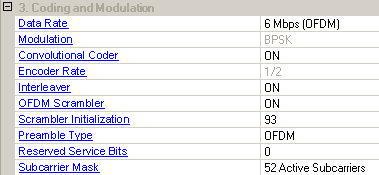
The selected Data Rate and Modulation determine the available choices of signal configuration parameters.

Use this cell to select the data rate. The data rate selected automatically sets the modulation and encoder rate according to the 802.11 standard. Given data rates are for the payload data and are valid when all 48 data subcarriers are on. The data rate decreases as the individual subcarriers are turned off from the Subcarrier menu.
The following table lists the selectable data rates for different 802.11 standards:
|
802.11a |
6 Mbps(OFDM), 9 Mbps(OFDM), 12 Mbps(OFDM), 18 Mbps(OFDM), 24 Mbps(OFDM), 36 Mbps(OFDM), 48 Mbps(OFDM), 54 Mbps(OFDM) |
|
802.11b |
1 Mbps (DSSS), 2 Mbps(DSSS), 5.5 Mbps(DSSS), 11 Mbps(DSSS) |
|
802.11g |
6 Mbps(OFDM), 9 Mbps(OFDM), 12 Mbps(OFDM), 18 Mbps(OFDM), 24 Mbps(OFDM), 36 Mbps(OFDM), 48 Mbps(OFDM), 54 Mbps(OFDM), 1 Mbps (DSSS), 2 Mbps(DSSS), 5.5 Mbps(DSSS), 11 Mbps(DSSS), 22 Mbps(DSSS), 33 Mbps(DSSS) |
|
802.11j |
20 MHz Channel Spacing: 6 Mbps(OFDM), 9 Mbps(OFDM), 12 Mbps(OFDM), 18 Mbps(OFDM), 24 Mbps(OFDM), 36 Mbps(OFDM), 48 Mbps(OFDM), 54 Mbps(OFDM) 10 MHz Channel Spacing: 3 Mbps(OFDM), 4.5 Mbps(OFDM), 6 Mbps(OFDM), 9 Mbps(OFDM), 12 Mbps(OFDM), 18 Mbps(OFDM), 24 Mbps(OFDM), 27 Mbps(OFDM) |
|
802.11p |
20 MHz Channel Spacing: 6 Mbps(OFDM), 9 Mbps(OFDM), 12 Mbps(OFDM), 18 Mbps(OFDM), 24 Mbps(OFDM), 36 Mbps(OFDM), 48 Mbps(OFDM), 54 Mbps(OFDM) 10 MHz Channel Spacing: 3 Mbps(OFDM), 4.5 Mbps(OFDM), 6 Mbps(OFDM), 9 Mbps(OFDM), 12 Mbps(OFDM), 18 Mbps(OFDM), 24 Mbps(OFDM), 27 Mbps(OFDM) 5 MHz Channel Spacing: 1.5 Mbps(OFDM), 2.25 Mbps(OFDM), 3 Mbps(OFDM), 4.5 Mbps(OFDM), 6 Mbps(OFDM), 9 Mbps(OFDM), 12 Mbps(OFDM), 13.5 Mbps(OFDM) |
Use this cell to select the modulation formats.
The following table lists the modulation formats for different 802.11 standards.
|
802.11a |
The modulation formats are automatically set according to the data rate and cannot be changed. 802.11a uses a multi-carrier modulation scheme called orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM). The following modulation formats are available for OFDM: BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM |
|
802.11b |
802.11b uses direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) with CCK or PBCCcoding schemes. For the 1 Mbps and 2 Mbps data rates, this cell is called Low Rate Modulation and the modulation format is automatically set to DBPSK and DQPSK respectively and cannot be changed. For 5.5 Mbps and 11 Mbps data rates, this cell is called High Rate Modulation and you can select CCK or PBCC as the modulation scheme. Refer to the Data Rate and Modulation Table for DSSS. |
|
802.11g |
802.11g uses either OFDM or DSSS as the modulation scheme. For OFDM, the modulation formats are set according to the data rate and cannot be changed. For DSSS with 1 Mbps and 2 Mbps data rates, the modulation formats are automatically set to DBPSK and DQPSK respectively and cannot be changed. For 5.5 Mbps and 11 Mbps data rates, you can select CCK or PBCC. For 22 Mbps and 33 Mbps data rates, it is automatically set to PBCC. Refer to the Data Rate and Modulation Table for DSSS. |
|
802.11j |
The modulation formats are set according to the data rate and cannot be changed. 802.11j uses OFDM as the modulation scheme. The following modulation formats are available for OFDM: BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM |
|
802.11p |
The modulation formats are set according to the data rate and cannot be changed. 802.11p uses OFDM as the modulation scheme. The following modulation formats are available for OFDM: BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM |

Use this cell to set the convolutional encoder to ON or OFF.
This cell is adjustable only for the Advanced Capability. In the Basic Capability, it is automatically set to OFF.
This cell displays the convolutional code rate, which is automatically set according to the data rate and cannot be changed.
This cell is applicable only for OFDM with the four selections: N/A, 1/2, 2/3, 3/4.
In the Basic Capability, it is automatically set to N/A.
Use this cell to set the interleaver to ON or OFF.
This cell is adjustable only for the Advanced Capability. In the Basic Capability, it is automatically set to OFF.
Use this cell to set the OFDM scrambler to ON or OFF.
This cell is adjustable only for the Advanced Capability. In the Basic Capability, it is automatically set to ON.
Use this cell to set the initial value of the scrambler. The range is 0 to 127. The default is 93.
For 802.11g OFDM mode, you can select Long DSSS, Short DSSS, or OFDM preamble.
Use this cell to set the 9 reserved service bits in the service field for OFDM mode. The Service Field has 16 bits. The bits from 0 to 6 of the Service Field, which are transmitted first, are set to zeros and are used to synchronize the de-scrambler in the receiver. The remaining 9 bits (from 7 to 15) of the Service Field are reserved for future use. All reserved bits shall be set to zero. Refer to the figure below.
Click the 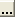 button in this cell to open the
button in this cell to open the ![]() Subcarrier
Mask Configuration window,
which enables you to configure the individual subcarriers for OFDM.
Subcarrier
Mask Configuration window,
which enables you to configure the individual subcarriers for OFDM.
Frequency-selective fading can be simulated by turning selected carriers off in this menu. There are a total of 52 subcarriers for an 802.11 OFDM signal; 48 are data subcarriers, and 4 are pilot subcarriers. The center frequency, which is the zero subcarrier, is nulled. The state of each of the subcarriers can be toggled On or Off, or you can select one of the following predefined setups:
All
Every 2nd
Every 4th
Upper Band
Lower Band
Outer Band
Outer Pair
None
User Defined

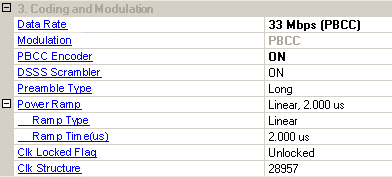
Use this cell to enable or disable the PBCC encoder.
This cell is valid only when high rate modulation (5.5, 11, 22 and 33 Mbps for DSSS) and PBCC modulation is enabled.
This cell is adjustable only for the Advanced Capability. In the Basic Capability, it is automatically set to OFF.
Use this cell to set the DSSS scrambler to ON, OFF, or Preamble Only.
This cell is adjustable only for the Advanced Capability. In the Basic Capability, it is automatically set to ON.
Use this cell to select the format of the preamble/header sections of the framed signal.
For DSSS mode, the selection is long or short.
Selects the shape of the RF burst in framed mode. The Power Ramp Configuration is relevant only in framed mode.
: Selects the power up/down ramp type as none, linear, or cosine. Cosine ramp gives the least amount of out of channel interference. None starts transmitting the signal at full power and is the simplest power ramp to implement. The linear ramp shapes the burst in a linear fashion.
: Sets the length (in microseconds) of the power up/down ramp.
Use this cell to set the status of the clock-locked-indicator for PBCC modulation 33 Mbps data rate. This is used to indicate to the receiver if the carrier and the symbol clock use the same local oscillator; the user can set this bit. This is relevant only in framed mode and PBCC 33 Mbps.
Click the  button in this cell to open the
button in this cell to open the ![]() Clk Structure Dialog.
Clk Structure Dialog.
When the clock is switched from 11 MHz to 16.5 MHz, the following clock switching structure defaults are implemented:
Tail: 2 clock cycles at 11 Mchips/s (default: 07 Hex or 111 binary)
Head: 3 clock cycles at 16.5 Msymbols/s (default: 000)
ReSync: 9 clock cycles at 16.5 Msymbols/s (default: 11D Hex or 100011101 binary)
The total clock switching time is 1 microsecond.