Setup Examples
The Option S9x070xB Modulation Distortion application measures the nonlinear
behavior of an RF microwave amplifier and
converters under a modulated signal.
A modulation file is created,
uploaded to a signal generator, then fed into the VNA to test the
behavior of the device by measuring band
power, ACP, and EVM.
In this topic:
See Also
Example Distortion
Setup Procedure
The following example describes how to set up a typical measurement
using an N5182B MXG. In this example, a modulation file for a Compact
modulation type is created. Compact
signals cut a slice of the IQ data from an original waveform. Learn
more.
Connect the
equipment as shown after this procedure.
On the VNA
front panel, press Preset.
Perform the
following steps to set up an external MXG signal generator:
On the
VNA front panel, press Setup >
External Hardware > External Device....
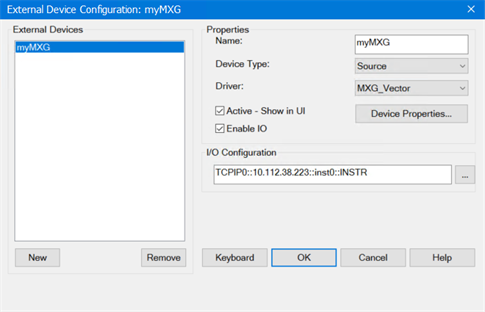
Click
on the New button.
Click
in the Name field and
type a name for the source. For example, myMXG.
For Device Type, select Source.
For the
Driver, select MXG_Vector.
(When you use VXG or VXT, select VXG
or VXT_Vector, respectively)
Select
Active - Show in UI.
Ensure
that Enable IO is checked.
In the
I/O Configuration field,
type the VISA address of the MXG.
Click
on the OK button. The
following is an example:
On the VNA
front panel, press Meas >
S-Param > Meas
Class....
Select Modulation Distortion, then either:
The Modulation Distortion Setup dialog
will be displayed.
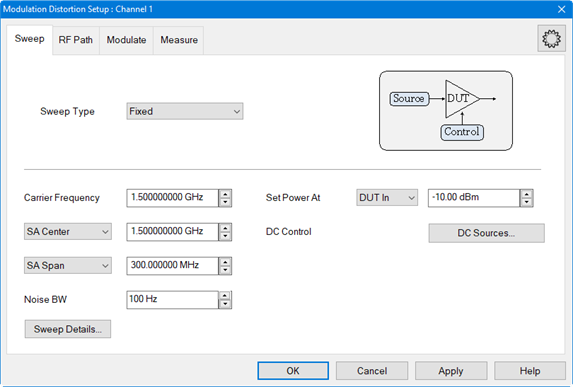
Click on the
Sweep tab and define the parameters
as shown below:
Click on the RF Path
tab and define the parameters as shown below:
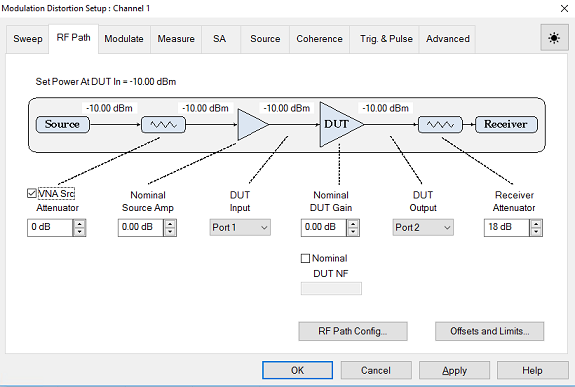
Nominal Src Amp - If there
is a loss between the MXG source output and Port 1 of the VNA, then
use a negative number. This value is used for power calibration and
to set the power level at the output of the DUT..
To access the Offsets and Limits dialog, click on the Offsets and Limits... button.
Nominal
DUT Gain - This
value is used for power calibration.
Click on the
Modulate tab.
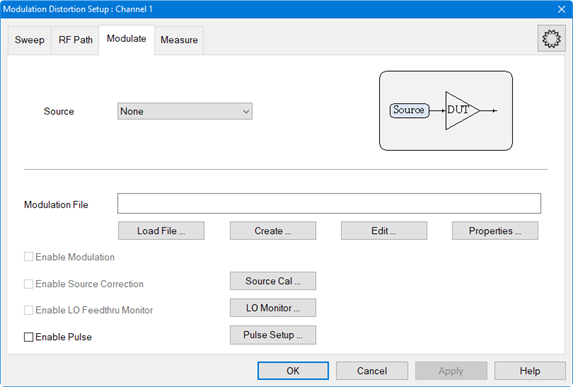
Select the
MXG source from the Source
pull down.
