Searching for Positions that Match Specified Criteria
Other topics about Data Analysis
You can search for a position that matches your specified criteria by using the Marker Search feature.
Marker Search allows you to search for a position that matches the following criteria:
-
Maximum value
-
Minimum value
-
Target (a point that has a target measurement value)
-
Target nearest to marker position
-
Target nearest to left-hand side of marker position
-
Target nearest to right-hand side of marker position
-
Peak
-
Maximum peak (for a positive peak), minimum peak (for a negative peak)
-
Peak nearest to left-hand side of marker position
-
Peak nearest to right-hand side of marker position
-
Spurious
-
Spurious nearest to left-hand side of marker position
-
Spurious nearest to right-hand side of marker position
The Marker Search feature allows you to set part of the sweep range as the search target (Bandmarker feature) as well as the entire search range.
Procedure to Set Search Range
-
Press Trace Next or Trace Max to activate the trace on which you want to use the marker.
-
Press Marker Fctn (or press Marker Search).
-
To set the search range for the X-Axis, turn on Bandmarker X.
-
Set the search range using X start, X stop, X center and X span.
Each value for the search range can be changed by one of the following methods.
" Enter a numeric value using the ENTRY block key on the front panel.
" Turn the rotary knob ( ) on the front panel.
) on the front panel.
" Press the up or down arrow key (
 ) on the front panel.
) on the front panel.
" Using the mouse, click one of the buttons (
 ) on the right side of the entry area.
) on the right side of the entry area.
You can move the search range by dragging and dropping either one of the bandmarker position pointers ( 
 ) above the graph (pressing the button on the object to be moved and releasing the button on the destination). You can also drag and drop the start/stop line of the search range.
) above the graph (pressing the button on the object to be moved and releasing the button on the destination). You can also drag and drop the start/stop line of the search range.
-
To set the search range for the Y-Axis, turn on Bandmarker Y.
-
Set the search range using Y start, Y stop, Y center and Y span.
Each value for the search range can be changed by one of the following methods.
" Enter a numeric value using the ENTRY block key on the front panel.
" Turn the rotary knob ( ) on the front panel.
) on the front panel.
" Press the up or down arrow key (
 ) on the front panel.
) on the front panel.
" Using the mouse, click one of the buttons (
 ) on the right side of the entry area.
) on the right side of the entry area.
You can move the search range by dragging and dropping either one of the bandmarker position pointers ( 
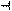
 ) above the graph (pressing the button on the object to be moved and releasing the button on the destination). You can also drag and drop the start/stop line of the search range.
) above the graph (pressing the button on the object to be moved and releasing the button on the destination). You can also drag and drop the start/stop line of the search range.
Procedure to Set Search Range
-
Press Trace Next or Trace Max to activate the trace on which you want to use the marker.
-
Press Marker Search.
-
To perform the partial search for the stimulus value (X-Axis), press Search Range(X) to select Bandmarker.
-
To perform the partial search for the response value (Y-Axis), press Search Range(Y) to select Bandmarker.
|
|
|
|
Full Range
(Full Scale)
|
All data are obtained from all traces.
|
|
Bandmarker
(Bandmarker)
|
Partial data are obtained from within bandmarker.
|
The bandmarkers can be set up and moved either in coupled operation for all traces in a channel or independently for each trace.
You can set up bandmarker coupling for frequency/power measurement, transient measurement and the user window.
Bandmarker Coupling
|
|
|
|
Bandmarker Couple is on
(Couple ON)
|
Bandmarkers are set up and moved in coupled operation on all traces in a channel.
|
|
Bandmarker Couple is off
(Couple OFF)
|
Bandmarkers are set up and moved independently for each trace.
|
Operational Procedure
-
Press Trace Next or Trace Max to activate the trace on which you want to use the marker.
-
Press Marker Fctn (or press Marker Search).
-
Now you can set up the bandmarker. For more information, refer to Setting Search Range (Bandmarkers).
-
Press Couple to turn the marker coupling on or off.
-
You cannot turn on the bandmarker coupling for the X-Axis.
Search tracking is a function that sets a search to be repeated every time a sweep is done. This function facilitates the observation of measurement results, such as the maximum value of traces.
Operational Procedure
-
Press Trace Next or Trace Max to activate the trace on which search tracking is set up.
-
Press Marker Search.
