. Note that the SYNC-UL ID, Scrambling Code and Basic Midamble Code belong to the code group determined by the SYNC-DL ID and change automatically as the SYNC-DL ID changes.
Leave all other parameters settings at their default values.
: Click PCCPCH in the tree view. The parameter view (right pane) now displays the Primary Common Control Channel Setup. Turn it OFF.
: turn the state of the DwPTS and UpPTS to OFF.
: Click Dedicated Channel in the tree view to configure
RMC parameters. The parameter view (right pane) now displays the Dedicated
Physical Channel Summary table. Add one uplink 12.2 Kbps
RMC channel by clicking the Add a new physical channel button  and selecting from the drop-down menu.
and selecting from the drop-down menu.
: Double click in the summary table to enter the RMC uplink 12.2 Kbps channel setup.
Set
the Payload type in the  physical
channel
to and leave all other parameters
settings in physical channel as their default values.
physical
channel
to and leave all other parameters
settings in physical channel as their default values.
Set
all of the Payload type in the  transport
channels
(DCH #1 and DCH #2) to .
transport
channels
(DCH #1 and DCH #2) to .
: Set it to 1 in this example. You can also set to other timeslots if there is no resource conflicts.
: Set it to 1 in this example. You can also set to other timeslots if there is no resource conflicts.
: Set it to your desired value.
Click in the tree view. The parameter view now shows seven panes: Configuration, Basic, I/Q, ALC, Dual ARB, Dual ARB Marker Utilities, Dual ARB trigger.
: Under Basic Pane, set it to 2 GHz.
: Under Basic Pane, set it to -8 dBm for this example
Click Generate a waveform button  in the tool bar. The software generates an
I/Q waveform file in accordance with the current channel configuration
and signal generation setup. Waveform generation time varies proportionally
to the complexity of the waveform.
in the tool bar. The software generates an
I/Q waveform file in accordance with the current channel configuration
and signal generation setup. Waveform generation time varies proportionally
to the complexity of the waveform.
To download the waveform file to the signal generator,
click Download  in the tool bar if you have configured the instrument connection..
The signal generator automatically begins to play the TD-SCDMA waveform.
Local control of the signal generator is re-enabled by pressing the hardkey, allowing signal generator
settings to be modified from the front panel. The waveform file, however,
cannot be modified after downloading it to the signal generator.
in the tool bar if you have configured the instrument connection..
The signal generator automatically begins to play the TD-SCDMA waveform.
Local control of the signal generator is re-enabled by pressing the hardkey, allowing signal generator
settings to be modified from the front panel. The waveform file, however,
cannot be modified after downloading it to the signal generator.