Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting (ISDB) systems including ISDB-S (Satellite), ISDB-T (Terrestrial) and ISDB-C (Cable) were developed in Japan to provide flexibility and commonality for the multimedia broadcasting services using each network.
ISDB-T has been established since 1999 the ISDB-T system was adopted as the Japanese standard for digital terrestrial television broadcasting (DTTB) and digital terrestrial sound broadcasting (DTSB, ISDB-TSB) in 1999. Brazil also adopted ISDB-T as national terrestrial digital TV standard.
ISDB-T signal consists of 13 OFDM segments in a 6MHz Transmission bands. The Hierarchical transmission supports up to 3 layers , and each consists of one or more OFDM segments. Partial reception in ISDB-T allows high and low data rate program be transmitted in the same frequency band. ISDB-T 1-Seg, and ISDB-T 3-Seg are mainly for mobile video or audio transmission while 13 segments are used for HDTV or SDTV transmission.

Filter Enable (not shown above) is a new parameter under 1. Basic.
AC Setup (not shown above) is a new parameter under 2. ISDB-T Settings.
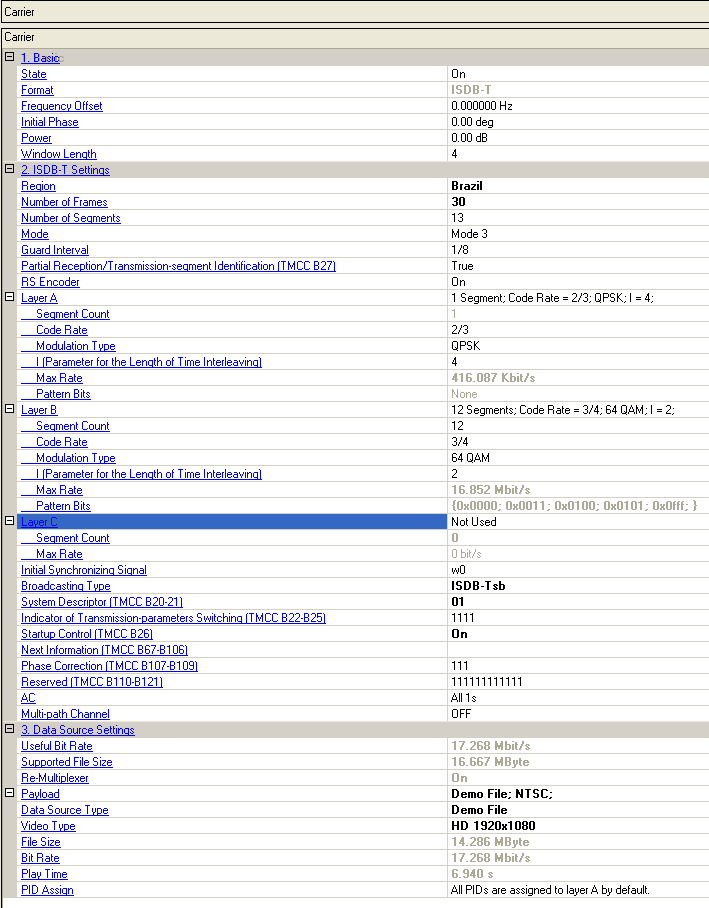
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to control the operating state of the carrier.
The format of the carrier.
Range: -40.0 to 40.0 MHz
Set the frequency offset for the carrier relative to the signal generator’s frequency setting. The valid range will be different for every format due to the different over-sampling ratios.
For example, for 2 carriers configuration, set the center frequency of signal generator to 1 GHz, and make the two carriers distributed on the both sides of the center frequency with 5 MHz offset each. Therefore, the actual frequency of each carrier would be 1GHz+5MHz and 1GHz-5MHz respectively.
Range: 0 to 359 degrees
Set the initial phase of the carrier.
Range: -50 to 0 dB
Set the carrier’s power relative to the signal generator’s amplitude setting.
