![]()
The software does not control any hardware
associated with the external conversion, nor does it control the external
LO frequency or amplitude.
The N7621 Signal Studio for multitone distortion software supports the use of an external mixer for signal frequency upconversion or downconversion. The software can be configured to use the products of the mixer's sum or difference.
|
|
The software does not control any hardware
associated with the external conversion, nor does it control the external
LO frequency or amplitude. |
When correctly configured, the N7621 software Frequency and Amplitude
values refer to the frequency and amplitude at the 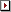 output of
the external conversion.
Three parameters are provided for external conversion: Frequency Offset, Amplitude
Offset, and Mirror
Spectrum.
output of
the external conversion.
Three parameters are provided for external conversion: Frequency Offset, Amplitude
Offset, and Mirror
Spectrum.
The Frequency Offset value is used by the N7621 software to correctly set the spectrum analyzer frequency during correction measurements. It also allows you to work using the final output frequency value.
The Amplitude Offset parameter is used by the N7621 software to account for external gain or loss. The correction measurement expects to find the output signal within a 10 dB amplitude window. If additional gain or loss is experienced during the conversion enter the actual value in the amplitude offset parameter.
The Mirror Spectrum parameter is used to mirror the frequency spectrum. It is only required when using the mixer difference products to achieve the desired output frequency.
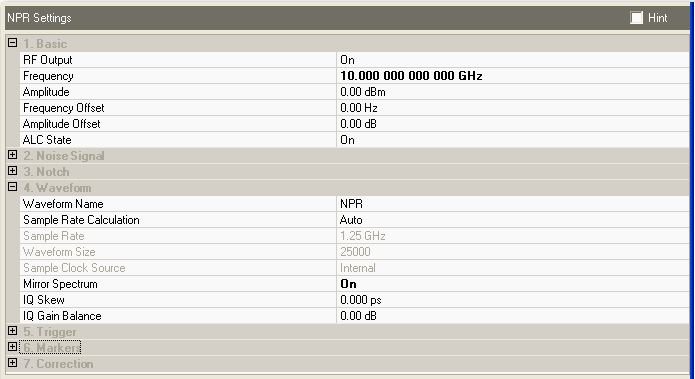
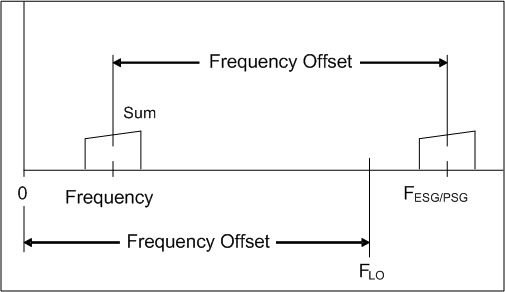
Using the mixer sum products to upconvert the signal frequency is illustrated in the following two figures. A benefit to using the sum products is, that once the Frequency Offset is set in the N7621 software, the Frequency value reflects the actual output frequency after the conversion. A change to the software frequency value results in a one to one change in the actual output frequency. However, this is not the case when using the mixer difference products.
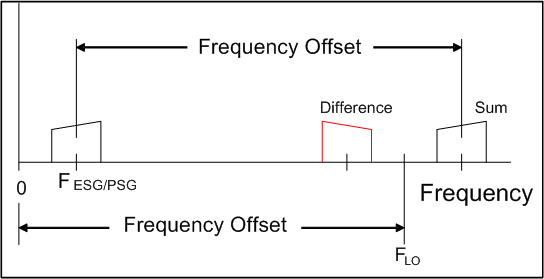
The Frequency Offset is equal to the LO Frequency when using the mixer sum products for upconversion.
Example values for upconversion using the mixer sum products, where:
Frequency = N7621 Frequency value, and the actual frequency after conversion
Frequency Offset = N7621 Frequency Offset value; also entered into the ESG/PSG
FESG/PSG = Actual frequency produced by the ESG/PSG
FLO
FESG/PSGDisplay = Frequency displayed on the ESG/PSG front panel
|
Frequency |
Frequency Offset |
FLO |
FESG/PSG |
FESG/PSGDisplay |
|
17 GHz |
15 GHz |
15 GHz |
2 GHz |
17 GHz |
|
18 GHz |
15 GHz |
15 GHz |
3 GHz |
18 GHz |
|
32 GHz |
20 GHz |
20 GHz |
12 GHz |
32 GHz |
|
33 GHz |
20 GHz |
20 GHz |
13 GHz |
33 GHz |
|
3 GHz |
–10 GHz |
10 GHz |
13 GHz |
3 GHz |
|
2 GHz |
–10 GHz |
10 GHz |
12 GHz |
2 GHz |
|
1.5 GHz |
–10 GHz |
10 GHz |
11.5 GHz |
1.5 GHz |
Using the mixer sum products to downconvert the signal frequency is illustrated in the following figure.
|
|
The LO frequency must be less than the actual frequency from the ESG/SPG signal generator. |
As you may recall, once the Frequency Offset is set in the N7621 software, the Frequency value reflects the actual output frequency after the conversion. A change to the software frequency value results in a one to one change in the actual output frequency.
