
Use this cell to set the MCS (Modulation and Coding Scheme) index, which determines the number of spatial streams, the modulation, and the coding rate and data rate values. The MCS index is from 0 to 32 for the HT (High Throughput) mode and is described in the MCS table.
The MCS index will automatically set the number of spatial streams.
In Legacy mode, the modulation is automatically determined by the data rate.
In HT mode, the modulation is automatically determined by the MCS index.
In Legacy mode, the coding rate is automatically determined by the data rate.
In HT mode, the coding rate is automatically determined by the MCS index.
In Legacy mode, use this cell to select the data rate. The data rate selected will automatically set the modulation and encoder rate (equal to 802.11a/g standard).
In HT mode, the data rate is determined by the MCS index.
Use this cell to set the number of transmit chains (NTX) for HT mode.
For transmitter test (the channel fading state is set to OFF):
In MxN (1 SG) MIMO system, the number of transmit chains is the value of M and must be not less than the number of spatial streams, which is set by the MCS index.
In Mx2 (2 SG), Mx3 (3 SG) and Mx4 (4 SG) MIMO systems, the number of transmit chains must be equal to the number of signal generators you use.
For receiver test (the channel fading state is set to ON):
The number of transmit chains is equal to the Number of Transmit Antennaeand must be not less than the number of spatial streams, which is set by the MCS index.
Use this cell to set the number of space time streams. When the number of space time streams is greater than the number of spatial streams, the STBC (Space Time Block Coding) scheme is enabled in which the spatial streams are mapped to the space time streams and then the space time streams are mapped to the transmit chains. Refer to the 802.11n transmitter block diagram.
Use this cell to set the number of extension spatial streams. The sum of the number of extension spatial streams and the number of space time streams should not exceed the number of transmit chains.
Use this cell to select the Bandwidth setting. This cell is only available for 40 MHz Bandwidth.
40 MHz Upper Mode - transmit a legacy or HT packet in the upper 20 MHz channel of a 40 MHz channel.
40 MHz Lower Mode - transmit a legacy or HT packet in the lower 20 MHz channel of a 40 MHz channel
N/A - transmit a legacy or HT packet in the full 40 MHz channel. In Legacy mode, 40 MHz transmission bandwidth, selecting N/A means the PHY in frequency domain operates in the Duplicate Legacy Mode. In this mode the device operates in a 40 MHz channel composed of two adjacent 20 MHz channels. The packets to be sent are in the legacy 11a format in each of the 20 MHz channels. To reduce the PAPR the upper channel (higher frequency) is rotated by 90º relative to the lower channel.
Use this cell to set the Short Guard Interval to either ON or OFF.
When turned ON, the Guard Interval is 400ns.
When turned OFF, the Guard Interval is 800ns.
The guard interval between symbols helps receivers overcome the effects of multipath delays. When you add a guard time, the back portion of useful signal time is copied and appended to the front. Enabling the Short Guard Interval increases the Data Rate. Refer to the MCS table for the relations between Guard Interval and Data Rate.
Use this cell to set the preamble and signal format to either Green Field or Mixed Mode.
Green Field - In Green Field mode, high throughput packets
are transmitted without a legacy compatible part.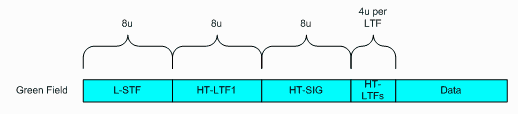
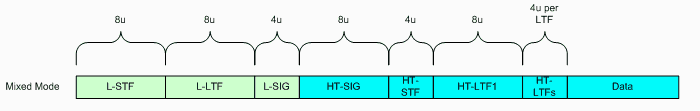
Mixed Mode - In Mixed Mode, packets are transmitted with a preamble compatible with the legacy 802.11a/g. The legacy Short Training Field (L-STF), the legacy Long Training Field (L-LTF) and the legacy signal field (L-SIG) are transmitted so they can be decoded by legacy 802.11a/g devices. The rest of the packet has a new format.
Use this cell to select the spatial mapping scheme, which maps spatial streams to different transmit chains. Refer to the Transmitter Block Diagram for the spatial mapping scheme function.
Direct mapping - each space time stream is directly mapped to a different transmit chain. When using the direct mapping scheme, the number of space time streams must be equal to the number of transmit chains.
Spatial Expansion - the space time streams are multiplied by a matrix, and then transmitted through different transmit chains. When using the spatial expansion mapping scheme, the number of space time streams can be fewer than the number of transmit chains. FFT transformation matrix is selected for spatial expansion.
Click spatial Mapping Matrix and the down arrow  to access the
to access the ![]() Q Matrix
window. For direct mapping and spatial expansion mapping schemes, this
window displays the corresponding Q matrix. For the User Defined Mapping
scheme, use this window to edit each element of the Q matrix.
Q Matrix
window. For direct mapping and spatial expansion mapping schemes, this
window displays the corresponding Q matrix. For the User Defined Mapping
scheme, use this window to edit each element of the Q matrix.
Save - Click this button to save a Q matrix into a text file.
Load - This button is only applicable for the User Defined spatial mapping scheme. Click this button to select a simple unformatted text file (*.txt) of element values, characterizing a user-defined Q matrix. Each line in the file contains one element value (default complex). The matrix elements are stored row by row. For example, for a 2x2 matrix, the two complex elements in the first row are stored in the 1-2 lines of the file respectively. Then the two complex elements in the second row are stored in the 3-4 lines of the file respectively.
Choices: ON | OFF
Default: ON
Coupling: Scrambler is fixed to ON when Capability is set to Basic.
Use this cell to enable or disable the scrambler. Enabling the scrambler scrambles the data to prevent long sequences of '0's or '1's.
Choices: 0 to 127
Default: 93
Use this cell to set the initial value of the scrambler.
Choices: BCC | LDPC
Default: BCC
Coupling: When Channel Coding Mode is LDPC, Interleaver is turned OFF.
Select either BCC or LDPC Channel Coding Mode to encode the data.
For information about the difference in processing procedures between BCC encoding and LDPC encoding, see BCC and LDPC Encoders.
Channel Coding Mode is fixed to BCC for the following configurations:
Choices: ON | OFF
Default:ON
Coupling: Channel Coding State is fixed to OFF when Capability is set to Basic.
Enable or disable the channel encoding function. When it is OFF, the Channel Coding Mode encoders are bypassed.
If the recalled setup file contains Convolutional Coder, the Channel Coding State will be set to the same state as the Convolutional Coder. Likewise,
changing the state of the Convolutional Coder, changes the Channel Coding State. For example, switching Convolutional Coder from ON to OFF, sets the Channel Coding State to OFF.
Use this cell to set the interleaver to either ON or OFF.
This cell is adjustable only for the Advanced Capability. In the Basic Capability, it is automatically set to OFF.