-
Press Tracking and specify the parameters of the search tracking function.
|
|
|
|
Off
|
Turns off search tracking function.
|
|
Maximum value
|
Specifies the maximum value for search tracking function.
|
|
Minimum value
|
Specifies the minimum value for search tracking function.
|
|
Peak
|
Specifies the peak for search tracking function.
|
|
Target
|
Specifies the target for search tracking function.
|
|
Spurious
|
Specifies the spurious for search tracking function.
|
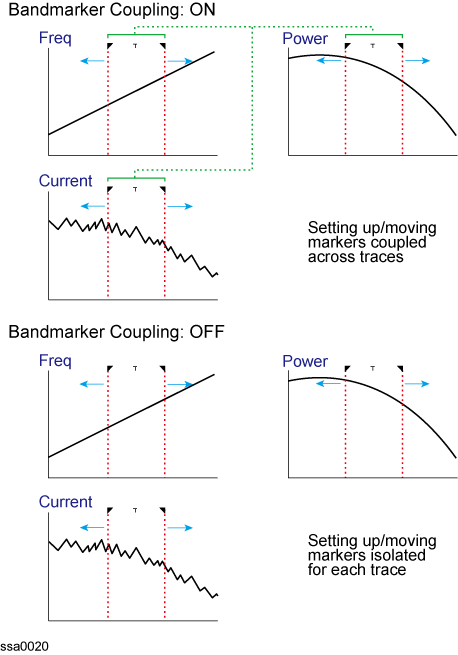
You can search for the maximum or minimum measured value on the trace and move a marker to that point.
Searching for Maximum and Minimum Measured Values
|
|
|
|
Search for maximum
(Max)
|
Moves active marker to point on trace where measured value is greatest.
|
|
Search for minimum
(Min)
|
Moves active marker to point on the trace where measured value is lowest.
|
Operational Procedure
-
Following Step1to Step3in Reading Values on Trace, activate the marker you will use to search for the maximum and minimum values.
-
Press Marker Search.
-
Press the corresponding softkey to move the marker to the maximum or minimum measured value.
|
|
|
|
Search Max
|
Performs a search for the maximum value.
|
|
Search Min
|
Performs a search for the minimum value.
|
Searching for Target Value (target search)
The target search function enables you to move the marker to the point that has the target measured value.
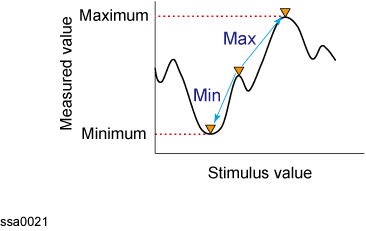
Target and Transition Types
A target is a point that has a specific measurement value on the trace. Targets can be divided into the two groups shown below depending on their transition type.
|
|
|
|
Transition type: positive
(Positive)
|
When the value of the target is larger than the measurement value that immediately precedes it (on the left side).
|
|
Transition type: negative
(Negative)
|
When the value of the target is smaller than the measurement value that immediately precedes it (on the left side).
|
Target and Transition Types
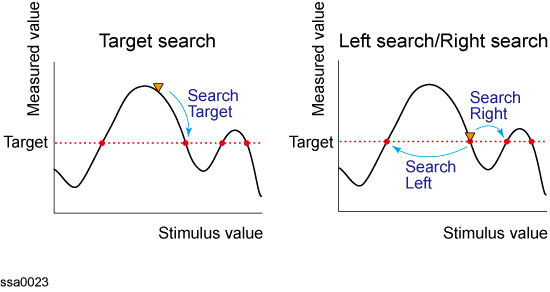
The target search is a function that searches for a target that matches the pre-defined target value and transition type(s) (positive, negative, or both positive and negative) and then moves to the peak with maximum response value if the peak polarity is Positive or Both or to the peak with minimum response value if the peak polarity is Negative.
The following three methods are available for executing the target search:
|
|
|
|
Search target
(Search Target)
|
The marker moves to the nearest target in the stimulus value from the position of a present marker.
|
|
Left search
(Search Left)
|
Executes search from current marker position to the smaller stimulus values and moves marker to first target encountered
|
|
Right search
(Search Right)
|
Executes search from current marker position to the larger stimulus values and moves marker to first target encountered
|
Target Search (when transition type is set to both positive and negative)
Operational Procedure
-
Following Step1through Step3 in Reading Values on Trace, activate a marker you are using for the target search.
-
Press Marker Search.
-
Press Target.
-
Press Target Value and enter a target value in the entry box that appears.
The marker target search will be executed based on the newly set target value and the transition type defined.
-
Press Target Transition.
-
Select a transition type.
|
|
|
|
Positive
|
Selects positive as transition type.
|
|
Negative
|
Selects negative as transition type.
|
|
Both
|
Selects both positive and negative as transition type.
|
The marker target search will be executed based on the definitions of the currently set target value and the newly set transition type. Each marker is allowed to have the peak excursion value and the peak polarity individually.
