
The frequency accuracy of the VNA source is defined as the difference between the CW frequency setting and the measured frequency. This value is divided by the frequency setting and expressed in parts-per-million (PPM).
A frequency counter is connected to the active test port of the network analyzer under test. The network analyzer is set to selected CW frequencies within its specified frequency range. The counter measures the frequency at each CW setting. The difference between the frequency setting and the counter reading is compared to the specification.
The frequency accuracy of the VNA is governed by the accuracy of the crystal oscillator. Since this oscillator is common to all test ports, only one test port will be tested.
The Maximum Output Port Power, Power Level Accuracy, and Noise Floor tests confirm that the VNA source operates over its full frequency range. This test confirms the accuracy of the frequencies produced by the source.
Click here for troubleshooting help.
|
Test Equipment |
Recommended Models1 |
|
Frequency counter |
53230A Option 115 |
|
Frequency reference2 |
Frequency counter internal |
|
Adapter, BNC (m) to Type-N (f) |
1250-1477 |
|
Adapter, 3.5 mm (m) to Type-N (m) |
1250-1743 |
|
Cable, RF 3.5 mm (m) to 3.5 mm (f) |
8121-2111 |
|

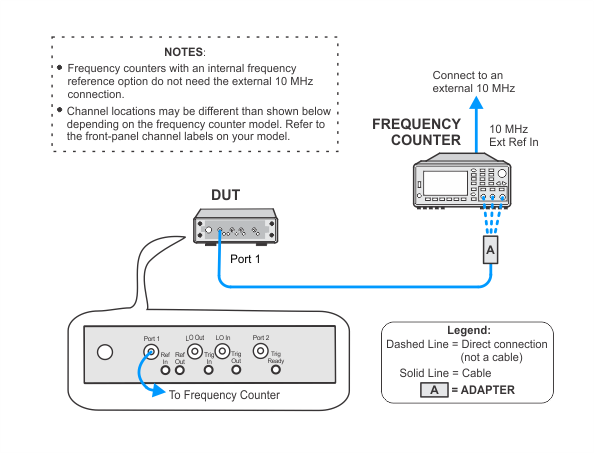
The equipment list for this test includes a FreqReference1. It is indicated as optional because it may or may not require a separate piece of test equipment. The model for this equipment type may be FreqCounter1 Internal Ref or 10 MHz External Reference. When FreqCounter1 Internal Ref is specified, the frequency counter uses its internal frequency reference for its time base; a separate piece of equipment is not required. When 10 MHz External Reference is specified, an external 10 MHz reference is required to be connected to the counter (this will often be a house standard).
The calibration date, etc, for FreqCounter1 Internal Ref should match the frequency counter. The calibration information for 10 MHz External Reference will depend on the source used for the 10 MHz.
When 10 MHz External Reference is specified, the user must provide a value for frequency accuracy. Frequency accuracy represents the worst case accuracy of the reference (maximum deviation from exactly 10 MHz) any time during the calibration period of the reference. The value is expressed in ppm and is entered via the Additional Properties key.
As an example, if the accuracy of an external frequency reference is +/– 1.0 Hz, then the accuracy is 1.0e–7. The value in ppm would be entered as 0.10.
If a separate counter is used as the 10 MHz External Reference instead of a house standard, here are some example frequency accuracy values:
|
Frequency Accuracy Value Examples |
||
|
Model |
Option |
Value |
|
53131A/32A |
no options |
8.6 ppm |
|
001 |
2.6 ppm |
|
|
010 |
0.1825 ppm |
|
|
53132A |
012 |
0.0385 ppm |
|
53181A |
no options |
8.6 ppm |
|
001 |
2.6 ppm |
|
|
010 |
0.1825 pp |
|
|
53230A |
no option |
1.7 ppm |
|
010 |
0.0155 ppm |
|
Note that values above 0.2 ppm will often give unsatisfactorily large measurement uncertainties.
Formulas used to calculate the above values:
Frequency Accuracy = Time Base Error = (monthly aging rate * 12) + Temperature Stability
