Chapter 6 Calibration for NA, CAT, and
VVM Modes
Calibration removes the systematic errors that are associated with measurements
in NA, CAT, and VVM Modes. Key presses are identical in all of these Modes.
In this Chapter
See Also
Learn How to Make 75 ohm Measurements
by referring to the FieldFox
Supplemental Online Help.
Why and When to Calibrate
There are well-defined and understood systematic errors that are measured
and calculated during the calibration process. These errors are caused
by leakage signals inside the FieldFox, by the frequency response of the
FieldFox receivers, and by reflections inside the FieldFox that interact
with the DUT. After calibration, these errors are removed from subsequent
measurements.
To maintain highest measurement accuracy, perform a new calibration
when any of the following changes occur:
- When any of the following measurement settings change: Frequency
Range, Power Level, IF BW, and Resolution. Therefore, make these measurement
settings before calibrating. Increased Averaging, lower IF BW, and
higher Resolution all cause slower sweeps and slower calibration times.
Learn about Interpolation and Questionable Accuracy in “Interpolation *”.
- When the FieldFox temperature changes more than about 10°F (5°C).
Learn more in “How
to monitor the internal FieldFox temperature:”.
- When the connection to the DUT changes, requiring a different jumper
cable or adapter.
Definitions
DUT (Device Under Test) The
cable, antenna, transmission line, amplifier, or anything else that is
connected to the FieldFox that is to be measured.
Calibration Standards - OPEN, SHORT, LOAD, and THRU
- OPEN, SHORT,
and LOAD are ‘reflection’
standards that are used during calibration. When an RF signal ‘hits’
these components, the signals are reflected in a predictable manner.
These components can also be used to terminate a DUT port during some
measurements.
- SHORT and OPEN standards both cause 100% of an RF signal to
be reflected. The difference between these two standards is what
happens to the phase of the reflected signal, which is beyond
the scope of this discussion. Although an OPEN standard is a precision
component, simply leaving nothing
connected at the end of a cable can be a reasonable substitute
for an OPEN.
- A LOAD standard absorbs almost ALL of the incident signal and
very little signal is reflected back to the source.
- A THRU standard is used
during some calibration steps to connect PORT 1 to PORT 2 in place
of the DUT. A Flush THRU connection can be made when cables that connect
with the DUT can mate with each other. Learn more in “Mechanical
Cal”. Otherwise, any reasonably short cable can be used as a THRU
standard.
Calibration Reference Plane
is the point (or points) at which the DUT and calibration standards are
connected during a calibration. This can be at the FieldFox test port
connectors, or at the end of jumper cables or adapters.
CalReady
Every FieldFox contains a factory calibration that was performed at
the port 1 and port 2 connectors, with -15 dBm input power, over the entire
frequency range of the FieldFox using a number of data points that allows
reasonable interpolation over the FieldFox frequency range
.
This calibration, known as CalReady, allows you to immediately make
measurements of a DUT that is connected directly at the test ports (PORT
1 and/or PORT 2). CalReady corrects measurements when the FieldFox is
turned ON and when a measurement is created with no other correction in
place.
When measuring a DUT using a jumper cable or adapter - NOT a direct
connection to a test port connector – then a Mechanical Cal is recommended.
CalReady can also be used to check the integrity of the jumper cable that
is attached to the test ports.
CalRdy is shown when a measurement
is corrected using CalReady.
You can change the properties of the CalReady calibration. Learn more
in “CalReady”.
Learn how to see when your factory CalReady calibration was performed
in “System
Information”.
How to Perform a Calibration

|
Press Esc at any time to end
the calibration process.
When performing a calibration that contains a large number of points
(5000 to 10,001 points) be aware that the calibration progress
bar may not move for 2 or 3 minutes during the calibration process. |
In CAT, NA, or VVM Mode, press Cal 5.
The following appears:
Choose Calibration Method screen
Response Cal – Used to quickly
calibrate ONE type of measurement using mechanical standards. Measurement
accuracy is generally low. Learn more in “Simple
Response Cals”.