Click on the
Create... button to access
the Create Modulation dialog.
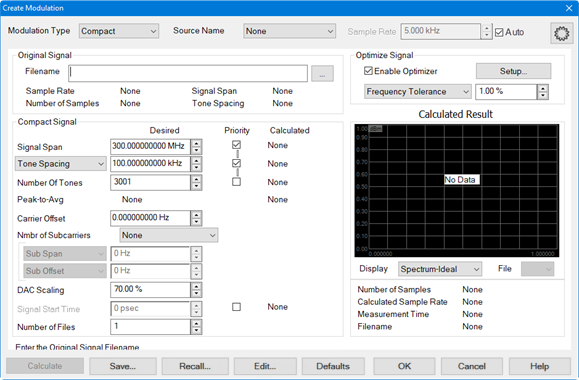
For the Modulation Type, ensure that Compact is selected from the pull
down menu. This is the default selection.
Click on the
"..." button to
the right of the Filename
field to load the original file from which to create a compact signal.
For Signal Span, use the default value.
For Tone Spacing and Number
of Tones, use the default values.
For DAC Scaling, use the default value.
For better S/N, increase the scaling value until a DAC overload occurs.
For Frequency Tolerance, use default
value of 1 %.
Click on the
Calculate button then verify
that the signal is reasonable.
Click the
Save... button and save the
compact signal file. The filename is displayed below the display window.
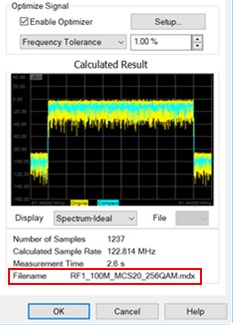
In the Display pull down menu, select Spectrum-Ideal. Signals similar
to the following should be displayed:
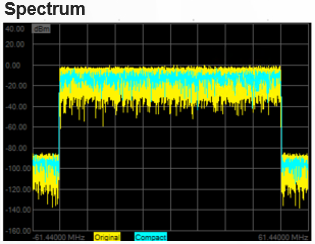
In the Display pull down menu, select Time. Signals similar to the following
should be displayed:
In the Display pull down menu, select CCDF. Signals similar to the following
should be displayed:
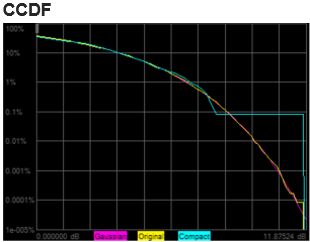
Increasing
the number of tones results in the following:
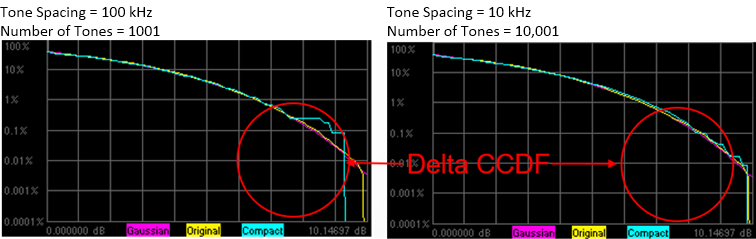
In the Create
Modulation dialog, click OK.
Click on the
Measure tab and define the
parameters as shown below:
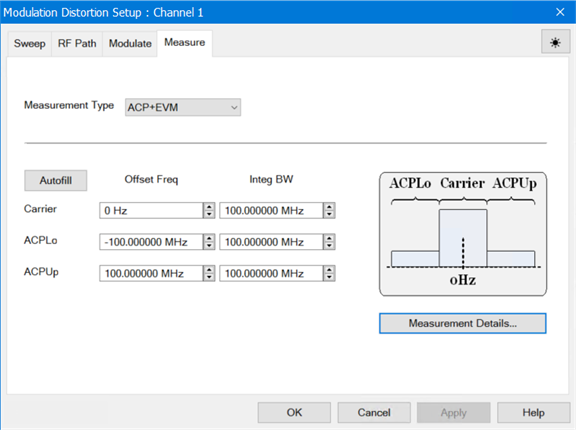
Selecting
ACP+EVM measures band power,
ACP, and EVM for the specified frequency settings in the Measure
tab.
Click OK.
To make a
measurement check without calibration, perform the following steps:
Make a
Thru connection between the Pin and Pout reference planes.
Press
Format > Format
1 > Log Mag then
select dBm/Hz.