Range: 0 to 128
Default: 4
Set the window length of OFDM symbol.
Choice: On | Off
Default: Off
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the baseband filter.
Choice: Japan \Brazil
Default: Japan
ISDB-T video used in Japan is NTSC and in Brazil is 1080i (HD video). When Region is Japan, the Video Type of demo file is NTSC and when Region is Brazil, video type of demo file is HD1920x1080.
Range: 1 to 5000
Default: 1
Set the number of frames of ISDB-T.
Choice: 1 | 3 | 13
Default: 13
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the number of segments used.
Choice: Mode 1 | Mode 2 | Mode3
Default: Mode 3
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the Mode.
Three system modes represent three different spacings between OFDM carrier frequencies offered by ISDB-T, catering for the different requirements of the distance between SFN stations and the robustness to Doppler shift during mobile-reception.
As shown in the following table
The available spacing between OFDM carrier frequencies are approximately 4 kHz, 2 kHz and 1kHz in mode 1, 2 and 3.
The number of carriers used varies depending on the mode
Information bit rate that can be transmitted remains the same in all three modes.
|
Transmission Parameter |
Mode 1 |
Mode 2 |
Mode 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
No. of OFDM segments |
13 |
||
|
Bandwidth |
5.575 MHz |
5.573MHz |
5.572MHz |
|
Carrier interval |
3.968 kHz |
1.984 kHz |
0.992 kHz |
|
No. of carriers |
1405 |
2809 |
5617 |
|
Carrier modulation |
QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM, DQPSK |
||
|
Effective symbol length (Tu) |
252 μs |
504 μs |
1.008 ms |
|
Guard-interval length (Tg) |
1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32 of effective symbol length |
||
|
No. of symbol per frame |
204 |
||
|
Time interleave |
Maximum 4 values: 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4 sec |
||
|
Frequency interleave |
Intra-segment and inter-segment interleaving |
||
|
Inner code |
Convolutional coding (1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, 7/8) |
||
|
Information bit rate |
3.65 Mbps - 23.23 Mbps |
||
|
Hierarchical transmission |
Maximum 3 levels (Layer A, B, and C) |
||
Choice: 1/4 | 1/8 | 1/16 | 1/32
Default: 1/8
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the Guard Interval.
The purpose of the guard interval is to introduce immunity to propagation delays, echoes and reflections, to which digital data is normally very sensitive.
ISDB-T has four choices of guard-interval length to enable better design of a single-frequency network (SFN).
Choice: True | False
Default: True
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to enable or disable partial reception.
Partial Reception represents the reception of only one OFDM segment at the center of a group of segment.
This configuration has enabled an ISDB-TSB receiver to receive one-segment service embedded in a hierarchical television signal.
Choice: ON | OFF
Default: ON
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the RS encoder. For ISDB-T, when the RS encoder is off, the payload is treated as the output of a RS encoder and fed into the energy dispersal directly.
Layer A of ISDB-T.
A mixture of fixed-reception programs and mobile-reception programs is made possible through the application of hierarchical transmission achieved by band division within a channel. ”r;Hierarchical transmission” means that the three elements of channel coding, namely, the modulation scheme, the coding rate of convolutional error-correcting code, and the time interleaving length, can be independently selected.
Range: the total number of all layers equals to the Number of Segments.
Set the number of segments assigned to this layer.
Choice: 1/2 | 2/3 | 3/4 | 5/6 | 7/8
Default: 2/3 for Layer A, 3/4 for Layer B
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the code rate of convolutional coder in this layer.
Choice: DQPSK | QPSK | 16QAM | 64QAM
Default: QPSK for Layer A, 64QAM for Layer B
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the modulation type in this layer.
Choice:
For Mode 1: 0 | 4 | 8 |16
For Mode 2: 0 | 2 | 4 | 8
For Mode 3: 0 | 1 | 2 | 4
Default:
For layer B: 2, the others: 4.
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the length of time interleaving in this layer.
The Maximum Bit Rate in this layer.
