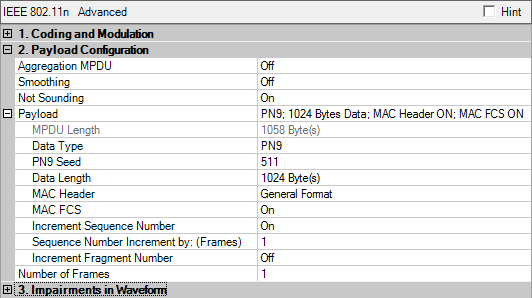
This section enables you to configure the MAC header, set the length and type of payload data, and choose to have an FCS added to the packet.

Option H with Aggregation MPDU On
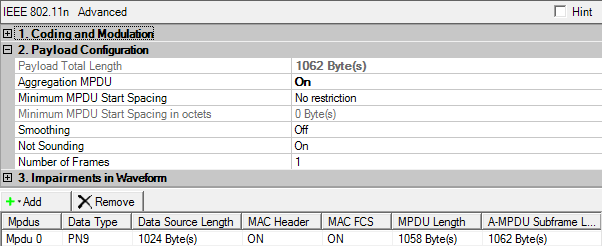
This cell displays the total number of bytes in the payload, including MPDU delimiter, the payload data, MAC header, FCS, and PAD octets for each MPDU. You cannot edit this cell.
Use this cell to enable or disable the A-MPDU format that allows aggregation of multiple MPDUs (MAC protocol data units) in one PSDU (PHY service data unit).
Choices: No restriction | ¼ us | ½ us | 1 us | 2 us | 4 us | 8 us | 16 us
Default: No restriction
Coupling: Invisible when Aggregated MPDU is set to OFF or without option N7617C-Hxx.
Select the minimum time between the start of adjacent MPDUs within an A-MPDU.
Default: 0
Coupling: Invisible when Aggregated MPDU is set to OFF or without option N7617C-H.
Displays the minimum octets between the start of adjacent MPDUs. Its value should be equal or greater than Minimum MPDU Start Spacing X Data Rate / 8.
Set the smoothing bit.
Indicates whether frequency-domain smoothing is recommended as part of channel estimation.
Set the not sounding bit.
Indicates whether this packet is a sounding packet or not.
Displays the number of octets in current MPDU, which is comprised of MSDU, MAC Header and MAC FCS.
Prior to N7617B version 1.12.0.0, this was named MAC Frame Length.
Use this cell to select the payload data source. The user data of the frame can contain the following data:
All 0s
The user file must be in binary form. The least significant bit (LSB) of the first byte in the user data file will be the first bit of the user payload; the LSB of the second byte in the user file will be the ninth bit of the user payload, and so on. If User file is selected as the Data Type, the value displayed in the Data Length field will be equal to the length of the user's data file, up to the maximum data length.
Range: 0 to 511
Default: 511
Coupling: Invisible without option N7617B-H
Specify a seed in decimal format to generate a PN9 data sequence. The LSB of the seed comes out first. For example, if you enter a seed value of 10 (1010 in binary), the first 9 bits of the PN9 sequence are 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0, with an increasing index from left to right. For more information, see PN Sequence Generation.
Range: 0 to 32767
Default: 32767
Coupling: Invisible without option N7617B-H
Specify a seed in decimal format to generate a PN15 data sequence. The LSB of the seed comes out first. For example, if you enter a seed value of 10 (1010 in binary), the first 15 bits of the PN15 sequence are 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0, with an increasing index from left to right. For more information, see PN Sequence Generation.
Click the  button in this cell to select a user file
as the data source.
button in this cell to select a user file
as the data source.
This cell displays the number of data bytes in the user file when it is selected as the payload data source.
Use this cell to set the number of data bytes in a frame. The range is 0 to 65535. (minus the length of the MAC header and FCS, if they are enabled).
User data longer than the maximum data length will be truncated.