Press
Scale > Main
> Scale then set the
scale to 10 dBm Per Division.
Press
Reference Level then set
it to -70 dBm.
Press
Reference Position then
set it to 10 Div.
Press
Display > Display
Setup > Show Table
then select Distortion.
Note the following:
The Modulation
Distortion channel makes multiple background sweeps to complete
the measurement. During the measurement, the carrier frequency
of the compact signal does not change, but the VNA local frequency
changes to cover the SA span (300 MHz in this example). The result
is stitched together and stored in the Modulation Distortion channel.
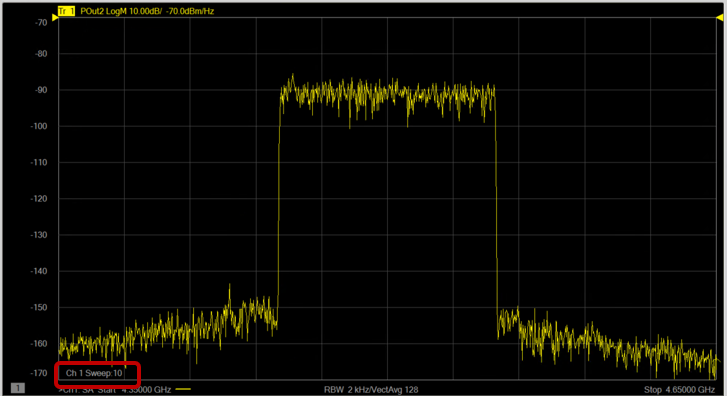
The Power
Spectral Density (PSD) dBm/Hz at the reference plane is displayed.
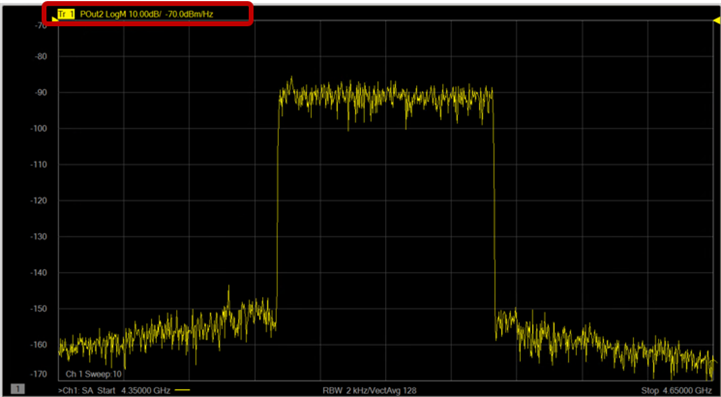
The power
level is not calibrated at this point. The result shown is based
on the factory calibration of the receiver.
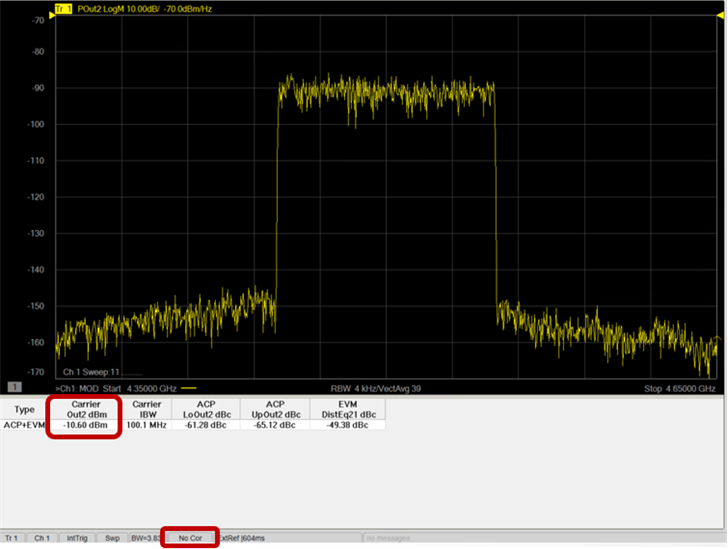
- Refer to
S-Parameter Calibration
for a procedure on calibrating the VNA receivers.
- After performing
an S-parameter calibration, refer to Source
Modulation Calibration for a procedure on calibrating source power
and flatness.
- After calibration,
perform the following steps:
- Press
Trace
> Trace
1-7 >
New
Traces....
- In
the New
Trace dialog,
select PIn1 (Power In), POut2 (Power Out) and MDist2 (Modulation Distortion
Out).