Sets the user defined pattern.
Click the right button
to open ![]() "Data Pattern Selection"
dialog and select test pattern to use.
"Data Pattern Selection"
dialog and select test pattern to use.
Layer B of ISDB-T.
Range: the total number of all layers equals to the Number of Segments.
Set the number of segments assigned to this layer.
Choice: 1/2 | 2/3 | 3/4 | 5/6 | 7/8
Default: 2/3 for Layer A, 3/4 for Layer B
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the code rate of convolutional coder in this layer.
Choice: DQPSK | QPSK | 16QAM | 64QAM
Default: QPSK for Layer A, 64QAM for Layer B
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the modulation type in this layer.
Choice:
For Mode 1: 0 | 4 | 8 |16
For Mode 2: 0 | 2 | 4 | 8
For Mode 3: 0 | 1 | 2 | 4
Default:
For layer B: 2;
The others: 4.
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the length of time interleaving in this layer.
The Maximum Bit Rate in this layer.
Sets the user defined pattern.
Click the right button
to open ![]() "Data Pattern Selection"
dialog and select test pattern to use.
"Data Pattern Selection"
dialog and select test pattern to use.
Layer C of ISDB-T.
of Layer C will be read only and determined by and of layer A and layer B.
Range: the total number of all layers equals to the Number of Segments.
Set the number of segments assigned to this layer.
The Maximum Bit Rate in this layer.
Choice: w0 | w1
Default: w0
An synchronizing signal is designed to establish synchronism between transmission and reception of a TMCC signal and an OFDM frame.
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the synchronizing signal used in TMCC.
|
B1 -B16 |
Synchronizing Signal (w0 = 0011010111101110, w1 = 1100101000010001) |
Figure 1 Initial Synchronizing Signal in OFDM frame
Choice: ISDB-T| ISDB-TSB
Default: ISDB-T
ISDB-T: Digital terrestrial television broadcasting system, in which transmission bands consist of 13 OFDM segments;
ISDB-TSB: Digital terrestrial television broadcasting system, in which transmission bands consist of one or three OFDM segments.
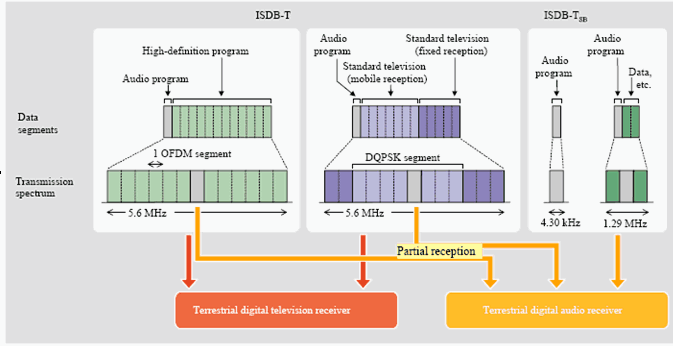
Figure 2 Frequency segmentation of ISDB-T and ISDB-TSB
Range: 1 to 40
Default: 23
To
set the sub channel number by clicking on the purple rectangular, or by
clicking on the  , a
, a ![]() selection drop down dialog
will pop up.
selection drop down dialog
will pop up.
Range: 00 to 11
Default: 00
Set system descriptor bits in TMCC from B20 to B21.
Range: 0000 to 1111
Default: 1111
Set the indicator of transmission-parameter switching specified in TMCC B22 to B25.
Choice: ON | OFF
Default: OFF
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to set the start flag for emergency-alarm broadcasting which is specified in TMCC B26.
includes the transmission parameters following switching. If the input of is null, it will be the same as Current information.
Range: 00 to 11
Default: 00
Set phase correction bits in TMCC from B107 to B109.
Range: 000000000000 to 111111111111
Default: 000000000000
Set reserved bits in TMCC from B110 to B121.
Choice: Data Pattern Editor | AC Builder Tool (N7623C-Mxx license required)
Default: Data Pattern Editor
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select the generation method of AC bits.
