Physical Mode: Basic Uplink Setup
This example shows how to configure and download a basic uplink waveform
to the signal generator using the Physical as the frame setup mode.
Step
1: Select a Quick Setup
Step
2: Configure the Project Property Parameters
Step
3: Configure the Signal Generator Settings
Step
4: Configure the Uplink Frame Structure
Step
5: Generate and Download the Waveform
Step 1: Select a Quick
Setup
Click Quick
Setup in the tree view and then click the 802.16-2004
WiMAX button in the right pane to access the main window.
Notice that Project is highlighted
and the parameter view displays three panes:
Project Property, Projected Waveform, and Signal Generator Settings.
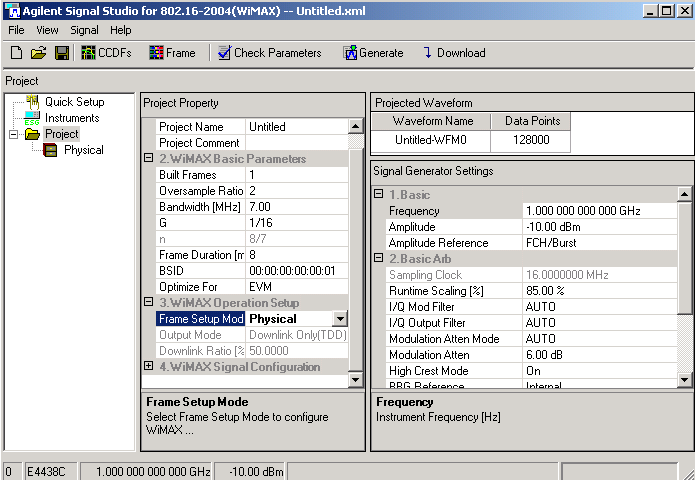
Step 2: Configure the
Project Property Parameters
In
the Project Setup table:
Change the default Project
Name (Untitled) to a unique name of eight characters or less. You
may also enter a Project Comment
to describe the waveform.
Use the WiMAX Basic Parameters
table to edit waveform generation parameters. Set up a waveform with the
following characteristics:
Select Physical
for the frame setup mode in the WiMAX Operation Set Up pane under Project
Property.
In the WiMAX Signal Configuration
table:
Leave
the default settings for MARKER1-4: Frame Start, None, Burst Envelope,
and ALC Hold, respectively.
|

|
These
markers are linked to the marker settings in the Basic Arb section of
Signal Generator Settings. Markers3-4 are used by the software to control
the RF blanking and ALC settings
for waveform playback, so they should not be modified. |
Observe the waveform's length
characteristics in the Projected Waveform pane. The Data
Points cell is calculated as follows: [Data Points] = [Sampling
Clock] * [Frame Duration] * [Built Frames].
Step 3: Configure the
Signal Generator Settings
Configure the signal generator's
frequency, amplitude, and arbitrary waveform playback parameters in the
Signal Generator Settings pane. Set Frequency
to 3.5 GHz and Amplitude to –10
dBm.
The signal generator amplitude setting refers
to the average power level of the FCH/Bursts, as indicated by Amplitude
Reference. The preamble power
level is defined in the standard to be 3 dB higher than the level of the
rest of the burst, so it will always be 3 dB higher than the amplitude
setting of the signal generator. If you create a waveform that only has
a preamble, select Preamble as the Amplitude Reference.
|

|
The Amplitude
Reference also determines the portion of the waveform that is used by
the signal generator for ALC leveling. In some cases, choosing the Amplitude
Reference to be the preamble instead of FCH/Burst may result in better
RCE (EVM) since, in some cases, the RCE
(EVM) of the signal can vary based on the data in the waveform. |
The sampling clock frequency
for the signal generator is automatically calculated as [Sampling Clock]
= floor(n * Bandwidth / 8000) * 8000* OSR.
This is the same as the “sampling frequency” defined in the IEEE 802.16-2004
standard.
