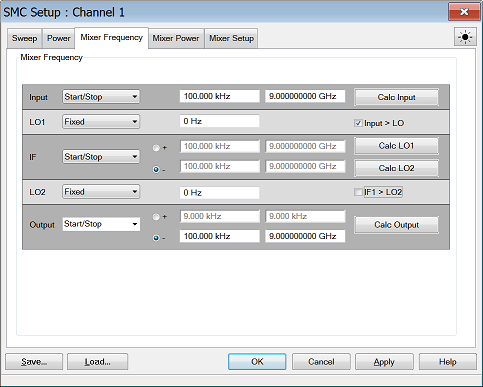
Settings
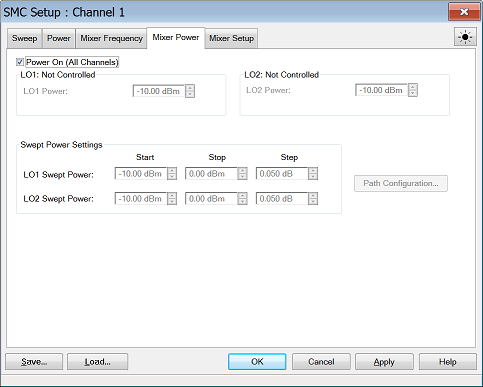
Frequency Format Select Start/Stop (Swept) or Fixed. For Linear sweep type, at least one of these must be fixed. For CW or Power, ALL must be Fixed.
Frequencies Enter the frequency values for each of the Mixer/Converter ports.
|
|
Mixer-Product Selector Determines whether the receivers will tune to the Sum (+) or the Difference ( - ) of the Input and LO frequencies. |
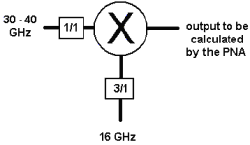
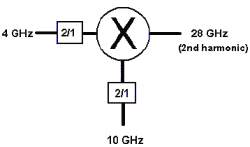
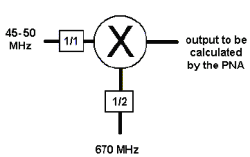
Calc buttons Calculates frequency settings based on your other mixer settings. For example, enter the Input frequency range and LO1 frequency range, then press Calc Output. The VNA will calculate and display the Output frequencies.
Input > LO or IF1>LO2 Removes ambiguity when using a Calc button to determine the INPUT frequency.
These check boxes are used ONLY when all 3 of the following conditions are TRUE:
(If ALL 3 are NOT true, the VNA does not read these check boxes).
-
Difference (Low) sideband
 is selected for the corresponding Calculate button AND
is selected for the corresponding Calculate button AND -
Output frequency is less than the LO frequency AND
-
One of the Calculate buttons are used to calculate the Input frequency.
Rules for Configuring a Mixer
A Red message across the bottom of the dialog indicates that one or more of the following settings are invalid:
-
Either ALL ranges (Input, LO, Output) must be Fixed, or ONE Range fixed. TWO ranges can NOT be Fixed or THREE ranges can NOT be Swept.
-
For determining a valid mixer configuration with 2 LOs, one Fixed LO and one Swept is equivalent to having a single-stage Swept LO. To configure a 2-stage LO, select Converter Stages: 2 on the Mixer Setup tab.
-
INPUT or OUTPUT frequencies cannot be outside the range of the VNA.
-
Any combination of INPUT and LO which results in an OUTPUT that sweeps through Zero Hz is NOT allowed.
About Mixer Configuration Files (.mxr and *.mxrx)Save Saves SOME of the mixer settings to a *.mxr or *.mxrx file. Load Recalls a previously-configured mixer *.mxr or *.mxrx file .
What Mixer Settings are Saved?
Converter App Compatibility The mixer setup files that are used with FCA, NFx, and GCx for PNA ARE compatible. However, *.mxr(x) files created in IMDx contain information that is NOT included with other *.mxr(x) files. External Sources A *.mxr(x) file includes an LO source name. However, It does NOT include the LO Source configuration. |
Apply Applies the settings for your mixer/converter test setup to the measurement. The mixer setup dialog box remains OPEN.
OK Applies the settings for your mixer/converter test setup to the measurement. The mixer setup dialog box CLOSES.
Cancel Closes the mixer setup dialog box and does NOT apply the settings.