Mechanical Cal/ECal – Using
mechanical calibration standards from a cal kit, perform an accurate calibration
at one or both test ports, adapters, or jumper cables. Full 2-port mechanical
calibration is the most accurate calibration available with FieldFox.
Learn more in “ECal”.
User Cal OFF ON – Turns ON and
OFF the effects of the user calibration that you performed. The OFF state
reverts to CalReady.
View Cal – Shows the properties
of the current calibration. Learn more in “View
Cal”.
More – Learn about Cal Ready
Properties in “CalReady”.

|
Source Unleveled errors - During calibration, the frequency
range of the measurement MAY be extended to provide maximum flexibility.
During the calibration, the output power may become unleveled
at the added high frequencies. You can ignore the “Source Unleveled”
error, or to avoid the error, select either High power or -15
dBm before calibrating. Learn more about setting Output Power
in “Output
Power”. |
Mechanical Cal
Mechanical Calibration is performed using discrete standards from a
Cal Kit. Several Cal Kit definitions are built into the FieldFox. To learn
about Cal Kit definitions, refer to the Application Note, “Specifying
Calibration Standards and Kits for Keysight Vector Network Analyzers,”
available online at https://www.keysight.com/us/en/assets/7018-01375/application-notes/5989-4840.pdf.

|
Visit www.keysight.com/find/fieldfoxsupport
to see a complete list of supported Cal Kits. Also at this website,
download Data-Link software that allows you to edit Cal Kit definitions
or add a new Cal Kit. |
Mechanical Cals are extremely accurate when performed using the correct
Cal Kits with standards that are clean and in good repair, and when using
correct connection procedures.
How to perform a Mechanical
Cal
- Disconnect the DUT from the FieldFox.
- If a jumper cable or adapter is required to connect the DUT to
the FieldFox, then connect those
components to the FieldFox connectors. The effects of those components
will be measured and removed during the calibration, and only the
effects of the DUT will be displayed in the measurement results. These should be high-quality components!
- In NA, CAT, or VVM Mode, press Cal 5.
- Then Mechanical Cal
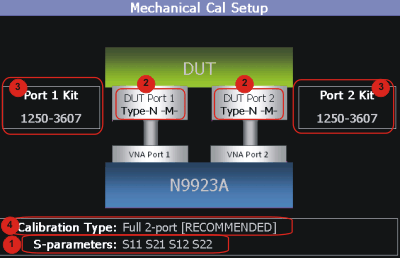
This page summarizes the Mechanical Cal to be performed and allows you
to make changes. For best results, review the screen and make changes
in the following order:
- S-parameters – Verify that
these are all of the S-parameters that you want calibrated. If not,
press Esc to terminate the calibration
process, then return to the Trace menu to display all of the traces
to be calibrated. Learn how in “Multi-Trace
Configurations”.
- DUT Connectors – For each
DUT port that is shown, verify the correct type and gender of the
DUT connector. If a DUT port is not shown, then that port is not included
in the list of S-parameters to be calibrated.
- Cal Kit - Verify the correct
Cal Kit for each DUT port to be calibrated. See a list of supported
Cal Kits in the FieldFox Data Sheet. Learn more in "Appendix
B", in the C-Series
N9915-90020 (Unabridged) User's Guide.
If the DUT connector type, gender, or Cal
Kit is NOT correct for the DUT ports to be calibrated, then:
- Press Change
DUT Connectors to select the correct connector types that
are on your DUT.
- For each port:
- Use the arrows (
 ) or rotary
knob to change the DUT connector type.
) or rotary
knob to change the DUT connector type.
- Press Change Gender to
change the gender of the DUT connector.
- Then press Next… to confirm
the selection and continue the process.
- For each port:
- Use the arrows (
 ) or rotary
knob to select the Cal Kit that you have, and are going to
use, for the specified ports.
) or rotary
knob to select the Cal Kit that you have, and are going to
use, for the specified ports.
- Press Next… to confirm
the selection and continue the process.
- Then press Finish to end
the selection process.
- Calibration Type - The
FieldFox always RECOMMENDS a Cal Type that will quickly and accurately
calibrate all of the displayed S-parameters. Change from the RECOMMENDED
Cal Type ONLY if you understand the implications. Learn more about
Cal Types in “Calibration
Type”.
