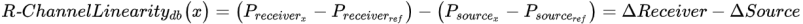R-Channel Linearity Performance Test
This test applies to the following models with Option 561:
-
N5241A/AS/B/BC, N5242A/AS/B, N5242AH85, N5244A/AS/B, N5245A/AS/B/BC, N5247A/AS/B/BC, N5249A/AS/B
|
|
This test is extremely sensitive. To minimize the chance of test failure, it is important to follow proper testing procedures:
-
Ensure all connectors are clean.
-
Properly torque all connections.
-
Check that all test equipment is attached to the correct connecter and has solid connections.
-
Ensure that the required equipment is being used.
-
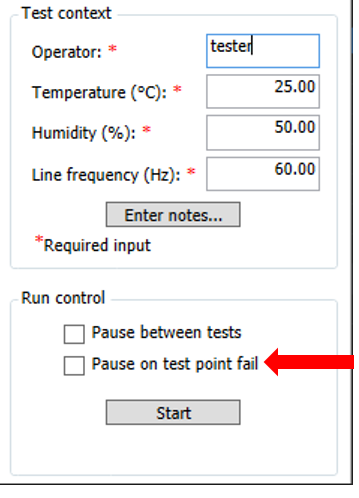
Be sure that  Pause on test point fail is not selected for this test. Pause on test point fail is not selected for this test.
|
R-Channel Linearity, as defined here, is a measure of an R-Channel receiver's relative power linearity. It is the measurement accuracy of a receiver as a function of power. At a CW frequency, a signal at a known power level is delivered to the receiver which establishes a power reference value. The signal—at a new power level x dB from the reference—is then delivered to the receiver. As a result, the receiver reading will change by 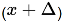 db. The difference between the delta power delivered and the delta power read by the receiver, Δ dB, will be the R-Channel Linearity. This process is repeated over the desired measurement range of the receiver. A mathematical expression for this specification (in dB) is:
db. The difference between the delta power delivered and the delta power read by the receiver, Δ dB, will be the R-Channel Linearity. This process is repeated over the desired measurement range of the receiver. A mathematical expression for this specification (in dB) is:
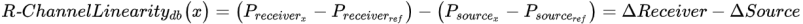
Before the test begins, a reference power must be selected. All subsequent measurements will use the reference power for computing the dynamic accuracy error. The reference power is normally selected somewhere well above the noise floor and safely below source and receiver compression.
Two sources are used to provide the source power to the receiver through a special combining network. The source power at the receiver is adjusted to deliver a target power with one source. The power at the receiver is then measured with the target power applied and the other source is adjusted, using the receiver as the measurement device, to achieve the same power at the receiver.
The variation in power is achieved by placing the two sources at a specific offset frequency from one another at a specific CW frequency which, when mixed in the receiver, will provide a modulated power to the receiver at the desired CW frequency. A declared power range of this measurement is taken and the measurement is repeated with the sources set to multiple power settings to provide further range. An attenuator is also used between the combining network and the receiver to further extend the measurement range.
At a specified CW frequency, the receiver and the source make power measurements which include the reference level. As the injected signal power is stepped away from the reference level, measurements of the input signal and the receiver are made. For each delta power away from the reference, the above equation is used to calculate the dynamic accuracy error. The injected power is continuously adjusted away from the reference and the above process is repeated to provide the dynamic accuracy measurements over the desired dynamic range of the receiver.
For troubleshooting help, see Dynamic Accuracy Troubleshooting since its procedure is very similar to the Dynamic Accuracy test.
Required Test Equipment
|
Test Equipment1
|
Recommended Model
|
Alternate Model
|
|
Dynamic Accuracy test set2
(DynAcc TestSet2)
|
U3020BD01
|
U3020AD01
|
|
Signal Generator
(SignalGenerator1)
|
E8257D
|
N5183B
N5182B
E8257C
E8267C/D
E8247C (not allowed for N5241x and N5242x PNA-X)
|
|
Load, 3.5 mm 50 W
(50OhmLoad)
|
909D
|
902C
|
- Refer to the main test equipment table for available cables and adapters listed by connector type.
-
If needed, the GPIB address on the test set can be modified by following these steps ( click here). click here).
- Connect the new test set to the LAN.
- Open Keysight IO from the PC.
- Select Add Instrument from the menu.
- In the Add LAN Instrument window, locate the new test set on the LAN.
- Select the web page for the new test set and select the View & Modify Configuration tab at the left.
- Select Modify Configuration.
-
Change the GPIB address and select Save.