-
Press the corresponding softkey to move the marker to the target.
|
|
|
|
Search Target
|
Executes target search.
|
|
Search Left
|
Executes left search.
|
|
Search Right
|
Executes right search.
|
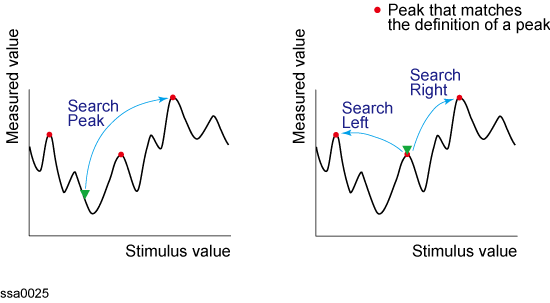
The peak search function enables you to move the marker to the peak on the trace.
Definitions of Peaks
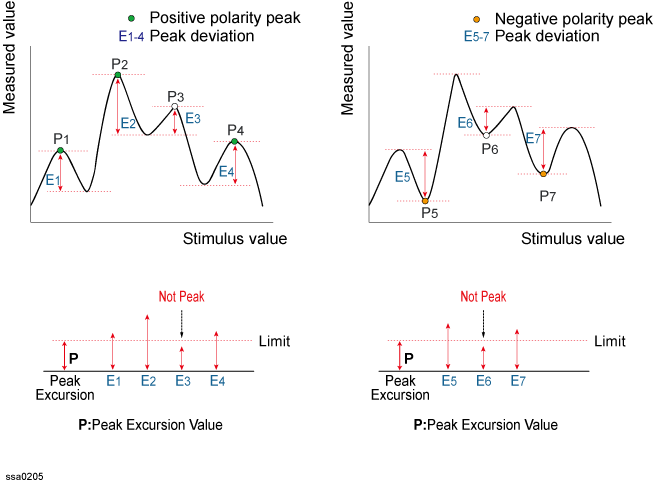
A peak is a measurement point whose value is greater or smaller than the adjoining measurement points on its right and left sides. Peaks are classified into the following types depending on the difference in magnitude from the measurement points on either side of it.
|
|
|
|
Positive peak (Positive)
|
A peak whose measurement value is greater than those of the measurement points on either side of it (peak polarity: positive)
|
|
Negative peak (Negative)
|
A peak whose measurement value is smaller value than those of measurement points on either side of it (peak polarity: negative)
|
About the peak search function
The peak search is a function that searches for a peak that matches a pre-defined lower limit for the peak excursion value and peak polarity (positive or negative) and then moves the marker to this peak.
The peak excursion is the smaller of the differences in measurement values from the adjoining peaks of the opposite polarity.
Positive Peak, Negative Peak and Peak Excursion
The following four methods are available for executing the peak search:
|
|
|
|
Search peak
(Search Peak)
|
Moves marker to the maximum peak when peak polarity is Positive or Both; moves marker to the minimum peak when peak polarity is Negative
|
|
Search all peaks
(Search Peak All)
|
Moves marker to the maximum peak when peak polarity is Positive or Both; moves marker to the minimum peak when peak polarity is Negative
|
|
Search left
(Search Left)
|
Executes search from current marker position to the smaller stimulus values and moves marker to the first peak encountered
|
|
Search right
(Search Right)
|
Executes search from current marker position to the larger stimulus values and moves marker to the first peak encountered
|
Peak Search (when peak polarity is positive)
-
Following Step1 through Step3 in Reading Values on Trace, activate a marker you are using for the peak search.
-
Press Marker Search.
-
Press Peak.
-
Press Peak Excursion and enter the lower limit for the peak excursion value.
The marker peak search will be executed based on the definitions of the newly set lower limit for the peak excursion value and the currently set peak polarity.
-
Press Peak Polarity.
-
Select a peak polarity.
|
|
|
|
Positive
|
Selects Positive as the peak polarity
|
|
Negative
|
Selects Negative as the peak polarity
|
|
Both
|
Selects Both Positive and Negative as the peak polarity
|
The marker peak search will be executed based on the definitions of the currently set lower limit for the peak excursion value and the newly set peak polarity. Each marker is allowed to have the peak excursion value and the peak polarity individually.
-
Press the corresponding softkey to move the marker to the peak.
|
|
|
|
Search Peak
|
Executes peak search
|
|
Search Left
|
Executes left search
|
|
Search Right
|
Executes right search
|
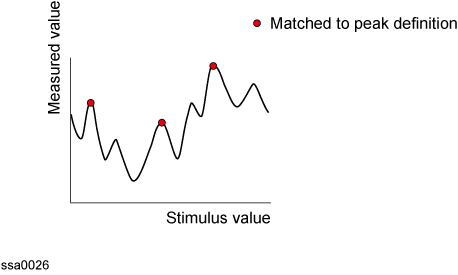
The multi-peak search function enables you to display markers on multiple peaks on traces.
