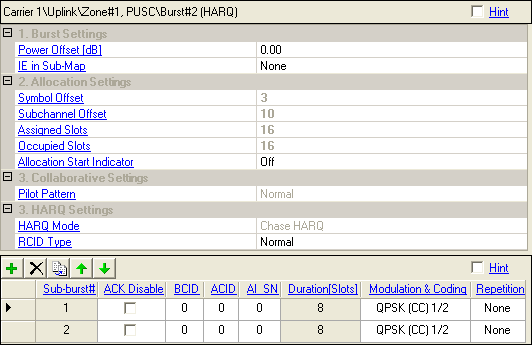
HARQ (Hybrid ARQ), a fast retransmission scheme, uses Chase Combining (CC) or Incremental Redundancy (IR) for transmitting the coded data packets.

Range: –40.00 to +9.00 dB
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the desired power offset of the HARQ burst in dB.
Choices: None, Sub-DL-UL-MAP #1, Sub-DL-UL-MAP #2, Sub-DL-UL-MAP #3
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to specify which Sub-DL-UL MAP the HARQ MAP IE will be placed. None represents that the HARQ MAP IE is placed into the normal or compressed MAP message.
To assign the HARQ MAP IE to the specific Sub-DL-UL MAP, the status of the corresponding Sub-DL-UL MAP must be on.
UL-MAP-IEs defined in one SUB-DL-UL-MAP must be consecutive ones by allocation order in a given uplink zone.
When Auto Allocation is on in the zone editing window, an algorithm configures the bursts automatically based on the number of occupied slots and maximum number of subchannels available in the zone, avoiding any burst overlap where possible. If Auto Allocation is off, you can manually position and allocate the data region by editing the number of symbols, subchannels, and their respective offsets.
You can view the automatic or manual  burst allocation
configurations in the zone
plot view. Any bursts that overlap, exceed the number of assigned
slots, or are too small are shown in red. Click Status
Windowin the tool bar for suggestions to resolve any conflicts.
burst allocation
configurations in the zone
plot view. Any bursts that overlap, exceed the number of assigned
slots, or are too small are shown in red. Click Status
Windowin the tool bar for suggestions to resolve any conflicts.
If Auto Allocation is off in the zone editing window, use this cell to manually position the burst on the horizontal axis (x), if necessary, to avoid any burst overlap.
If Auto Allocation is off in the zone editing window, use this cell to manually position the burst on the vertical axis (y), if necessary, to avoid any burst overlap.
Displays the total available  slots
in this burst. If Auto Allocation is off, you can edit this cell to manually
set the assigned slots.
slots
in this burst. If Auto Allocation is off, you can edit this cell to manually
set the assigned slots.
If Auto Allocation is off in the zone editing
window, use this cell to manually set the number of  slots
needed for the burst based on the total length in bytes of all MAC PDUs.
It also depends on the rate ID and coding type selected for each burst.
slots
needed for the burst based on the total length in bytes of all MAC PDUs.
It also depends on the rate ID and coding type selected for each burst.
Choices: On, Off
Select the state of Allocation Start Indicator that indicates start symbol index and start subchannel index will be included in the HARQ UL MAP IE.
When Channel State is Off, if a uplink PUSC zone has collaborative bursts, all its bursts must be collaborative bursts. The combination of the collaborative bursts and other bursts is not supported.
Choices: Normal, Pattern A, Pattern B
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the pilot pattern.
- For non-collaborative burst, it’s always set to Normal.
& - For collaborative burst pair, if the first subscriber (subscriber0, corresponding to the master instrument) of the burst will be with pilot pattern A, the second subscriber (subscriber1, corresponding to the slave instrument) of the burst will be with pilot pattern B.
Displays the HARQ mode as the Chase HARQ.
The Chase HARQ scheme enables BS and SS to enhance performance of HARQ enabled connection by means of chase combining scheme. This scheme is supported for all coding schemes. Each burst is appended with a CRC that is checked by the receiver. An uplink and a downlink ACK channels are defined (see 8.4.5.4.13 and 8.4.5.4.24). The receiver replies with an ACK in the corresponding ACK channel if the decoding succeeded and with a NACK if the decoding failed.
If the burst was not ACK-ed, the transmitter may transmit a burst with exactly the same data contents again. The receiver may combine the newly received burst with the formerly received burst(s) to enhance decoding performance.
Choices: Normal, RCID 11, RCID 7, RCID 3
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the Reduced CID type used in constructing HARQ DL MAP IE. BS may use RCID instead of basic CID or multicast CID to reduce the size of HARQ MAP message. The RCID type is determined by BS considering the range of basic CIDs of MS connected with the BS and specified by the RCID_Type field of the Format Configuration IE.
Use the button  to add a new HARQ sub-burst. When a sub-burst is added, the software displays
the sub-burst in the tree view and adds it to the frame plot view.
to add a new HARQ sub-burst. When a sub-burst is added, the software displays
the sub-burst in the tree view and adds it to the frame plot view.
Use the button  to delete the selected sub-burst. The burst to be deleted is indicated
by the
to delete the selected sub-burst. The burst to be deleted is indicated
by the  in the first column.
in the first column.
Use the button  to add a new sub-burst that has the same configuration as the currently
selected one (indicated by the
to add a new sub-burst that has the same configuration as the currently
selected one (indicated by the  in the first column).
in the first column).
Use the and
arrows  to reposition the currently selected sub-burst (indicated by
the
to reposition the currently selected sub-burst (indicated by
the  in the first column).
in the first column).
Displays the HARQ Sub-burst index number.
There should be at least one sub-burst defined in an HARQ burst. If not, an error message will be displayed on the status bar.
Choices: On, Off
Select the ACK Disable status that indicates whether the allocated sub-burst requires an ACK to be transmitted by subscriber station. See also ACK Disable.
Range: 0 to 65535
Enter the Basic Connection ID that indicates a specific subscriber station where the HARQ DL MAP IE are described for. See also Basic CID.
Range: 0 to 15
Enter the ARQ Channel ID that indicates a specific HARQ transmission between a base station and subscriber station. See also ACID.
Range: 0 to 1
Enter the AI_SN (ARQ Identifier Sequence Number) value of a specific HARQ transmission. See also AI_SN
Displays how many slots are needed for the HARQ sub-burst based on the total length of sub-burst after CRC calculation. See also Duration [Slots].
Use the pull down menu to select a modulation and coding type. See also Modulation and Coding.
Choices: None, 2, 4, 6
Use the pull-down menu to select the number of times the data is repeated. See also Repetition Coding.