To select a different Cal Type:
Press Change Cal Type.
- Then using the arrows (
 ) or
rotary knob, select a Cal Type,
) or
rotary knob, select a Cal Type,
- Then press Select and Finish.
Begin Calibration
- Press Start Calibration.

|
If an error appears (“Failure
to compute calibration steps…”), check to ensure that the
frequency range of the Cal Kit covers the frequency range of the
measurement. You can verify the frequency range of your Cal Kit
at: www.keysight.com/find/fieldfoxsupport.
Click Cal Kits. |
- Follow the Cal Wizard prompts. Connect the specified standard at
the point where the DUT will be connected, then press Measure.
- At any time, press Back to re-measure
a standard if you feel it was not properly connected.
- Press Finish to complete the calibration.
CAL ON U is shown on the screen for
all displayed measurements that are corrected with the Mechanical Cal.
ECal
 |
ECals each have a recommended input power level. Depending
on the measurement setup, the FieldFox may default to an input
power level that exceeds your ECal’s recommended input power level.
Refer to the reference guide for your ECal module to determine
the correct input power levels. Exceeding an ECal’s recommended
input power level results in a compression and an invalid data
condition. Refer to www.keysight.com/find/ecal.
|
ECal is a complete solid-state calibration solution. Every ECal module
contains electronic standards that are automatically switched into position
during a calibration. These electronic standards have been measured at
the factory and the data stored within the memory of the ECal module.
The FieldFox uses this stored data, along with the measured data, to calculate
the error terms for a measurement calibration.
You can perform the following calibrations with ECal:
- 1-Port Reflection calibration
- Full 2-Port calibration
 |
Simple ECal ON:
When choosing Full 2-port
calibration, if you are able to connect your ECal simultaneously
to both device ports, you should use Simple
ECAL (i.e., this ensures that you are using the correct
Thru calibration model).
Simple ECal OFF: Set
simple ECal to OFF when you have a test setup where you cannot
connect port 1 and port 2 simultaneously to the ECAL module (Then
during the calibration when prompted: “Connect
port 1 to port 2", use a coaxial cable or an appropriate
thru adapter to connect port 1 to port 2).
’Unknown THRU’: When
prompted: “Connect port 1 to
port 2", then you can connect them, using a coaxial
cable or an appropriate thru adapter. Do NOT use the internal
ECal THRU, because the thru calibration will be incorrect.
‘Flush THRU’: When prompted:
“Connect port 1 directly to port
2", then you must connect the ports directly together
at the calibration reference plane with no adapter or other cabling.
Learn more in “Calibration
Type”. |
All Keysight USB ECal modules are supported. ECal modules are available
in a variety of connector types, covering many frequency ranges. For information
about available ECal modules, see http://www.keysight.com/find/ecal.
Select an ECal module that has connectors of the same type and gender
as the DUT. If such an ECal module is not available, a module with connectors
different from the DUT can be used by selecting a User Characterization.
This selection is located on the Mechanical Cal Setup page of the CalWizard.
However, a User Characterization can NOT be PERFORMED using the FieldFox.
It must be performed using a bench top Keysight VNA, such as the PNA or
ENA. Learn more about "User Characterization" at the PNA Help
website here: https://rfmw.em.keysight.com/wireless/helpfiles/N52xxB/S3_Cals/ECal_User_Characterization.htm.
How to Perform
a Calibration Using ECal
- Make measurement settings on the FieldFox (frequency range, number
of points, etc.)

|
The frequency range of the measurement MUST be within the
frequency range of the ECal module or an error will appear when
“Calculating Steps” during the calibration. |
- Connect the ECal module USB cable to the FieldFox USB.
- Allow the module to warm up until it indicates READY. This may
take several minutes.
- Connect the ECal module ports to the FieldFox at the calibration
reference plane (where the DUT will be connected).
- Press Cal 5 to start the Calibration.
- Press Mechanical Cal / ECal
- Press Change DUT Connectors. For
each test port to be calibrated, select the Connector
Type and Gender of
the DUT / ECal module. The connected ECal module and relevant User
Characterizations will appear, with the ECal factory default as the
default Cal Kit.