If the N7623-Mxx (ISDB-Tmm Advanced, ISDB-T enhancement) license is not installed in the connected instrument (MXG/EXG/ESG/PSG), the AC Builder Tool is not available. Then the AC Setup cell will be grayed out and the default value will be Data Pattern Editor.
Click on the right side of the cell to set the
AC information.
If the AC Setup is set to
Data Pattern Editor, a ![]() Data Pattern Selection
dialog will be opened up to set the test pattern to be used as AC bits.
Data Pattern Selection
dialog will be opened up to set the test pattern to be used as AC bits.
If the AC Setup is set to
AC Builder Tool, an ![]() ISDB-T AC Builder
dialog will pop up. See the topic "Using the AC Builder Tool to generate the AC
signal" for the detailed steps of using ISDB-T AC builder to
configure the earthquake alarm information sent in the AC bits.
ISDB-T AC Builder
dialog will pop up. See the topic "Using the AC Builder Tool to generate the AC
signal" for the detailed steps of using ISDB-T AC builder to
configure the earthquake alarm information sent in the AC bits.
AC (Auxiliary Channel) is used to transmit additional information. AC1 is available in an equal number in all segments, while AC2 is available only in different modulated segments.
Default: OFF
To enable static multi-path channel.
Click on in the right side of the cell, and
![]() Multi-path
Channel configuration window will pop up.
Multi-path
Channel configuration window will pop up.
The useful bit rate. The bit rate can be transmitted by current encoding, modulation and framing configurations.
The maximum file size supported by 64MSa memory of MXG/EXG/ESG/PSG.
Choice: ON | OFF
Default: OFF
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to enable or disable the Re-Multiplexer.
The TS payload settings.
Choice:
Normal: Test Pattern | Demo File | TS File | TS File Wizard
When RS Encoder is off: Test Pattern | TS File
For DVB-H: Test Pattern | TS File
For one-seg ISDB-T: Test Pattern | TS File | TS File Wizard
Default: Test Pattern
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select which type to be used as the data source.
If TS File" is selected, "File Name" is required; If "TS File Wizard" is selected, "File Wizard" is available.
Learn more about the different Data Source Types, refer to the page Data Source Type.
The data bits used as test pattern.
Click the right button to open "Test Pattern Edit" dialog and select test pattern to use.
Choice: True | False
Default: False
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to determine whether a SYNC byte (0x47) should be inserted into the test pattern.
Choice: NTSC | PAL| HD 1920x1080
Default: PAL
Double-click or use the drop-down menu to select whether the PAL or NTSC file is demo File. This cell is only enabled when Data Source Type is Demo File.
There are two predominant worldwide video-based source material formats, shown as follows:
NTSC: National Television System Committee, the system used in America & Canada
PAL: Phase Alternating Line, the system used in Western Europe and Australia
|
N T S C National Television System Committee |
|
|
Lines/Field |
525/60 |
|
Horizontal Frequency |
15.734 kHz |
|
Vertical Frequency |
60 Hz |
|
Color Sub-carrier Frequency |
3.579545 MHz |
|
Video Bandwidth |
4.2 MHz |
|
Sound Carrier |
4.5 MHz |
|
P A L Phase Alternating Line |
|||
|
SYSTEM PAL |
PAL |
PAL N |
PAL M |
|
Line/Field |
625/50 |
625/50 |
525/60 |
|
Horizontal Freq. |
15.625 kHz |
15.625 kHz |
15.750 kHz |
|
Vertical Freq. |
50 Hz |
50 Hz |
60 Hz |
|
Color Sub Carrier |
4.433618 MHz |
3.582056 MHz |
3.575611 MHz |
|
Video Bandwidth |
5.0 MHz |
4.2 MHz |
4.2 MHz |
|
Sound Carrier |
5.5 MHz |
4.5 MHz |
4.5 MHz |
The size of opened file.
The bit rate of the opened file.
The time that file can be played.
The PIDs assignment information.