The peak-search-all is a function that searches for peaks that match a pre-defined lower limit for the peak excursion value and peak polarity (positive or negative) and then displays the markers on these peaks. Up to 10 markers can be displayed.
The peak excursion is the smaller of the differences in measurement values from the adjoining peaks of the opposite polarity.
Peak Search All (when peak polarity is positive)
Operational Procedure
-
Following Step1 through Step3 in Reading Values on Trace, display the multiple markers you are using for the peak search.
-
The peak search is executed as many times as the number of markers displayed (up to 10).
-
Press Marker Search.
-
Press Peak.
-
Press Peak Excursion and enter the lower limit for the peak excursion value.
This sets the multiple peak searches to be executed based on the definitions of the newly set lower limit for the peak excursion value and the currently set peak polarity.
-
Press Peak Polarity.
-
Select a peak polarity.
|
|
|
|
Positive
|
Selects Positive as the peak polarity.
|
|
Negative
|
Selects Negative as the peak polarity.
|
|
Both
|
Selects both Positive and Negative as the peak polarity.
|
This sets the multiple peak searches to be executed based on the definitions of the currently set lower limit for the peak excursion value and the newly set peak polarity.
- Press Search Peak All to move the marker to the peak.
The spurious search function enables you to move the marker to the peak value on the trace. You can use this function when the spurious judgment is enabled. For more information, refer to Confirming Spurious.
The spurious search is a function that searches for a spurious and then moves the marker to this spurious.
The following three methods are available for executing the spurious search:
|
|
|
|
Search spurious
(Search Spurious)
|
Moves marker to the maximum spurious
|
|
Search left
(Search Left)
|
Executes search from current marker position to the smaller stimulus values and moves marker to the first spurious encountered
|
|
Search right
(Search Right)
|
Executes search from current marker position to the larger stimulus values and moves marker to the first spurious encountered
|
Spurious Search
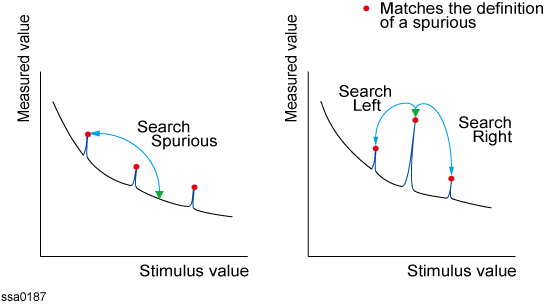
Operational Procedure
-
Following Step1 through Step3 in Reading Values on Trace, activate a marker you are using for the peak search.
-
Press Marker Search.
-
Press Spurious.
-
Press the corresponding softkey to move the marker to the peak.
|
|
|
|
Search Spurious
|
Executes spurious search
|
|
Search Left
|
Executes left search
|
|
Search Right
|
Executes right search
|
The multi-peak spurious function enables you to display markers on multiple spurious on traces.
The spurious-search-all is a function that searches for spurious and then displays the markers on these spurious. Up to 10 markers can be displayed.
Spurious Search All
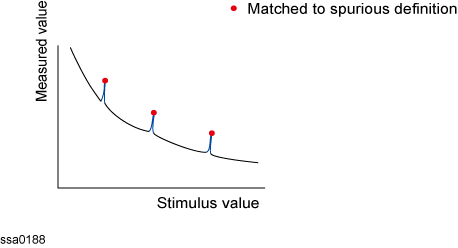
Operational Procedure
-
Following Step1 through Step3 in Reading Values on Trace, display the multiple markers you are using for the peak search.
-
The spurious search is executed as many times as the number of markers displayed (up to 10).
-
Press Marker Search.
-
Press Spurious.
-
Press Search Spurious All to move the marker to the spurious.
![]() ) on the front panel.
) on the front panel.![]()
![]() ) on the front panel.
) on the front panel.![]()
![]() ) on the right side of the entry area.
) on the right side of the entry area.![]()
![]()
![]() ) above the graph (pressing the button on the object to be moved and releasing the button on the destination). You can also drag and drop the start/stop line of the search range.
) above the graph (pressing the button on the object to be moved and releasing the button on the destination). You can also drag and drop the start/stop line of the search range.![]() ) on the front panel.
) on the front panel.![]()
![]() ) on the front panel.
) on the front panel.![]()
![]() ) on the right side of the entry area.
) on the right side of the entry area.![]()
![]()
![]() ) above the graph (pressing the button on the object to be moved and releasing the button on the destination). You can also drag and drop the start/stop line of the search range.
) above the graph (pressing the button on the object to be moved and releasing the button on the destination). You can also drag and drop the start/stop line of the search range.