- Optionally press Advanced then
ECal Auto Orient.
- ON
(default) The FieldFox automatically senses the direction in which
the ECal module ports are connected to the FieldFox ports.
- OFF
If power to the ECal module is too low, it cannot detect which
FieldFox ports it is connected to. If you are having this problem,
select OFF. Then during the calibration, the FieldFox will prompt
you to connect the ECal module ports to specific FieldFox ports.
- Optionally press Advanced then
Extended Cal (N995xB/6xB Only).
- ON The FieldFox Extended Cal
measures additional points outside the current frequency range
in order to enable adjusting the frequency range after the calibration
procedure. With these extra points, the error correction may be
applied when it otherwise might not. Without extended cal, if
you adjust your frequency outside the calibrated range after the
calibration has been completed, the error correction is turned
off.
- OFF (default) The FieldFox
does not measure any frequency points outside the current displayed
frequency range. If the frequency is adjusted outside of the set
of points calibrated the error correction is turned off and the
following message is displayed:
"Error
correction disabled. Stimulus outside calibrated range."
- Press Start Calibration. When
prompted, verify the ECal module connection, then press Measure. The
standards within the ECal module are automatically connected and measured.
 |
’Unknown THRU’: When prompted: “Connect port 1 to port 2",
then connect port and port 2, using a coaxial cable or an appropriate
thru adapter. Do NOT use the internal ECal THRU, because the ECal
thru calibration model is incorrect for this calibration type.
‘Flush THRU’: When prompted: “Connect port 1 directly to port
2", then you must connect the ports directly together at
the calibration reference plane with no adapter or other cabling.
Learn more in “Calibration
Type”. |
Simple Response Cals
Simple Response Cals are used to quickly calibrate the magnitude and
phase of a measurement using any Open, Short, or Thru component. These
may be calibration standards, but because a Cal Kit is not selected, they
are not modeled. Measurement accuracy is generally low. Use a Simple Response
Cal to make quick measurements when using a jumper cable to connect the
DUT to the FieldFox. Otherwise, CalReady is usually more accurate.
 |
IMPORTANT!
The Simple Response calibration assumes an ideal response for the
standard. DUT measurements after a Simple Response calibration
will have a measurement bias equivalent to the deviation of the
response of the device used as the Simple Response standard from
the ideal response. Note, that an Open Response is simply a normalization,
a Short response is a normalization with 180 degree phase offset.
When selecting a standard from the 85058B calibration kit for
a Short Response we suggest using short # 1 because it has the
smallest delay of the four shorts and would thus be most similar
to an ideal short.
For better accuracy, perform a mechanical calibration by referring
to “Mechanical
Cal”. |

|
You can perform a Simple Response Cal for either: S11, or
S22, or S21 AND S12. |
When prompted, choose a standard based on the displayed measurements
to be calibrated. For example, to calibrate S11, connect either an OPEN
or SHORT to the port 1 reference plane.
When Simple Response Cals are performed, the source match and reflection
tracking terms from CalReady are updated by the measured Short or Open
that is used during the calibration.
1-port response cals are also available from the Mechanical Cal menu.
Learn more in “Calibration
Type”.
Normalize uses a THRU standard
or cable between port 1 and port 2 to cal an S21 and S12 Transmission
measurement (NA Mode) and a 2-port Insertion Loss measurement (CAT Mode).
In VVM Mode, this is performed using Zero.
When a Normalization is performed, the forward and reverse transmission
tracking terms from CalReady are updated to account for the THRU that
is used during the normalization process.
How to perform a
Simple Response Cal
- Select the measurements to be calibrated. See the relevant Mode
(NA, CAT, or VVM) for measurement selections.
- Press Cal 5 then Response
Cal
- For 1-port measurements:
- Select either Open
Response or Short Response
for the port to be calibrated. The availability of this calibration
on Port 2 may require an option.