The new test set should now have the updated GPIB address.
|
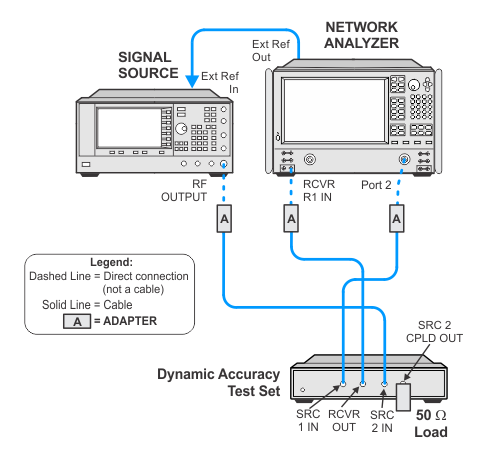
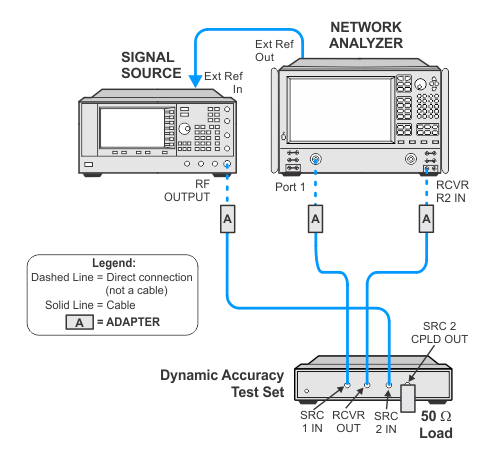
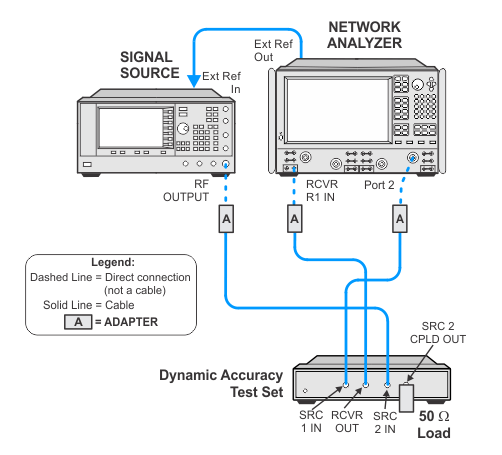
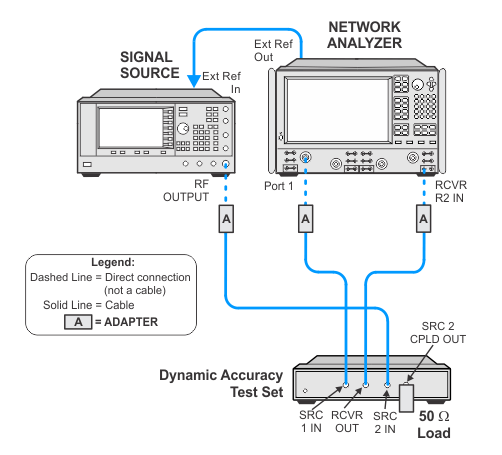
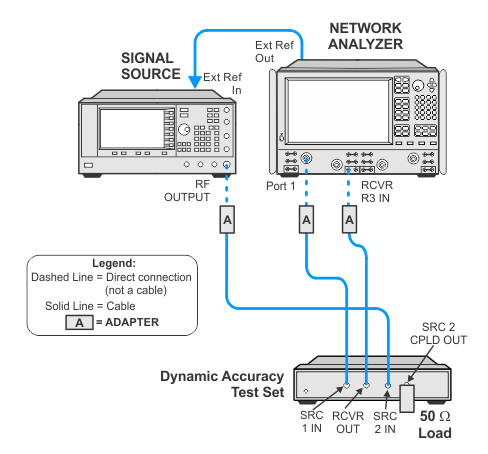
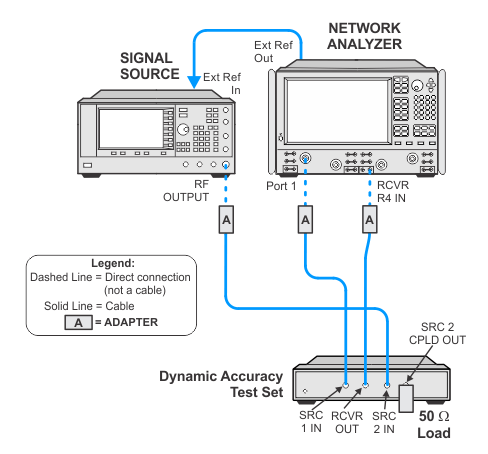
Connection Setups

 Pause on test point fail is not selected for this test.
Pause on test point fail is not selected for this test.
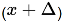 db. The difference between the delta power delivered and the delta power read by the receiver, Δ dB, will be the R-Channel Linearity. This process is repeated over the desired measurement range of the receiver. A mathematical expression for this specification (in dB) is:
db. The difference between the delta power delivered and the delta power read by the receiver, Δ dB, will be the R-Channel Linearity. This process is repeated over the desired measurement range of the receiver. A mathematical expression for this specification (in dB) is: