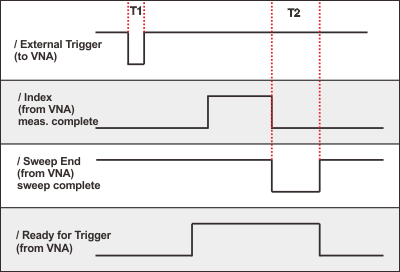
All signals are active low.
T1 = 1 ms External Trigger pulse width
T2 > 10ms Sweep End pulse width (both High and Low)
This rectangular 36-pin female connector provides communication signals between the VNA and a handler. You can change the settings on the Handler IO connector using SCPI commands. The settings are NOT accessible through the front-panel keys or display menu.
Note: On early VNAs this connector is labeled "GPIO". It is covered to indicate that the connector is not functional.
Overview - Controlling a Handler I/O
The VNA is capable of interacting with an external handler. This allows the VNA to be used in an automated test environment, where devices to be tested are inserted into a test fixture by a part handler, and sorted into pass/fail bins by the handler after testing is complete. By connecting the part handler to the VNA Handler I/O ports, the VNA and part handler can synchronize their activities in a way that makes automated testing possible.
Define the measurements that you want to make.
Define limits for each of the measurements.
Configure the VNAs Material Handler port so that it is compatible with your part handler. This usually involves setting the handler logic, pass/fail logic, pass/fail scope, and pass/fail mode. These settings are made remotely using SCPI commands.
Use a cable to connect the VNA to your part handler.
Put the VNA in External Trigger mode.
Load parts in handler per manufacturer instructions.
Text Descriptions
(Optional). The VNA sends values out the Material Handler to configure external instruments. The A,B,C, and D ports of the Material Handler can be used to control devices used in testing, such as step attenuators, part handlers, or even the DUT itself. Also, the DAC1 and DAC2 lines on the Power I/O connector can be used to provide bias voltages for devices and instruments. If you wish to use the Material Handler for testing, you will need to write a program to send values out the various lines and ports, as there is no activity on these lines by default.
The part handler receives a Ready for Trigger signal from the VNA. This indicates that the VNA is properly configured and ready to take a measurement.
The part handler sends an External Trigger signal to the VNA. This signals that the part handler has settled, and allows the VNA to begin taking measurements.
The VNA takes measurements on all triggerable channels.
The Index line on the material handler goes to a Low state, which means that all required data has been collected by the VNA.
The part handler removes the DUT from the test fixture, and inserts a new DUT into the fixture. This operation is often referred to as part handler indexing. The device just tested is staged (removed from the fixture and prepared for binning), and the next part to be tested is put into the fixture. The removed DUT cannot be assigned to a Pass/Fail bin yet, as the Pass/Fail status is not available.
The VNA sends the Pass/Fail Status.
The VNA sends the Pass/Fail Strobe meaning that the Pass/Fail status has been determined.
The part handler reads the Pass/Fail Status line.
The part handler bins the staged part based on the Pass/Fail Status.
The test process repeats at step 1, waiting for Ready for Trigger from the VNA.
A slash (/) symbol preceding signal names means that they are negative logic (active low).
Pin number |
Signal name |
Input/Output |
Description |
1 |
GND |
N/A |
Ground. |
2 |
/INPUT1 |
Input |
When this port receives a negative pulse, /OUTPUT1 and /OUTPUT2 are changed to the Low level. |
3 |
/OUTPUT1 |
Output |
Changes to the Low level when /INPUT1 receives a negative pulse. A command can be available for altering the Low/High level logic. |
4 |
/OUTPUT2 |
Output |
Changes to the Low level when /INPUT1 receives a negative pulse.A command can be available for altering the Low/High level logic. |
5 |
/PORT A0 |
Output |
Bit 0 of port A (8 bit parallel output port) |
6 |
/PORT A1 |
Output |
Bit 1 of port A. |
7 |
/PORT A2 |
Output |
Bit 2 of port A. |
8 |
/PORT A3 |
Output |
Bit 3 of port A. |
9 |
/PORT A4 |
Output |
Bit 4 of port A. |
10 |
/PORT A5 |
Output |
Bit 5 of port A. |
11 |
/PORT A6 |
Output |
Bit 6 of port A. |
12 |
/PORT A7 |
Output |
Bit 7 of port A. |
13 |
/PORT B0 |
Output |
Bit 0 of port B (8 bit parallel output port) |
14 |
/PORT B1 |
Output |
Bit 1 of port B. |
15 |
/PORT B2 |
Output |
Bit 2 of port B. |
16 |
/PORT B3 |
Output |
Bit 3 of port B. |
17 |
/PORT B4 |
Output |
Bit 4 of port B. |
18 |
/EXTERNAL TRIGGER |
Input |
An external trigger signal. When the trigger source is set to the "External," this port generates a trigger in respond to the trailing edge of a negative pulse. |
19 |
/PORT B5 |
Output |
Bit 5 of port B. |
/PORT B6 |
Output |
Bit 6 of port B. |
|
/INDEX |