- Connect an OPEN or SHORT standard
to the specified port and press Measure
- For 2-port measurements:
- Select Normalization
- Connect a short, high-quality, phase
stable cable between the FieldFox port 1 and port 2 connectors,
then press Measure

|
With a Normalization Cal, all subsequent insertion loss
measurements are made relative to the insertion loss of the cable
used as the THRU standard. For example, if you use a cable with
1 dB of loss, then after Normalization, the display will show
0 dB of loss with this cable in place. Therefore, for highest
accuracy, when measuring the DUT also attach the cable that was
used in the normalization cal. |
- Press Finish.
- Connect the DUT.
CAL ON U is shown on the screen
when a User Cal (Ex: Response Cal) is correcting ONLY the appropriate
measurement. For example, when an Open Response Cal on Port 2 is performed,
CAL ON U is shown for an S22 measurement
only.
View Cal
From the Choose Calibration
screen (see “How
to Perform a Calibration”), press View Cal to see the following screen:
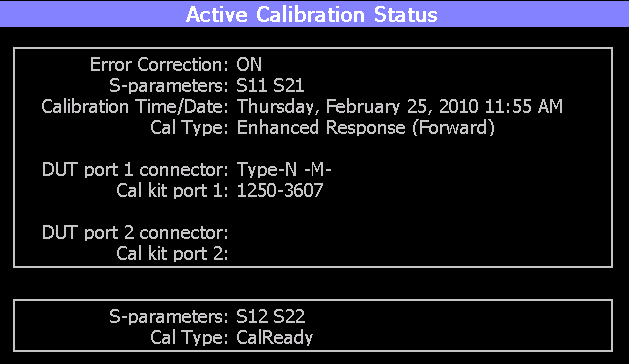
The top box shows the properties of the current calibration that you
performed and the displayed S-parameters that it is correcting.
The bottom box shows the S-parameters that are displayed but NOT corrected
by the current performed calibration, but rather the CalReady calibration.
Learn more about CalReady in “CalReady”.
Calibration Type
The FieldFox simplifies the calibration process by recommending the
most accurate and efficient calibration type based on the displayed S-parameters.
However, there may be times when you may want a little more accuracy
or a little faster sweep time. The following information can help you
learn about the various calibration choices.
Definitions:
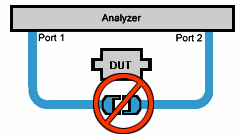
Non-insertable DUT – A device whose connectors could NOT mate together.
They either do not have the same type of connector or they have the same
gender. This also means that the test port cables could NOT mate together
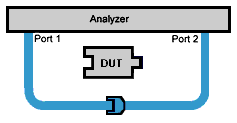
as in the above diagram. Insertable DUT – A device whose connectors could
mate together. They have the same type of connector and opposite or no
gender. This also means that the test port cables could mate together,
as in the above diagram.
 |
 |
| Non-insertable DUT – A device whose connectors could NOT mate
together. They either do not have the same type of connector or
they have the same gender. This also means that the test port
cables could NOT mate together as in the above diagram. |
Insertable DUT – A device whose connectors could mate together.
They have the same type of connector and opposite or no gender.
This also means that the test port cables could mate together,
as in the above diagram. |
Defined THRU – A THRU standard
for which there is a Cal Kit definition such as in the 8551xA Cal Kits.
Flush THRU (also known as Zero
length THRU) – When the test port cables mate together when measuring
an Insertable DUT. No actual THRU standard is required because the test
port cables are directly connected. Flush THRU is also a Defined THRU
with a definition of zero loss and zero length.
Unknown THRU - Any THRU connection
between the test ports. For more information, refer to the FieldFox
Supplemental Online Help.
Sweep Directions – Both FULL
2-Port Cals listed below result in correction that requires background
measurements sweeps in both directions, regardless of the displayed measurements.
The displayed traces are updated at a slower rate than Enhanced Response
and 1-port calibrations, which require sweeps in one direction only.
1-Port (OSL)
DUT: No restrictions
S-parameters Corrected: S11 or S22
Standards: OPEN, SHORT, LOAD
Sweeps in ONE direction.
FULL 2-Port (May
require an option)
Most comprehensive calibration. Corrects all S-parameters
DUT: Non-Insertable or Insertable
Standards: OPEN, SHORT, LOAD on BOTH ports. Any THRU between ports.
