DUT Routing State
Last updated: January 16, 2009
Description
The test set allows you to test the router function of a device. The test set acts as a router and it enables the routing of packets to the DUT.
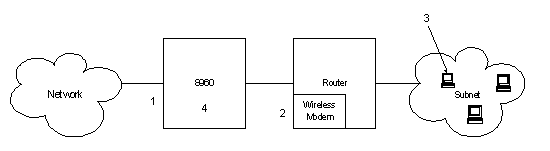
How does the DUT work as a router
As in the above figure, if the test set is set as follows:
1. 8960 Ext IP = 130.129.183.15
Dest Mask Gateway Interface
130.29.179.201 0xFFFFFFFF 192.168.200.1 fap0
192.168.104.0 0xFFFFFF00 192.168.200.1 fap0
The IP packets that are addressed to the DUT are sent via the over-the-air interface to the DUT. When the DUT Routing State is enabled, any packet that has an address that matches the subnet mask (any address in the range 192.168.104.0 to 192.168.104.255) is sent over the air to the DUT. The DUT forwards the packet to its controller (typically a router). The router then takes care of forwarding the packet to the intended host.
How to Configure the DUT Routing State
This test set allows you to enter a maximum of four DUT IP addresses. For GSM/GPRS/EDGE LA application, you may use all four DUT IP Addresses. For all other LA applications, you are allowed to use only one DUT IP Address. For each DUT IP address, there is one associated subnet route. These subnet routes are hardcoded as follows:
| DUT | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 255.255.255.0 | |
| 2 | 192.168.105.0 | 255.255.255.0 |
| 3 | 192.168.106.0 | 255.255.255.0 |
| 192.168.107.0 | 255.255.255.0 |
Configuring the CDMA2000 DUT Routing State
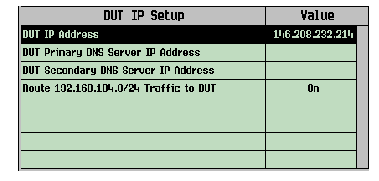
If the test set's DUT IP Address is set to 146.208.232.214, the Route 192.168.1.4.0/24 Traffic to DUT is set to On, as shown below. This is done by performing that the address in the range 192.168.104.0 to 192.168.104.255 forward to the DUT which IP address is 146.208.232.214.
Route Choosing Requirements
There are two requirements for choosing routes:
- Allows ease of reference: the set of all four subnets can be denoted by 192.168.104.0/22.
- The subnets are chosen in an attempt to minimize the chances that you might already be using the same address for other nodes on the network. For example, it is assumed typical private networks tend to use IP address in the 192.168.1.x and 192.168.100.x ranges.
The routes can not be set over MUI and not be available over RUI.
The LAN IP Address, LAN IP Address 2 and the DUT IP Address are all required on the same subnet. If you turn on DUT routing, any attempt to enter a LAN IP Address, LAN IP Address 2 or DUT IP Address within the range of any of the fixed network routes is rejected and an error message generated.
Operating Consideration
For CDMA2000, the DUT Routing State can not be changed when operating mode is set to Active Cell and the call or data status is other than IDLE.
For 1xEV-DO, the DUT Routing State can not be changed when operating mode is set to Active Cell and the data status is other than IDLE .
For WCDMA and GGE, the DUT Routing State can be changed when the operating mode is Cell Off
The 8960 can not be proxy ARPing for any of the new routed packets or advertising these new routes via RIP (Routing Information Protocol) or OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) or similar traffic management protocols.
The targeting of the IP address ranges to the 8960 for forwarding OTA (Over-The-Air technology) is the responsibility of the external LAN configuration.
If the Secondary PDP context is being used and the Primary PDP context clears off, no DUT routing subnet packets is forwarded to the DUT. Similarly, if the Secondary PDP context is at a higher priority than the Primary PDP context and the traffic on the Secondary PDP context takes up all the available bandwidth, DUT routing subnet packets is not forwarded to the DUT.