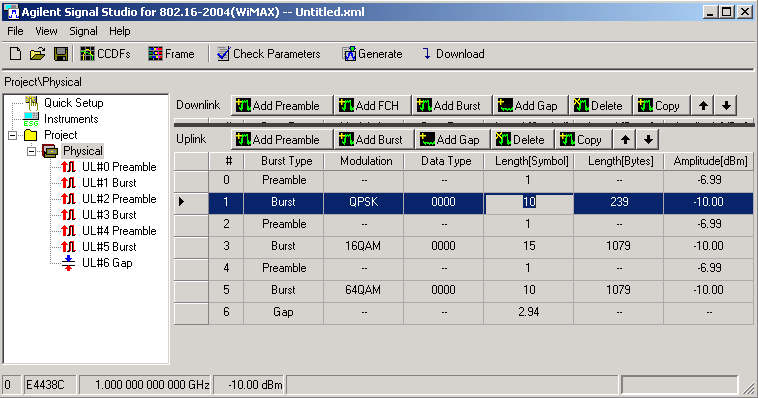
Step 4: Configure the
Uplink Frame Structure
Click Physical
in the tree view. The frame view displays the frame structure in the right
pane, with the downlink subframe on the top half and the uplink subframe
on the bottom half.
In the uplink subframe, click
Add Preamble followed by Add Burst three times to add three
uplink bursts from three different subscribers, each preceded by a preamble.
Click Add Gap to end the subframe
with a gap. The new frame components are added to the table and the tree
view. The gap (also referred to as the receive/transmit transition gap
or RTG) allows the base station time to change from receive to transmit
mode.
Click Frame in the tool bar to display a plot of the
frame layout with the new preambles and bursts. Clicking Frame again will
hide the plot.
Edit
the burst parameters. Double-click in the first column in the table for
the item, or click on the item in the tree view on the left. A window
appears that shows parameters specific to the selected burst type. Change
the parameters as follows:
For UL Burst #1, change the
OFDM Symbol Length to 10.
For UL Burst #3, change the
Modulation Type to 16QAM, Coding Rate to 3/4 and the OFDM
Symbol Length to 15.
For UL Burst #5, change the
Modulation Type to 64QAM, Coding Rate to 3/4 and the OFDM
Symbol Length to 10.
Click Physical
in the tree view to go back to a view of the overall
frame.
Click the Check
Parameters button in the tool bar to verify that the configured
bursts do not exceed the length of the defined frame. If the configuration
is valid, a result message "Parameters are fine" will be shown
in the status bar at the bottom of the window. If not, a message "Defined
frame exceeds the maximum frame length" appears.
Step 5: Generate and Download
the Waveform
From the tool bar, click Generate. The software generates an
I/Q waveform file in accordance with the current physical channel configuration
and waveform generation setup. Waveform generation time varies proportionally
with the complexity and length of the waveform. Messages showing the waveform
generation progress and status are displayed in the status bar.
From the tool bar, click CCDFs to toggle the graph view on and
off. The graph view enables you to examine waveform characteristics, such
as baseband spectrum, I and Q signals, and CCDF curves, prior to downloading
the file to the signal generator.
From the tool bar, click Download to generate and download the
waveform to the signal generator. The waveform file automatically begins
to play. You can re-enable local control of the signal generator by pressing
the Local hardkey, enabling you
to modify signal generator settings from the front panel. The waveform
file cannot be modified after downloading it to the signal generator.
However, the carrier frequency and amplitude can be changed.
You can use the 89601A software (version 5.3) with Option B7S (802.16
Modulation Analysis) to view the waveform on a signal analyzer such as
the E4406A (VSA) or others in the PSA family.
Related Topics
User
Interface Basics
Using
the MAC Editor
Frame
Plot View
Graph
View
Understanding CCDF Curves
Related Websites
IEEE 802-16-2004 standard
ESG product information
PSG product information
MXG product information
Agilent Signal Studio software