- Change
the format to dBm/Hz.
- Scale
as needed.
- If
the Distortion Table is not displayed, Press Display
> Display Setup >
Show Table
then select Distortion.
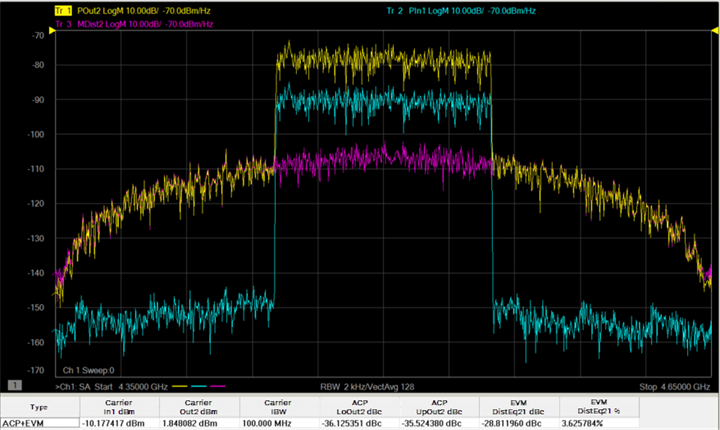
- The following
is an example showing input signal and output signal measuring ACPR
and EVM.
- Add/remove parametric values by right-clicking in the
distortion table at the bottom of the measurement area to access the
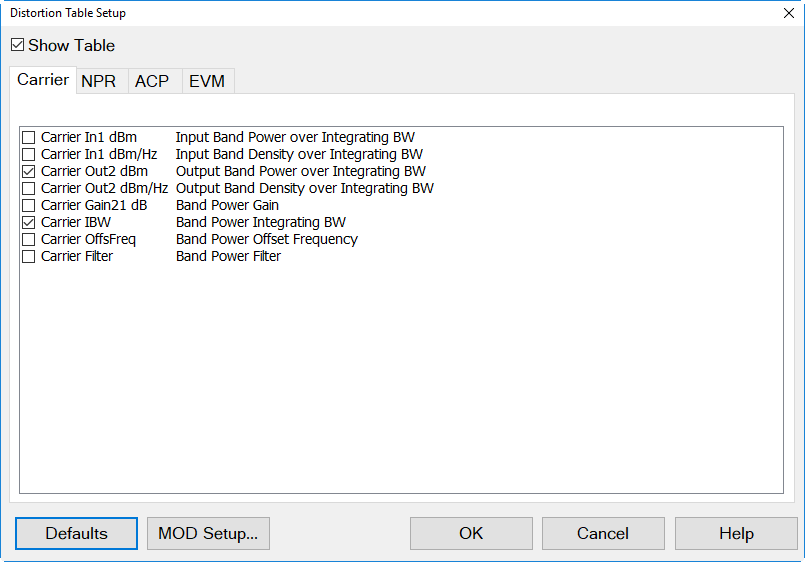
pop up menu then selecting Edit Columns....
- Make desired selections from the Distortion
Table Setup dialog.
Physical
Setup - Typical
The following diagram shows a typical
hardware setup using an N5182B MXG with the signal connected to the VNA
rear-panel Port 1 J10 input connector.
Note:
Though this example uses an N5182B MXG, an M8190A with E8267D PSG, or
an M9383A MCS can be used as the external source.
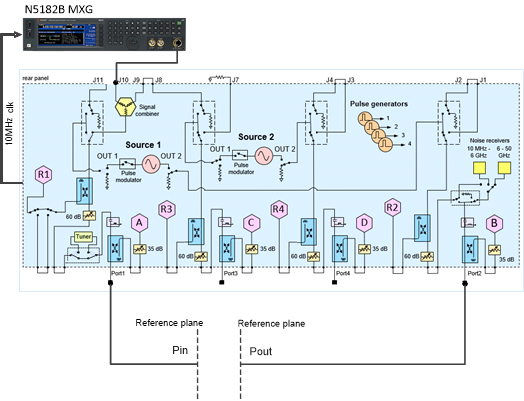
Key Parameters
Frequency: 4.5 GHz
BW Signal: 100 MHz
Pin Max: -10 dBm at reference plane
SA Span: 300 MHz
Physical
Setup - High Power
The following diagram shows a typical
high power hardware setup using an M8190A with E8267D PSG with the signal
connected to the VNA rear-panel Port 1 J10 input connector.