Based on the SOLR/Unknown THRU calibration. For more information on
the Unknown THRU process, refer to the FieldFox
Supplemental Online Help).
Sweeps in BOTH directions.
FULL
2-Port (QSOLT) – Mechanical Cal ONLY (May require an option)
Quicker to perform QSOLT than Full 2-port. Corrects all S-parameters.
DUT: Insertable only
Standards: OPEN, SHORT, LOAD on port 1. Flush THRU between ports.
Recommended cal type for Insertable DUTs. A Cal Kit is NOT required
for port 2.
Sweeps in BOTH directions.
Enhanced
Response Cal - Forward OR Reverse (May require an option)
Faster measurements than Full 2-Port.
DUT: Non-Insertable or Insertable. S-parameters PARTIALLY Corrected:
S21 and S11 (Forward) OR S12 and S22 (Reverse)
Standards: OPEN, SHORT, LOAD on ONE port. Defined or Flush THRU between
ports.
Sweeps in ONE direction.
TRL
– Mechanical Cal ONLY
A complete 2-Port calibration with potentially better accuracy than
Full 2-port. Corrects all S-parameters.
DUT: Non-Insertable or Insertable
Standards: Thru, Reflect, Line or variations of these. A TRL Cal Kit
MUST be selected to see this Cal Type
Sweeps in BOTH directions.
Learn more about TRL Calibration, refer to the FieldFox
Supplemental Online Help.
1-port Response
Cals (Open or Short)
Calibrate the magnitude and phase of a measurement using ‘modeled’ mechanical
standards. Measurement accuracy is better than Simple Response Cals (available
on the main Cal page - see “Calibration
Type”) but NOT as good as full 1-port cal. Corrects either S11 or
S22. Can be used with Isolation (see following section). Learn more in
“Simple Response
Cals”.
DUT: Non-Insertable or Insertable
S-parameters Corrected: S11 or S22
Standards: OPEN or SHORT on ONE port
Sweeps in BOTH directions.
Isolation Step
The optional isolation step of a calibration corrects for crosstalk
which is the internal signal leakage between the test ports. The Isolation
step measures Load standards that are connected to one or both FieldFox
test ports.
Perform an isolation calibration when you are testing a device with
high insertion loss, such as the stop band of a filter or a switch in
the open position.
The isolation step can add noise to the error model when the measurement
is very close to the noise floor of the analyzer. To improve measurement
accuracy, set a narrow IF Bandwidth during the calibration.
The Isolation step is NOT allowed with ECal.
How to perform the
Isolation step
- Press Cal 5 then Mechanical
Cal / ECal
- Then Advanced
- Then Omit Isolation
- OFF
Perform the Isolation step
- ON
(default) Omits the Isolation step
- Then <Back
- Configure and perform the calibration as usual. At the first step
of the Cal you will be prompted to connect a Load standard to one
or both test ports.

|
If the first calibration step does NOT prompt you to connect
Load standards, then the Cal Kit probably does not contain an
Isolation standard. You can use DataLink software to edit the
Cal Kit and add an isolation standard using a Load standard. See
Data Link Help for more information: Keysight
FieldFox Library, Help and Manuals | Keysight . |
- This setting survives an Instrument Preset.
Waveguide Calibrations
In general, calibrating with Waveguide is very similar to calibrating
with coax. However, most coax mechanical Cal Kits have standards that
can be used over a very wide frequency range. Waveguide Cal Kits are used
over a narrow frequency range. Therefore, it is VERY IMPORTANT to set
the frequency range of the measurement WITHIN the frequency range of the
waveguide Cal Kit. Otherwise, an error message will appear during the
‘Calculating Steps’ portion of the calibration.
Waveguide Cal Kits
Keysight sells two waveguide Cal Kit series: the premium 11644A series
and the economy N9911X series. Both are available online at www.Keysight.com
Effective Velocity Factor
Velocity factor is the speed at which an electromagnetic signal passes
through the transmission medium relative to the speed of light. This value
is important when distance is being calculated in DTF measurements (CAT
mode) and Time Domain (NA mode).