Indicates that analog measurement is complete. The /INDEX signal changes to the Low level when analog measurement (all sweeps of all channels) is complete. When the handler receives the signal, it assumes that it is ready to connect the next DUT. However, no measurement data are available until data calculation is completed. When the point trigger function is on, it goes to the High level before staring measurement of the first measurement point and returns to the Low level after completing measurement of all measurement points. |
||
/PORT B7 |
Output |
Bit 7 of port B. |
|
/READY FOR TRIGGER |
Indicates that the instrument is ready for triggering.This signal is changed to the Low level when the instrument is ready for receiving a trigger signal. With the point trigger function on, it goes to the Low level when the instrument is ready to accept the trigger signal for the first point and goes to the High level when the trigger signal for the first point is received. When measurement of all measurement points is completed and the instrument is ready to receive the trigger signal for the first point of the next sweep, this signal goes to the Low level again. |
||
22 |
/PORT C0 |
Input/Output |
Bit 0 of port C (4 bit parallel I/O port) |
23 |
/PORT C1 |
Input/Output |
Bit 1 of port C. |
24 |
/PORT C2 |
Input/Output |
Bit 2 of port C. |
25 |
/PORT C3 |
Input/Output |
Bit 3 of port C. |
26 |
/PORT D0 |
Input/Output |
Bit 0 of port D (4 bit parallel I/O port) |
27 |
/PORT D1 |
Input/Output |
Bit 1 of port D. |
28 |
/PORT D2 |
Input/Output |
Bit 2 of port D. |
29 |
/PORT D3 |
Input/Output |
Bit 3 of port D. |
30 |
PORT C STATUS |
Output
|
Port C status signal.This signal is changed to the High level when the port C is configured to output port. It is changed to the Low level when the port is configured to input port. |
31 |
PORT D STATUS |
Output |
Port D status signal. This signal is changed to the High level when the port D is configured to output port. It is changed to the Low level when the port is configured to input port. |
32 |
/WRITE STROBE |
Output |
A output port write strobe signal. When data is present (that is, output level changes) on any of the output ports, this signal provides a negative pulse. |
33 |
/PASS FAIL |
Output
|
Each limit test's results signal. This signal changes to the High level when limit test, bandwidth test, or ripple test results return FAIL. It changes to the Low level when all limit test results return PASS. |
34 |
/SWEEP END |
Output
|
A sweep completion signal. When measurement (all sweeps of all channels) and data calculation are completed, this signal provides a negative pulse. |
35 |
+5V |
Output |
Provides +5V DC power supply for external instruments. |
36 |
/PASS FAIL STROBE |
Output |
Each limit test's results write a strobe signal. When limit test result is present on /PASS FAIL, this signal provides a negative pulse. |
Input1When this Input line receives a Low pulse from the material handler, data is latched on the OUTPUT1 and OUTPUT2 lines. See OUTPUT1|2 Data Output Write Timing |
|
The Input Line activity can be read: |
|
SCPI |
COM |
get_Input1 Method
|
|
Output1, Output2See OUTPUT1|2 Data Output Write Timing The current state of these latched TTL outputs may be set High or Low (Default setting) using the (non-user) SCPI put_Output (COM) commands. The next state (following a negative edge on the INPUT1 line) may be pre-loaded to High or Low (Default setting) using the user commands. For example, on the next negative pulse on the INPUT1 line, you want the OUTPUT1 line to go from 0 to 1. To do this: CONT:HAND:OUTP1:DATA
0 'Force the OUTPUT1 line
to 0 |
||
|
SCPI |
COM |
Write User Data |
put_Output Method |
|
Read last value written |
get_Output Method. |
|
Write non-user data |
put_Output Method |
|
Read last value written |
get_Output Method
|
|
Output Ports A and BThese two general purpose, 8-bit output ports are used to write data to the material handler. When any line changes state, all output lines are latched to the I/O connector as the Output Write Strobe goes Low. The default state for data is Low. |
|
Set Port Logic: The logic for the data lines can be set to either: Positive (1 = High) or Negative (1 = Low). This setting affects all data ports. They cannot be set independently. |
|
SCPI |
COM |
PortLogic Property
|
|
Combine to read or write data to Port F: Ports A and B can be virtually combined to write data to one 16-bit I/O port F. |
|
SCPI |
COM |
put Port (F)
|
|
Input/Output Ports C and DThese two general purpose 4-bit Input/Output ports are used to write data (Output) or read data (Input). These lines could be used to write to an external device such as a step attenuator. When any line changes state, all output lines are latched to the I/O connector as the Output Write Strobe goes Low. See Data Output Write Timing.
