Pulse Search (Digital Demod)
demodulates pulsed (burst) transmissions. Selecting the check box turns on ; clearing it disables .
When the Digital Demodulation measurement type is first selected, the default setting for is disabled (cleared).
Digital communication systems that use pulsed transmissions send and receive information in bursts (such as those in mobile units). In other words, carrier power is switched on and off. The carrier switches on when the transmitter transmits data and switches off when the transmitter finishes transmitting data. If is on, the demodulator searches within the defined to locate the first complete pulse, which can occur anywhere in the . Pulses beyond the first complete pulse are disregarded and are not demodulated. In order for the algorithm to detect a pulse edge, the pulse must be at least 15 dB above the noise floor. The resultant pulse is then demodulated. If Constellation Sync Search is selected in addition to , the demodulator performs first then performs sync search on the resultant demodulated pulse as illustrated below.
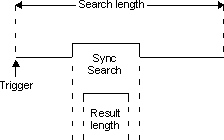
The , which includes both the offset and the sync word, must not violate the boundaries of the demodulated pulse.
Using Pulse Search
There are two ways to use :
- with Constellation Sync Search OFF
- with ON
Pulse Search with Constellation Sync Search OFF
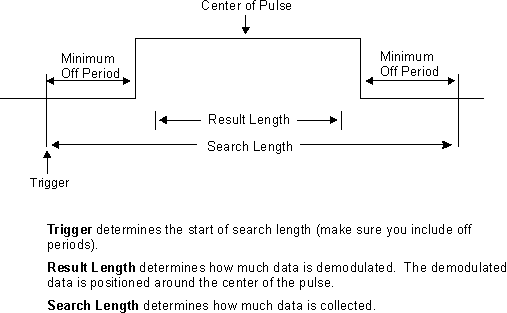
When is used and is disabled, these parameters determine how the demodulator searches for the pulse and the data that is demodulated:
determines the length of time over which the demodulator searches for a complete pulse (off-on-off).
The trigger signal determines when the demodulator begins its search.
determines how much information is demodulated. Only the first pulse detected in the search region is demodulated.
The demodulator automatically centers the with respect to the pulse. In other words, the demodulator positions the around the center of the pulse, as shown below.
Pulse Search With Constellation Sync Search ON
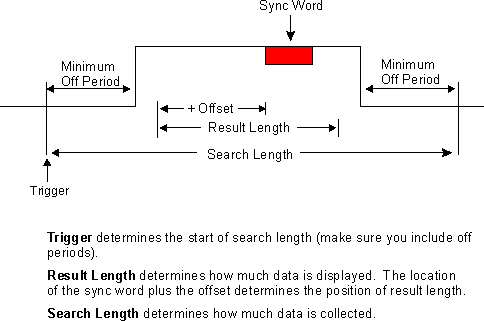
When is used and is enabled, these parameters determine how the demodulator searches for the pulse and the data that is demodulated:
When is ON, the demodulator searches for a pulse within the . The demodulator demodulates the entire pulse to locate the synchronization pattern (also called sync pattern or sync word). If there are multiple pulses within the , the demodulator demodulates only the first pulse.
The demodulator uses the and the to position the ¾the is NOT centered around the center of the pulse.
The following example shows the operation of when sync search is ON. The example uses a positive (+) offset (for details about offset, see Search Offset).
Tips When Using Pulse Search
Here are some additional tips for using :
- Determining when performing a :
Search Length = (2*MaxOn) + MaxOff
where Search Length is in seconds.
MaxOn is the maximum on time of a pulse in seconds.
MaxOff is the maximum off time between pulses in seconds.
If a single measurement contains more than one pulse, the demodulator examines only the first pulse. The demodulator ignores all other pulses in the measurement¾even when sync search is used and the first pulse does not contain the sync word. This situation can occur for large search lengths. For example, if the pulse consists of 100 symbols and the is 500 symbols, a single measurement may contain up to 4 pulses. Use external triggering to align the desired pulse near the beginning of the search record.
Increasing the may improve pulse-position repeatability. Narrow spans may distort the pulse shape, whereas wider spans offer better time resolution in the pulse detector. For spans below twice the symbol rate, you will see about 1 symbol of jitter Variation in the amount of time that it takes packets to traverse the network and arrive at a destination.. For more stable results, set the equal to or larger than three times the symbol rate.
It is often helpful to view the Search Time and Time trace data when setting up or troubleshooting pulsed measurements. The trace data shows data before applying ; the trace data shows data after applying .
Status Bits: The status bits for "Pulse Not Found" only apply to Digital Demodulation Vector Modulation Analysis (Option AYA) and is not meaningful for any other measurements.