When the media is waveguide, the velocity factor changes with frequency.
FieldFox calculates this ‘effective’ velocity factor automatically. However,
the settings are different for CAT mode and NA mode.
CAT Mode -
How to make Waveguide settings
These settings are necessary ONLY when making DTF measurements.
- Press Measure 1 then Distance
to Fault (dB) to select a DTF measurement.
- Press Meas Setup 4
- Then Settings (Learn how to use
the Quick Settings table in “How
to view and change Quick Settings”).
- Set Media = Waveguide.
Frequency Mode = BandPass
is automatically selected for you.
- Scroll down to Waveguide Definitions.
Select the Waveguide Standard
being used. If your waveguide standard is NOT listed:
- Select User Waveguide.
Then press Done.
- Then DTF Cable Specifications
> Edit/Save/Recall Cables >
Edit Cable.
- Scroll to set Waveguide Definition.
The default setting is VF Corr
= Auto.
- Set the Min, Max, and Cutoff Frequencies.
- Press Done, then press Back.
- Cable Correction = Auto
is the default setting. The Effective Velocity Factor is calculated
automatically based on the frequencies of the waveguide standard.
To override this setting, set Cable Corr = Man.
NA Mode - How
to make Waveguide settings
These settings are necessary ONLY when your measurement requires electrical
delay or port extensions, or if using Time Domain Transform.
- Press Meas Setup 4 > Transform
> Transform Settings
- Under Transform Stimulus Settings,
set the Start and Stop
frequencies to those of the Waveguide.
- Set Stimulus = Bandpass Impulse
- Press Done
- Press Meas Setup 4 or Back
- Then Calibration Settings
- Set Media = Waveguide
- Set Cutoff Frequency. This
is the absolute minimum frequency of the waveguide. This value must
be less than the Start Frequency of the Waveguide.
- Enter the calculated Effective
VF value into the Velocity Factor setting.
Enhanced Response Optimization
When Enhanced Response Cal Type is selected, either for one calibration
or for CalReady, this setting optimizes the calibration based on the type
of DUT being measured. See also: CalReady Properties in “CalReady”.
This setting does NOT survive Preset.
- Press Cal 5 > More
> Enh.Response
- Then choose from:
- NonReciprocal (default) An amplifier
is a Non-Reciprocal device because it has gain in the forward direction,
and very high loss (isolation) in the reverse direction. This choice
provides the best correction for non-reciprocal devices, and reasonable
correction for reciprocal devices.
- Reciprocal A reciprocal DUT is
a device in which the insertion loss through the device is equal in
both the forward (S21) and reverse (S12) directions. A cable is a
reciprocal device. This choice provides the best correction for reciprocal
devices. However, S11 measurements on non-reciprocal devices will
appear to have more return loss than the non-reciprocal choice.
Interpolation *
Highest measurement accuracy is achieved when the frequency range or
resolution settings remain the same during the measurement as when the
FieldFox was calibrated. If these settings change after performing a calibration,
the FieldFox will interpolate the calibration so that VERY accurate measurements
continue to be made.
Interpolated Calibrations are only slightly less accurate than a calibration
performed at the measurement settings. Learn more about the relative accuracy
of FieldFox calibrations in “Cal
ON? – Questionable Accuracy”.
When a calibration that you performed is being interpolated, an asterisk
is added to the Cal annotation. For example: Cal
ON U* is shown on the screen when the current Response or Mechanical
cal is being interpolated. An * is never added to a CalRdy.
Cal ON? – Questionable
Accuracy
When the Output Power, Interference Rejection, or IF BW (NA Mode ONLY)
setting is changed AFTER performing a calibration, a question mark is
added to the Cal annotation.
The resulting measurement accuracy depends on how much the setting has
changed. For highest accuracy, recalibrate using the new settings.
Compatible Mode Calibrations
The FieldFox can have only ONE calibration present for all modes. Because
NA, CAT, and VVM modes are very similar, a calibration that is performed
in one mode can also be applied in the other modes with the same type
of measurements (1-port or 2-port).
To apply a Cal that was performed in a different mode, press Cal
5 then select User Cal ON.
