About Synchronization (Flex Frame)
In Flex Frame measurements, synchronization is the process of detecting the frame start in time domain, determining the symbol timing, and estimating the initial frequency offset, phase offset, IQ offset and power scaling.
The synchronization algorithm used depends on whether there is any known signal defined in the frame:
Known signal: A known signal is an allocation whose bits are known sequence (PN 1) part number, or 2) packet number sequence or customer defined sequence) or IQ symbols that are known IQ symbols. If there is any known signal defined in the frame (besides the estimation based on generic QPSK Quadrature phase shift keying/QAM Quadrature Amplitude Modulation signals), additional cross correlation is done to detect the frame start and frequency/phase/power offset.
No known signal: If there is no known signal defined in the frame, the VSA uses generic characteristics of QPSK/QAM signals to estimate the symbol timing offset and frequency offset. In this case, there is no clear frame structure defined (similar to Custom IQ or Digital Demod signals). No frame start is detected, so it is assumed that the first valid symbol is the frame start.
Synchronization with Known Signals
Under, you can choose which segments (Allocations) are used for Synchronization and whether Frequency Estimation Mode is on (Normal) or off.
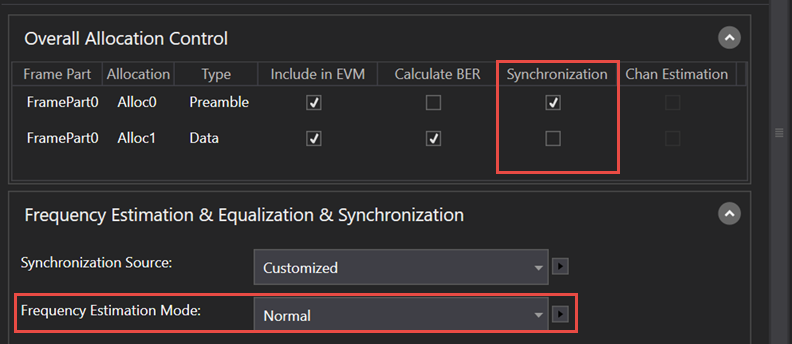
If the signal is burst, the burst start and burst end are found first, then synchronization is done on the active burst. If the signal is periodic, synchronization is done on the input signal.
-
Detect the symbol timing offset (like the peak of QPSK/QAM signal) based on the characteristic of QPSK/QAM signal), then compensate the timing offset by resampling the signal to get the peak sample on each symbol interval. This step is also executed when there is no known signal.
-
Detect the location of the sync signal by doing cross correlation between the timing-compensated signal and the ideal sync signal to get the frame start.
-
Estimate the frequency offset, phase offset, IQ Offset and power scaling using the received sync signal and the ideal sync signal, then compensate for these offsets.
Fine frequency estimation/tracking and equalization is done after the initial synchronization is completed.
See Also
