See other Frequency Converting Device Measurements
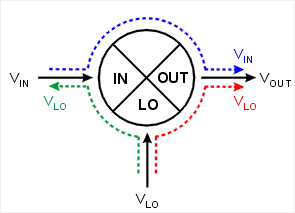
Isolation is a measure of the leakage, or feedthrough, from one port to another. The more isolation a mixer provides, the lower the amount of feedthrough. Isolation is measured at the same frequency as the stimulus, not the converted or shifted frequency. Therefore, Frequency Offset capability is not necessary for these measurements.
Three main isolation terms are of interest for mixer measurements:
LO-to-OUT isolation (VLO)
LO-to-IN isolation (VLO)
IN-to-OUT feedthrough (VIN)

Any unwanted signal "leaking" through the device will mix with the desired output signal creating intermodulation products, adding to intermodulation distortion. These unwanted signals may be difficult to filter out.
Use the following setups to measure the isolation of a mixer:
Note the following:
The Input to Output isolation is very dependent on the LO power level. Isolation should be measured with the LO power at its normal operating level.
Each of the ports not being tested should be terminated with an impedance typical of actual operation. This may not always be the characteristic impedance, Z0 (usually 50 or 75 ohms). For example, if the OUT port of a mixer is intended to be directly connected to a filter, then this filter should be used when measuring the
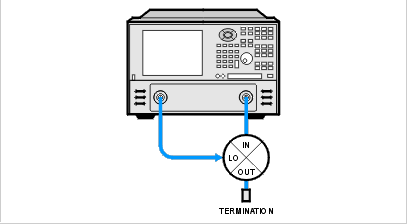
LO-TO-IN ISOLATION
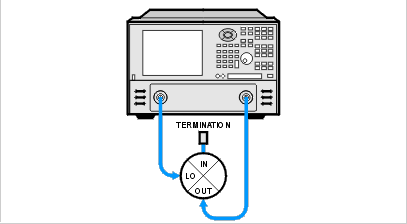
LO-TO-OUT ISOLATION
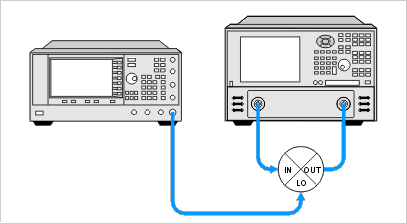
IN-TO-OUT ISOLATION
Measuring IN-to-OUT feedthrough of a converter is identical to that of a mixer. The IN-to-OUT feedthrough is generally very small for a converter due to the inclusion of an IF filter in the device. Because of this, the measurement may require the PNA to have increased dynamic range.
Measuring LO leakage (LO-to-OUT and LO-to-IN) of a converter requires a different technique because the LO port is typically not accessible:
The PNA can be tuned to the frequency of the LO signal and either the OUT or IN port connected to the PNA receiver port. The PNA source port is not connected.
A spectrum analyzer can be connected to either the OUT or IN port and tuned to the frequency of the LO signal.