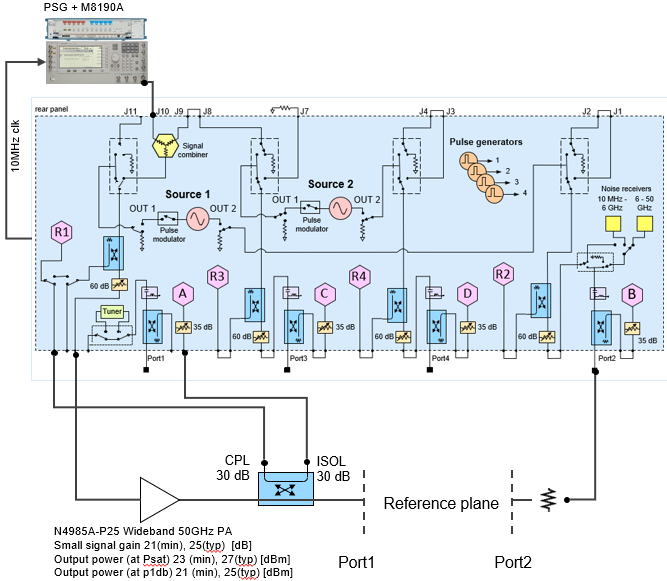
Key Parameters
Frequency: 28 GHz
BW Signal: 400 MHz
Pin Max: 10 dBm at reference plane
SA Span: 1.2 GHz
Physical
Setup - External
The following diagram shows a typical
external hardware setup using an M8190A with E8267D PSG with the signal
connected externally.
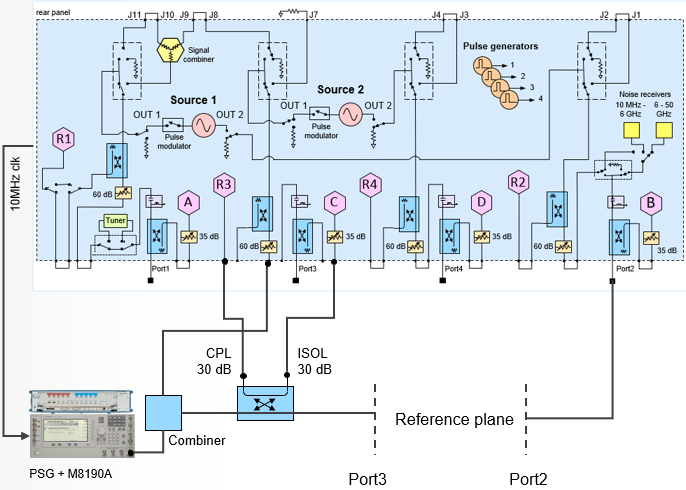
Key Parameters
Frequency: 28 GHz
BW Signal: 400 MHz
Pin Max: 0 dBm at reference plane
SA Span: 1.2 GHz
Physical
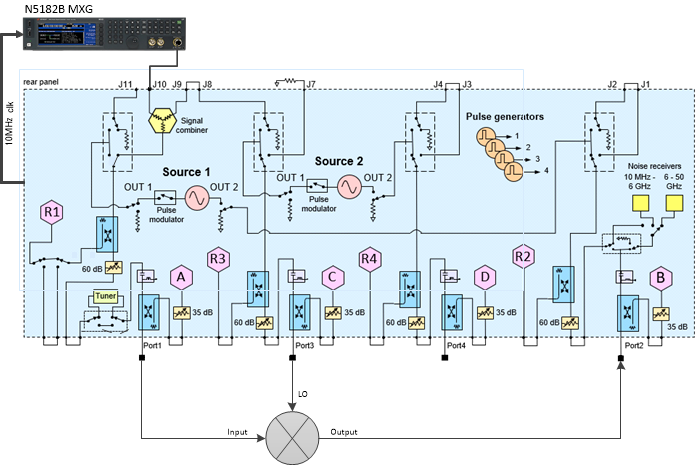
Setup - Converter
The following diagram shows a typical
hardware setup using an N5182B MXG with the signal connected to the VNA
rear panel Port 1 J10 input connector. Another method of connecting an
N5182B MXG is with the signal connected to the VNA rear panel Port 1 J9
and connecting J10 to J11. This allows switching between the MXG and Source
1 without a mechanical switch.
Key Parameters
The Key Parameters
are dependent upon the mixer setup and the measurement setup.
Carrier Frequency
Carrier Power
SA Center/Span
Noise BW
LO Frequency
LO Power
Measurement Type
Measurement Offset
Frequency
Measurement IBW




















