IQ Normalization Enable (Custom IQ)
enables or disables IQ trace normalization. Selecting the check box enables normalization; clearing the check box disables normalization.
When normalization is ON, the VSA normalizes, or scales, the demodulated trace data results. The normalization factor depends on the EVM Normalization Reference selection and the type of signal format.
Normalization is performed on these traces:
-
QAM Quadrature Amplitude Modulation/PSK Phase Shift Keying: A broad classification of modulation techniques where the information to be transmitted is contained in the phase of the carrier wave. formats
- Error Vector Spec and Error Vector Time
- IQ Meas Spec and IQ Meas Time
- IQ Ref Spec and IQ Ref Time
- IQ Mag Error
- The Instantaneous versions of any of these traces (like Inst IQ Meas Spec)
EVM Normalization Reference = Constellation Maximum
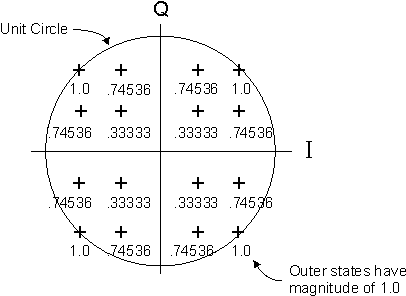
When is set to , the traces are normalized to the maximum constellation magnitude, which is the outermost state in the ideal (IQ Ref) constellation diagram. For example, the constellation for a 16QAM IQ Ref trace is shown below after normalization. All the points in the trace have been normalized by the magnitude of the outermost state, which sets the outermost states to 1.
A 32QAM constellation diagram does not have corner states. For these "cross-QAM" constellations, the VSA normalizes the constellation diagram to the corner state of an ideal, square constellation diagram. In other words, when normalization is ON for 32QAM, traces are normalized by the magnitude of the corner state of an ideal 36QAM constellation diagram. 128QAM is normalized to 144QAM. 512QAM is normalized to 576QAM, etc.
OQPSK Offset Quadrature Phase Shift Keying: A type of QPSK modulation that offsets the bit streams on the I and Q channels by a half bit. This reduces amplitude fluctuations and helps improve spectral efficiency. signals are normalized to the QPSK Quadrature phase shift keying constellation so that the corners of the QPSK constellation have a magnitude of one. For more information, see the OQPSK Offset note in the Error Vector Magnitude (EVM Error vector magnitude (EVM): A quality metric in digital communication systems. See the EVM metric in the Error Summary Table topic in each demodulator for more information on how EVM is calculated for that modulation format.) topic.
EVM Normalization Reference = Reference RMS
For modulation formats whose constellations have multiple magnitude levels (16QAM, APSK, StarQAM, etc.), can be set to . When this is selected, IQ traces are normalized by the RMS level of the constellation itself (EVM in the table is still normalized to the RMS average of the IQ Reference symbol points).
In other words, the normalization value is an RMS average of all possible states in the IQ Ref Time ideal QAM constellation. This is in contrast with the normalization value used when is set to , which is the outermost constellation state of IQ Ref Time trace.
How Normalization Affects the Trace Measurement Units
For most configurations, the measurement data determines the units of the normalized trace. With normalization on, the y-axis units (for rectangular traces) or polar units (for polar traces) become unitless or are converted to a percentage. If the Log Mag trace format is selected, the units are decibels.
As mentioned previously, normalization scales the demodulated data onto the unit circle. This process of scaling yields a unitless scalar (number). For some traces, such as error vector time, the number is multiplied by 100 to display the percentage error. Thus an error vector of 0.10 is 10%.
See Also
