Receiver Calibration
Other topics about Advanced Calibration
The E5072A has a function to calibrate the gain of the individual receivers in absolute value measurement.
The receiver calibration function calibrates the gain of the receiver by inputting the output power of a stimulus port that has been assigned a correct value by the power calibration to the port of the receiver you need to calibrate.
The receiver calibration data are acquired for each channel/test port, so the gain error correction can be turned ON/OFF independently for any channel or port.
The status of the gain error correction for each channel is indicated by one of the symbols in the channel status bar in the lower part of the window, as shown in the following table.
|
|
|
|
RC (displayed in blue)
|
Error correction is performed for all of the receiver ports.
|
|
RC (displayed in grey)
|
Error correction is performed for some of the receiver ports.
|
|
RC? (displayed in blue)
|
Error correction is performed for all of the receiver ports. Interpolated calibration data is used.
|
|
RC? (displayed in grey)
|
Error correction is performed for some of the receiver ports. Interpolated calibration data is used.
|
|
RC! (displayed in blue)
|
Error correction is performed for all of the receiver ports. Extrapolated calibration data is used.
|
|
RC! (displayed in grey)
|
Error correction is performed for some of the receiver ports. Extrapolated calibration data is used.
|
|
--- (displayed in gray)
|
Error correction is not performed.
(At least one receiver port is turned on for error correction, but valid calibration data are not available.)
|
|
None
|
Error correction is not performed.
(Error correction is turned off for all of the receiver ports.)
|
Turning receiver error correction ON/OFF
The error correction of the receiver is automatically turned ON when the calibration data is measured. You can also turn this ON/OFF explicitly by following the steps below.
-
Press Cal .
-
Click Receiver Calibration, then select a port.
-
Click Correction to toggle Each time the key is pressed, ON and OFF switches over alternately.
-
The power calibration information on both the receiver port and source port is used to calculate calibration coefficients. The accuracy of receiver calibration will increase if power calibration is implemented for both the receiver port and the source port before starting receiver calibration. For information on power calibration, refer to Power Calibration.
- Press Cal.
-
Click Receiver Calibration.
-
Click Source Port, then select the stimulus port for which you want to perform power calibration.
-
Connect the selected stimulus port by cable to the port you want to calibrate.
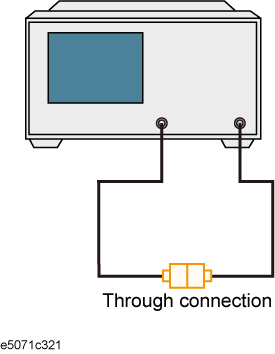
-
Click Receiver Calibration > Power Offset, then enter the offset value.
Receiver calibration is done at the condition of (source power)+(Specified offset).
For example, if the source Power is -10 dBm (Sweep Setup > Power > -10 dBm), then:
-
If specified offset is 0 dB, then Source Power Reading after calibration would be -10 dBm.
-
If specified offset is 10 dB, then Source Power Reading after calibration would be 0 dBm.
-
If specified offset is -10 dB, then Source Power Reading after calibration would be -20 dBm.
-
The offset value is independent for each channel.
-
Click Receiver Calibration > Calibrate to start the measurement of calibration data. This step allows the gain of the receiver to be calibrated, turning ON the error correction function automatically.
Just as in Power Calibration, you can set the power offset for receiver calibration as well. See Power Calibration: Setting Power Offset for Source. Receiver power calibration allows you to make very accurate absolute power (amplitude) measurements. It mathematically removes frequency response errors in the specified receiver and adjusts readings to the same or a value offset from the source power calibration level.
Power offset for receiver allows you to specify a gain or loss (in dB) to account for components you connect between the source and reference plane of the measurement. This should be set prior to receiver calibration.
To set the receiver power offset, follow the steps below:
-
Press Cal.
-
Click Receiver Calibration > Power Offset, then set the power offset value.