The Frequency Offset is equal to minus the LO frequency when using the mixer sum products for down conversion.
Frequency Offset = –FLO.
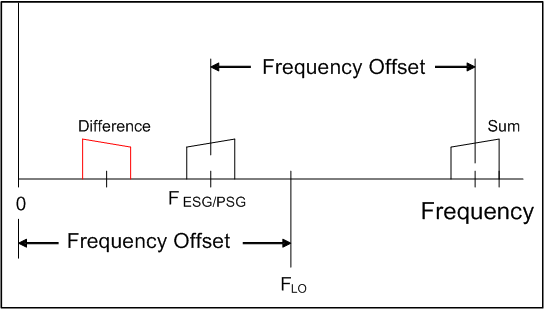
The N7621 software supports upconversion and downconversion with the products of the mixer's difference. However, the Frequency Offset value must be recalculated each time the frequency is changed.
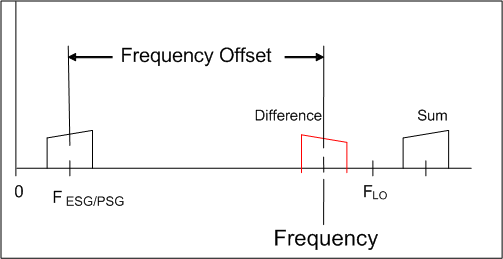
Upconversion requires that the LO frequency be greater than twice the signal generator frequency.
|
|
The spectrum is not the same as the ESG/PSG.
Set |
The Frequency Offset value is:
Frequency Offset = FLO – 2*FESG/PSG
Example values for upconversion using the mixer difference products, where:
Frequency = N7621 Frequency value, and the actual frequency after conversion
Frequency Offset = N7621 Frequency Offset value; also entered into the ESG/PSG
FESG/PSG = Actual frequency produced by the ESG/PSG
FLO
FESG/PSGDisplay = Frequency displayed on the ESG/PSG front panel
|
Frequency |
Frequency Offset |
FLO |
FESG/PSG |
FESG/PSGDisplay |
|
18 GHz |
16 GHz |
20 GHz |
2 GHz |
18 GHz |
|
17 GHz |
14 GHz |
20 GHz |
3 GHz |
17 GHz |
|
16 GHz |
12 GHz |
20 GHz |
4 GHz |
16 GHz |
Downconversion using the mixer difference
products is shown in the following figure. The LO frequency must be between
the actual ESG/PSG frequency and twice the ESG/PSG frequency for this
condition to occur.  Mirror Spectrum
must be enabled and the frequency offset must be recalculated each time
the frequency is changed.
Mirror Spectrum
must be enabled and the frequency offset must be recalculated each time
the frequency is changed.
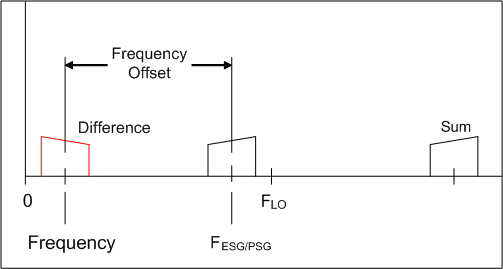
Here the Frequency Offset calculation is the same as for the low-side upconversion, except that the result will be a negative number.
Frequency Offset = FLO – 2*FESG/PSG
Example values for downconversion using the mixer difference products, where:
Frequency = N7621 Frequency value, and the actual frequency after conversion
Frequency Offset = N7621 Frequency Offset value; also entered into the ESG/PSG
FESG/PSG = Actual frequency produced by the ESG/PSG
FLO
FESG/PSGDisplay = Frequency displayed on the ESG/PSG front panel
|
Frequency |
Frequency Offset |
FLO |
FESG/PSG |
FESG/PSGDisplay |
|
2 GHz |
–6 GHz |
10 GHz |
8 GHz |
2 GHz |
|
2.5 GHz |
–5 GHz |
10 GHz |
7.5 GHz |
2.5 GHz |
|
3 GHz |
–4 GHz |
10 GHz |
7 GHz |
3 GHz |