|
|
Set Input | Output Mode: Each port may be independently defined as Output or Input. |
|
SCPI |
COM |
PortMode Property |
|
|
|
|
Set Port Logic: The logic for the data lines can be set to either: Positive (1 = High) or Negative (1 = Low). This setting affects all data ports. They cannot be set independently. |
|
SCPI |
COM |
PortLogic Property
|
|
Read or write data: Ports C and D can be virtually combined to read or write data to one 8-bit I/O port E. When combined, both C and D ports must be set to either INPUT or OUTPUT mode. |
|
SCPI |
COM |
get_Port(x) put Port (x) |
|
Port C Status, Port D StatusThese two output lines indicate the Read / Write mode of the C and D ports.
These logic of these status outputs cannot be changed. See Input/Output Ports C and D to learn how to set I/O Mode
|
Output Port Write StrobeThis Output line goes Low to write data from Ports A and B and Ports C and D when a change is detected on any of the data lines. These logic of this strobe output cannot be changed.
|
External TriggerWhen trigger source is set to external, this Input line accepts a trigger signal from the material handler. This usually means that a part is in place and ready to be tested.
|
IndexA Low signal on this Output line indicates to the material handler that the measurement is complete. This usually means that the handler can connect the next device. However, measurement data is not available until data is calculated. See Trigger Timing Diagram. |
|
Set Function: This line also serves as a data line. Set the function using the following commands: |
|
SCPI |
COM |
IndexState
|
|
Pass/Fail StateThis Output line indicates to the handler whether the limit test has passed or failed. Pass/Fail state is valid only when the limit test function is ON and while Pass/Fail strobe line is Low. See Pass/Fail Timing Diagram |
|
Set Pass / Fail Logic:
|
|
SCPI |
COM |
PassFailLogic Property
|
|
Set Default Conditions:
|
|
SCPI |
COM |
PassFailMode Property
|
|
Set Pass/Fail Scope:
|
|
SCPI |
COM |
PassFailScope Property
|
|
Pass/Fail Write StrobeA Low pulse indicates that Pass/Fail line is valid and the Pass / Fail State is output to the material handler. The Pass/Fail Strobe is fixed in duration and timing. However, when the strobe occurs depends on the Pass/Fail Mode and Pass/Fail Scope (Channel or Global) settings. See Pass/Fail State
|
+5V+5V nominal output (100mA max). Protected by self-healing fuse. |
|
All signals are active low. T1 = 1 ms External Trigger pulse width T2 > 10ms Sweep End pulse width (both High and Low) |
|
T1 = 1 ms Pulse width and response time of Pass / Fail Strobe T2 > 10 ms Ready for Trigger lag |
|
T1 = 1 ms Write Strobe response time T2 = 1 ms Write Strobe pulse width |
|
The old state to new state transition can be either low to high (as shown) or high to low. T1 = .6 ms Output1|2 response time T2 = 1 ms Input1 Strobe pulse width |
All Material Handler I/O Input and Output lines are TTL compatible.
Lines carrying information IN (or bidirectional) to the VNA from the material handler.
Maximum Input Voltages: |
-0.5 V to 5.5 V |
TTL High level: |
2.0 V to 5.0 V |
TTL Low level: |
0 V to 0.5 V |
VNA Input and Input/Output Circuit Diagram
|
To Handler I/O Port |
Note: The INPUT1 line does NOT have the 10K pull up resistor.
Lines carrying information OUT of the VNA to the material handler.
Maximum Output Current: |
-10 mA to 10 mA |
|
Output Current |
TTL High level: |
-5 mA |
TTL Low level: |
3 mA |
|
Output Voltage |
TTL High level: |
2.0 V to 3.3 V |
TTL Low level: |
0 V to 0.8 V |
|
VNA Output Circuit Diagram
|
To Handler I/O Port |
Last modified:
28-Nov-2025 |
First Release |
![]()