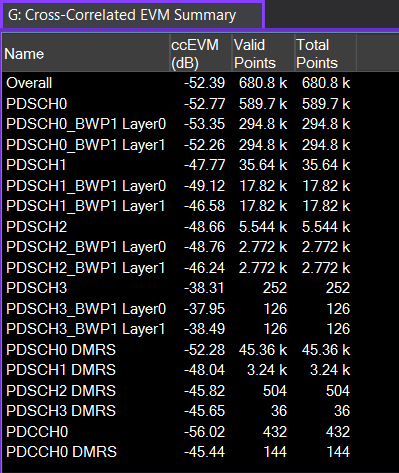
Cross-Correlated EVM Summary (5G NR/5G-Advanced)
The trace displays calculated cross-correlated EVM Error vector magnitude (EVM): A quality metric in digital communication systems. See the EVM metric in the Error Summary Table topic in each demodulator for more information on how EVM is calculated for that modulation format. results when Cross-Correlated EVM Enable is selected (true). The first row of the matrix displays the overall result. For MIMO Multiple Input, Multiple Output: A physical layer (PHY) configuration in which both transmitter and receiver use multiple antennas. signals, a separate result for each channel and layer will be shown after the overall result.
Analysis Start Boundary should be set to Frame to make sure that the same data is being analyzed by both component carriers in the ccEVM measurement.
-
ccEVM - Cross-correlated EVM result (in dB).
There are various factors that can contribute to unexpected ccEVM results. To ensure a good ccEVM measurement, do the following:
- Increase the Result Length to get more accurate symbol clock error estimation and compensation
- Turn on Symbol Clock Offset Compensation
-
Valid Points - All active points except those with reference values that are different between measurements 1 and 2.
-
Total Points - All active points.
Active points are all subcarrier points in all symbols in the Measurement Interval except for those which are inactive (for example, inactive RUs or punctured bands).
Averaging
The Cross Correlated EVM Summary trace participates in measurement averaging (MeasSetup > Average) when average type is RMS or RMS Exponential. The "Vect: NNN" annotation at the top of the trace indicates that averaging is done as a complex average rather than RMS averaging ("RMS: NNN") used on other traces.
For more information on ccEVM, see Cross-Correlated EVM.
See Also