Save the Calibration
After performing any type of calibration, you can save the FieldFox
settings along with the calibration into a STATE (*.sta) file. These settings
and calibration can then be recalled as necessary. To learn how, see “Saving
and Recalling Files”.
CalReady Properties
There are several factory calibrations (CalReady) on every FieldFox.
These can be selected based on the type of DUT that you measure most often,
and the compromise that you prefer to make between measurement speed versus
measurement accuracy. Remember, CalReady was performed at the test ports.
Therefore, a CalReady calibration is most accurate when the DUT is directly
connected to the test ports. Learn more in “CalReady”.
This setting does NOT survive Preset or Power ON/OFF.
- Press Cal 5 > More
- Then press CalReady to toggle
between the following selections:
- 2-Port Cal (default) Corrects
all four S-parameters. Requires a forward and reverse sweep, which
causes slower trace measurements. Learn why in “Calibration
Type”.
- Enh. Response Corrects forward
(S21 and S11) and reverse (S12 and S22) measurements separately.
Therefore, when measurements in only one direction are required,
this choice provides faster trace measurements than a full 2-port
cal. Also choose an Enhanced Response Optimization. Learn more
in “Enhanced
Response Optimization”.
To find the best choice for your DUT:
- Press Preset > Preset.
- Select the appropriate S-Parameter and other settings (frequency
range, resolution, and so forth).
- Press Trace 6 > Math
and Memory > Data->Mem.
- Press Data & Memory.
- Press Cal 5 > More
- Select a CalReady Cal to compare with the current setting.
- Press Esc to exit the cal menu.
- View the differences in the two traces.
Apply Nearest (NA Mode Only)
When Apply Nearest is pressed,
interpolation is turned off and the nearest calibration point is applied
when the start stop frequencies are changed for the current sweep.
 |
IMPORTANT!
– Apply Nearest needs to re-selected after each pair of start
and stop frequency
points is entered, because the Apply Nearest feature is disabled
when a new start
stop frequency pair is selected.
– Apply Nearest calculates the number of points based on the
start and stop frequency
points entered.
– Apply Nearest will display the following error when there
is no valid calibration
found:
“Error: 225, The required user
calibration is not present." |
To use Apply Nearest:
Press Cal 5 > More
> Apply Nearest
Verifying
Calibration and Jumper Cable Integrity
After calibrating, it is important to verify that the calibration is
good. When using a jumper cable, also verify that the cable is of high
quality.
Verify a Calibration
Verifying Phase Accuracy
- Connect a LOAD standard at the calibration reference plane (where
calibration standards were connected).
- In NA Mode, select a S11 Reflection with Polar or Smith Chart format.
- Because all LOAD standards have delay, you should see a small amount
of phase rotation as a function of frequency. In general, the measurement
result should agree with the characteristics of the calibration standard.
Test the Jumper Cable
With the LOAD standard still connected, move the jumper cable while
observing the trace.
- If the measurement trace is relatively stable, the jumper cable
is of good quality.
- If you observe significant movement in the peaks of the measurement
trace when moving the cable (>5 dB), the jumper cable may need
to be replaced.
Calibration Method Summary
- Mechanical Full 2-port Cal
is ALWAYS the most accurate Cal method. The quality of a Mechanical
Cal is completely dependent on the quality of the OPEN, SHORT, LOAD
standards and the quality of the standard connections. Use the correct
high quality standards to ensure the most accurate calibration.
- Even with the optional Load, phase accuracy begins to degrade
when the return loss is greater than about 20dB.
- .
- Even with the optional Load, phase accuracy begins to degrade
when the return loss is greater than about 20dB.
- CalReady is accurate ONLY
when the DUT is directly connected at the test ports and most accurate
at room temperature.
- For highest accuracy, a
new Mechanical Cal should be performed:
- When the temperature changes more than about 10°F (5°C)
- When the connection to the DUT requires a different jumper
cable or adapters.
- When any of the following measurement settings change: Frequency
Range, Power Level, IF BW, and Resolution.


 ) or rotary
knob to change the DUT connector type.
) or rotary
knob to change the DUT connector type. 