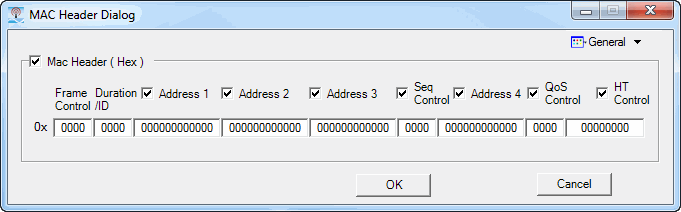
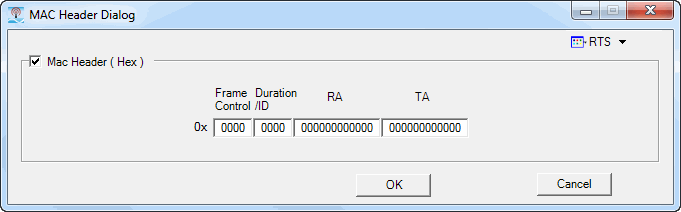
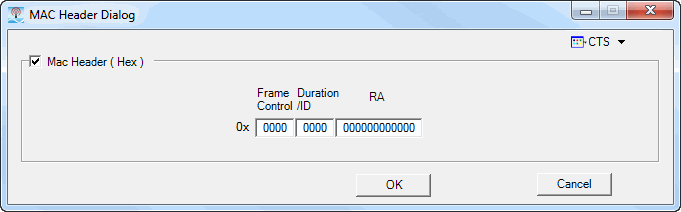
Click the  button in this cell to open the MACHeaderDialog
(see the dialogs below), which enables or disables pre-pending the MAC
header to the data payload. You can select General, RTS, or CTS MAC frame
format by clicking the down arrow in the top right corner of the MacHeaderDialog.
You can set the desired data in each of the individual fields for each
format. You can also disable these fields if the data is no longer desired
by clearing the Mac Header (hex) checkbox.
button in this cell to open the MACHeaderDialog
(see the dialogs below), which enables or disables pre-pending the MAC
header to the data payload. You can select General, RTS, or CTS MAC frame
format by clicking the down arrow in the top right corner of the MacHeaderDialog.
You can set the desired data in each of the individual fields for each
format. You can also disable these fields if the data is no longer desired
by clearing the Mac Header (hex) checkbox.
Use this cell to enable or disable appending the MAC FCS to the data payload. The FCS is automatically calculated by the software if this cell is enabled. Note: When the MAC header is not selected, then the FCS is applied to just the payload.
This cell is adjustable only for the Advanced Capability. In the Basic Capability, it is automatically set to OFF.
Use this cell to enable or disable incrementing
the Sequence Number within the ![]() Sequence
Control field
in the MAC Header. When it is turned ON, the Sequence Number increments
by one after each user-specified interval of new frames. For an example
of how incrementation works, see Incrementing Sequence and Fragment Numbers.
Sequence
Control field
in the MAC Header. When it is turned ON, the Sequence Number increments
by one after each user-specified interval of new frames. For an example
of how incrementation works, see Incrementing Sequence and Fragment Numbers.
This cell is only applicable for the Advanced Capability.
The number of frames you set in this cell determines when the Sequence Number within the Sequence Control field in the MAC Header is incremented. For an example of how incrementation works, see Incrementing Sequence and Fragment Numbers.
This cell is only applicable for the Advanced Capability.
Use this cell to enable or disable incrementing the Fragment Number
within the ![]() Sequence Control field
in the MAC Header. When it is turned ON, the Fragment Number increments
by one after every assignment of a new frame. This field uses the Increment
Sequence Number by: (Frame) value as the upper limit. When the upper limit
is reached, incrementation wraps back to zero. For an example of how incrementation
works, see Incrementing Sequence and Fragment Numbers.
Sequence Control field
in the MAC Header. When it is turned ON, the Fragment Number increments
by one after every assignment of a new frame. This field uses the Increment
Sequence Number by: (Frame) value as the upper limit. When the upper limit
is reached, incrementation wraps back to zero. For an example of how incrementation
works, see Incrementing Sequence and Fragment Numbers.
This cell is applicable only for the Advanced Capability.
Use this cell to set the number of frames to be used in the waveform. Choosing a value greater than one causes the creation of multiple frames containing a continuous data payload.
Select in the Aggregation MPDU cell to open this table.
This table enables you to view the key parameters for each MPDU. You can also add or delete MPDUs using the buttons above the table (see descriptions below). Double-clicking an MPDU row activates the setup table for that MPDU. You can use a maximum of 64 MPDUs.
 The button
adds an MPDU to the setup table.
The button
adds an MPDU to the setup table.
 The
button deletes the currently highlighted MPDU in the
setup table. You can highlight multiple MPDUs by holding down the CTRL
key while selecting the carriers. You can also use the SHIFT key to select
a succession (group) of MPDUs.
The
button deletes the currently highlighted MPDU in the
setup table. You can highlight multiple MPDUs by holding down the CTRL
key while selecting the carriers. You can also use the SHIFT key to select
a succession (group) of MPDUs.