Name
Unit
Description
Rise Time
Second
Rise Time Def=10%-90%: Time at 90% level - Time at 10% level
Rise Time Def=20%-80%: Time at 80% level - Time at 20% level
Fall Time
Second
Rise Time Def=10%-90%: Time at 90% level - Time at 10% level
Rise Time Def=20%-80%: Time at 80% level - Time at 20% level
Jitter RMS
Second
1σ width of the histogram at the eye crossing point
Jitter p-p
Second
Full width of histogram at the eye crossing point
Crossing Percentage
%
Crossing Height / Amplitude × 100
Opening Factor
None
(Level One - σ one) - (Level Zero + σ zero) / Amplitude
Signal/Noise Ratio
None
(Level One - Level Zero)/( σ one+ σ zero)
Duty Cycle Distortion
Second
|T rise middle - T fall middle|
Duty Cycle Distortion (%)
%
Duty Cycle Distortion (s)/ Bit period × 100
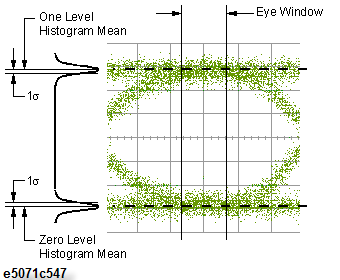
Level Zero
Voltage
Histogram mean for level zero
Level One
Voltage
Histogram mean for level one
Level Mean
Voltage
(Level Zero + Level One) / 2
Amplitude
Voltage
Level One - Level Zero
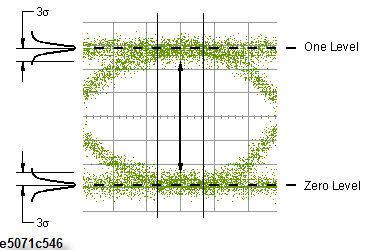
Height
Voltage
(Level One - 3 σ one) - (Level Zero + 3 σ zero)
Width
Second
Bit Period - 2 × 3 × Jitter RMS
-
Bit Period = 1/Bit Rate
-
Input Amplitude = Setting of Level One - Setting of Level Zero
-
T rise middle = The time at which the rising edge cross the middle threshold (50%)
-
T fall middle = The time at which the falling edge cross the middle threshold (50%)